Steroid Hormones and Steroid Receptors – Pt. 1
... Mechanism of Transcriptional Activation by Androgen Receptor ...
... Mechanism of Transcriptional Activation by Androgen Receptor ...
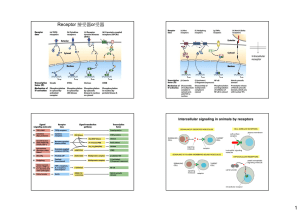
Receptor 接受器or受器
... hormones and neurotransmitters Many different mammalian cell-surface receptors including GPCRs are coupled to a trimeric signal-transducing G protein – made of an alpha, beta and gamma subunit complex Ligand binding activates the receptor, which activates the G protein, which activates an effector e ...
... hormones and neurotransmitters Many different mammalian cell-surface receptors including GPCRs are coupled to a trimeric signal-transducing G protein – made of an alpha, beta and gamma subunit complex Ligand binding activates the receptor, which activates the G protein, which activates an effector e ...
PPT
... Paracrine signaling. The signaling molecules released by one cell act on neighboring target cells (neurotransmitters). Autocrine signaling. Cells respond to signaling molecules that they themselves produce (response of the immune system to foreign antigens and cancer cells). ...
... Paracrine signaling. The signaling molecules released by one cell act on neighboring target cells (neurotransmitters). Autocrine signaling. Cells respond to signaling molecules that they themselves produce (response of the immune system to foreign antigens and cancer cells). ...
Molecular Physiology: Enzymes and Cell Signaling Proteins Binding
... • intracellular signal generated in response (transduction) • signaling cascades – Signals passes from one intracellular carrier to another until an enzyme is activated – Behavior of cell changes ...
... • intracellular signal generated in response (transduction) • signaling cascades – Signals passes from one intracellular carrier to another until an enzyme is activated – Behavior of cell changes ...
video slide
... into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all C body cells. ...
... into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all C body cells. ...
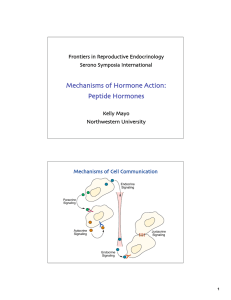
Cell Communication Lecture
... into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all C body cells. ...
... into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all C body cells. ...
AP Biology
... into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all C body cells. ...
... into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all C body cells. ...
The Hippo-YAP Pathway: New Connection between
... Salvador homolog 1 (Sav1), MOB kinase activator 1 (Mob1), and large tumor suppressor 1 & 2 (Lats1/2). Once Lats1/2 is activated, it phosphorylates YAP (Yes-associated protein)4. This phosphorylation of YAP sequesters it outside of the cell and leads to its proteosomal degradation and thus blocking i ...
... Salvador homolog 1 (Sav1), MOB kinase activator 1 (Mob1), and large tumor suppressor 1 & 2 (Lats1/2). Once Lats1/2 is activated, it phosphorylates YAP (Yes-associated protein)4. This phosphorylation of YAP sequesters it outside of the cell and leads to its proteosomal degradation and thus blocking i ...
Adenosine
... factor of activated T cells) → DNA recognition → bind with activator protein-1 (AP-1, transcription factor ) (fig. 2) Activated calcineurin 5. Cn → dephosphorylates NF-AT → into nucleus → transcription of the T cell gene↑→ IL-2↑ ...
... factor of activated T cells) → DNA recognition → bind with activator protein-1 (AP-1, transcription factor ) (fig. 2) Activated calcineurin 5. Cn → dephosphorylates NF-AT → into nucleus → transcription of the T cell gene↑→ IL-2↑ ...
ß-arrestin signaling and regulation of transcription
... and this underpins important physiological functions, such as immune responses. Notably, regulation of p53- and NF-Bmediated transcription by -arrestins is indirect, involving interactions with a variety of molecules, such as MDM2, IB␣ and TRAF6, and occurs in response to activation of GPCRs as w ...
... and this underpins important physiological functions, such as immune responses. Notably, regulation of p53- and NF-Bmediated transcription by -arrestins is indirect, involving interactions with a variety of molecules, such as MDM2, IB␣ and TRAF6, and occurs in response to activation of GPCRs as w ...
11_Lecture_picture version
... Cell communication processes share common features that reflect a shared evolutionary history. • The basics of cell communication are found in all living things. • Signals from other cells or the environment can be stimulatory (turn on a gene or protein) or inhibitory (turn off a gene or protein) • ...
... Cell communication processes share common features that reflect a shared evolutionary history. • The basics of cell communication are found in all living things. • Signals from other cells or the environment can be stimulatory (turn on a gene or protein) or inhibitory (turn off a gene or protein) • ...
The Effect of Melatonin on CREB and NF-κB Levels on LPS
... Melatonin, beyond regulating the circadian cycle, is a powerful neuroprotective antioxidant that modulates immune responses. To mediate these responses, it is hypothesized that melatonin regulates NF-κB levels in the brain. For this project, suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) 2.2 cells were chosen. These ...
... Melatonin, beyond regulating the circadian cycle, is a powerful neuroprotective antioxidant that modulates immune responses. To mediate these responses, it is hypothesized that melatonin regulates NF-κB levels in the brain. For this project, suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN) 2.2 cells were chosen. These ...
Notes for website #1..
... member of the MAPK (from mitogen activated protein kinase) family which in turn activates additional MAP kinases, like ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kiase), which enters the nucleus to phosphorylate and activate transcription factors a number of which are also protooncogenes. The cartoon shows ...
... member of the MAPK (from mitogen activated protein kinase) family which in turn activates additional MAP kinases, like ERK (extracellular signal-regulated kiase), which enters the nucleus to phosphorylate and activate transcription factors a number of which are also protooncogenes. The cartoon shows ...
Cell Communication Lecture ppt
... into cellular responses Are similar in microbes and mammals, suggesting an early origin ...
... into cellular responses Are similar in microbes and mammals, suggesting an early origin ...
MHC MOLECULES 1) Describe three important differences between
... Adapters lack PTK activity, but contain both SH2 domains and phosphorylatable tyrosines. They serve as scaffolds for the building of signaling complexes. 6) What T cell signaling phenotype would you predict for a tyrosine to phenylalanine mutation in an ITAM of the CD3γ chain? The ITAMs on the CD3 c ...
... Adapters lack PTK activity, but contain both SH2 domains and phosphorylatable tyrosines. They serve as scaffolds for the building of signaling complexes. 6) What T cell signaling phenotype would you predict for a tyrosine to phenylalanine mutation in an ITAM of the CD3γ chain? The ITAMs on the CD3 c ...
AP Cell Signaling
... • Apoptosis – A response that is a programmed or controlled cell suicide • A cell is chopped and