review for elec 105 midterm exam #1 (fall 2001)
... av vin (where av is the small-signal voltage gain) and output (Thévenin equivalent) resistance rout ...
... av vin (where av is the small-signal voltage gain) and output (Thévenin equivalent) resistance rout ...
Operational Amplifiers and Other Integrated Circuit Usage
... Quick to “burn out” if shorted! Contained only 9 transistors Cost was $300. in 1963 dollars! ...
... Quick to “burn out” if shorted! Contained only 9 transistors Cost was $300. in 1963 dollars! ...
ECE 322L Lab 7: Differential Amplifiers
... stage. The differential output versions (Figures 17-1 (A) and 17-2 (B)) have a resistor in each branch and the output is measured between the two collectors (drains). Many differential amplifiers are designed as single ended outputs since the information contained in either of the collector (drain) ...
... stage. The differential output versions (Figures 17-1 (A) and 17-2 (B)) have a resistor in each branch and the output is measured between the two collectors (drains). Many differential amplifiers are designed as single ended outputs since the information contained in either of the collector (drain) ...
Operational amplifier
... SR can cause the output of real OpAmp very different from an ideal one if input signal frequency is too high Full Power bandwidth: the range of frequencies for which the OpAmp can produce an undistorted sinusoidal output with peak amplitude equal to the maximum allowed voltage output ...
... SR can cause the output of real OpAmp very different from an ideal one if input signal frequency is too high Full Power bandwidth: the range of frequencies for which the OpAmp can produce an undistorted sinusoidal output with peak amplitude equal to the maximum allowed voltage output ...
Kang_vector_control_algorithm
... required amplitudes and phases of RF voltages at the cavities only with phase shifters – Any cavities missing or need to be disabled in the system can be set to have 0 voltage vector Phase delays and reactive loads at the cavity ports of the transmission line network are found by solving a network ...
... required amplitudes and phases of RF voltages at the cavities only with phase shifters – Any cavities missing or need to be disabled in the system can be set to have 0 voltage vector Phase delays and reactive loads at the cavity ports of the transmission line network are found by solving a network ...
AN-536: Dimensional Gaging Measurements with Model
... the computer or control system will subtract this total from the known distance between the LVDTs. Taper or slope measurements are done by positioning the two LVDTs at the same level at a known distance apart. If the object to be measured is on the same level as the LVDTs, both LVDTs would have the ...
... the computer or control system will subtract this total from the known distance between the LVDTs. Taper or slope measurements are done by positioning the two LVDTs at the same level at a known distance apart. If the object to be measured is on the same level as the LVDTs, both LVDTs would have the ...
H – Parameter model :-
... → These equivalent circuits will aid in analyzing transistor circuits easily and rapidly. ...
... → These equivalent circuits will aid in analyzing transistor circuits easily and rapidly. ...
Lecture 7 Overview
... • With the black box model, it is simple to measure the input and output impedances of an amplifier • To measure the input impedance, vary RS until the output voltage has dropped to half ; then RS=RIN= input impedance •To measure the output impedance, vary RL until the output voltage has dropped to ...
... • With the black box model, it is simple to measure the input and output impedances of an amplifier • To measure the input impedance, vary RS until the output voltage has dropped to half ; then RS=RIN= input impedance •To measure the output impedance, vary RL until the output voltage has dropped to ...
SERIES: SIN45 Loop-powered Signal Isolator INDUMART INC.
... - "Low" (3 mA) or "High" (22 mA) output status at input failure; - Thermocouple non-linear conversions providing temperature linear output. The isolation level is normally 3750 VAC for the non-programming version and 4000 VAC for the programming version (SIN45P). The device is factory calibrated and ...
... - "Low" (3 mA) or "High" (22 mA) output status at input failure; - Thermocouple non-linear conversions providing temperature linear output. The isolation level is normally 3750 VAC for the non-programming version and 4000 VAC for the programming version (SIN45P). The device is factory calibrated and ...
(EIS): Part 1 – Basic Principles
... varying the frequency of the applied signal one can get the impedance of the system as a function of frequency. Typically in electrochemistry, a frequency range of 100 kHz – 0.1 Hz is used. ...
... varying the frequency of the applied signal one can get the impedance of the system as a function of frequency. Typically in electrochemistry, a frequency range of 100 kHz – 0.1 Hz is used. ...
sensorProbe8-X60
... Introducing the sensorProbe8-X60 The sensorProbe8-X60 comes with 8 autoSense Intelligent sensor ports for connecting a wide range of our intelligent sensors. An additional 60x 2-wire dry contact ports are provided giving a total of up to 68 dry contact ports. The specially designed 2 wire dry contac ...
... Introducing the sensorProbe8-X60 The sensorProbe8-X60 comes with 8 autoSense Intelligent sensor ports for connecting a wide range of our intelligent sensors. An additional 60x 2-wire dry contact ports are provided giving a total of up to 68 dry contact ports. The specially designed 2 wire dry contac ...
review for elec 105 midterm exam #1 (fall 2001)
... frequency; however, phasors can be expressed as functions of frequency - in EE, square root of –1 is j, not i - phasors can only be used to evaluate the sum (or difference) of two or more sinusoids at the same frequency, but not their product (or quotient) - although impedances are complex numbers, ...
... frequency; however, phasors can be expressed as functions of frequency - in EE, square root of –1 is j, not i - phasors can only be used to evaluate the sum (or difference) of two or more sinusoids at the same frequency, but not their product (or quotient) - although impedances are complex numbers, ...
Op amp I - My Webspace files
... PART D: The voltage follower. Another op-amp configuration using feedback is the voltage follower. Despite its simplicity, it’s one of the most useful op-amp applications. The follower provides a buffer between one circuit stage and the next. It has a large input resistance (that of an FET input) an ...
... PART D: The voltage follower. Another op-amp configuration using feedback is the voltage follower. Despite its simplicity, it’s one of the most useful op-amp applications. The follower provides a buffer between one circuit stage and the next. It has a large input resistance (that of an FET input) an ...
Document
... (ii) The input offset current of the MOSFET differential pair contributes by mismatching the load resistances, mismatching in W/L, and mismatching in the threshold voltage Vt. (iii) It is not necessary to use the input coupling capacitor in the BJT’s differential amplifier, since the differential pa ...
... (ii) The input offset current of the MOSFET differential pair contributes by mismatching the load resistances, mismatching in W/L, and mismatching in the threshold voltage Vt. (iii) It is not necessary to use the input coupling capacitor in the BJT’s differential amplifier, since the differential pa ...
NM-251B Speed Log to NMEA-0183 Converter User
... General Purpose Output Port NM-251B has five general purpose output ports that are able of transmitting NMEA sentences in both RS422 and TTL signal levels, depending on the connection topology and each one can fan out one instrument. Current drawn from each output port can be up to 20mA, efficient e ...
... General Purpose Output Port NM-251B has five general purpose output ports that are able of transmitting NMEA sentences in both RS422 and TTL signal levels, depending on the connection topology and each one can fan out one instrument. Current drawn from each output port can be up to 20mA, efficient e ...
Telemetry 1 I/O Interface Card User`s Guide
... 1. Voltage Monitoring Port - Measures the input voltage level and the internal temperature of the unit. It can also be used to provide a power source for the Digital-In port. 2. Relay I/O Port - The relay will make or break a circuit depending on the state of the digital in port. 3. Digital-In Po ...
... 1. Voltage Monitoring Port - Measures the input voltage level and the internal temperature of the unit. It can also be used to provide a power source for the Digital-In port. 2. Relay I/O Port - The relay will make or break a circuit depending on the state of the digital in port. 3. Digital-In Po ...
700924 NEW Differential Probe Capable of Wide-Band, High-Voltage Floating Measurements
... Signals floating from ground Waveform observed on oscilloscope ...
... Signals floating from ground Waveform observed on oscilloscope ...
hw9
... ii. Calculate the bias voltages on all nodes, assuming VI,CM=1V. Specifically: tail, G2, G3, G5, G6, S3B, S4AB, and out. iii. the gm and ro parameters for M1 through M5 b. Calculate Gm, Ro, and Av c. Calculate the input common mode range and output swing. d. What is the minimum voltage that could be ...
... ii. Calculate the bias voltages on all nodes, assuming VI,CM=1V. Specifically: tail, G2, G3, G5, G6, S3B, S4AB, and out. iii. the gm and ro parameters for M1 through M5 b. Calculate Gm, Ro, and Av c. Calculate the input common mode range and output swing. d. What is the minimum voltage that could be ...
Digital Order Wire Brochure - Raven Electronics Corporation
... communications through a 64 Kbps digital service between different locations without using revenue-generating bandwidth. This is done by including voice codecs in the Orderwire Terminal. The 61684 Digital Bridge module provides four 64 Kbps RS-422 (V.11) ports ports for connection to the service cha ...
... communications through a 64 Kbps digital service between different locations without using revenue-generating bandwidth. This is done by including voice codecs in the Orderwire Terminal. The 61684 Digital Bridge module provides four 64 Kbps RS-422 (V.11) ports ports for connection to the service cha ...
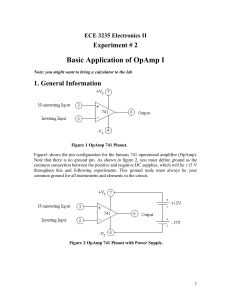
ECE 3235 Electronics II
... 1) Measure the voltage gain and the phase shift at that frequency. Limit the voltage at the input to 80 mV peak-to-peak maximum. 2) Measure accurately the –3 dB frequency fc (sometimes called corner or break frequency) and the phase shift there. 3) Additionally, measure the voltage gain and phase sh ...
... 1) Measure the voltage gain and the phase shift at that frequency. Limit the voltage at the input to 80 mV peak-to-peak maximum. 2) Measure accurately the –3 dB frequency fc (sometimes called corner or break frequency) and the phase shift there. 3) Additionally, measure the voltage gain and phase sh ...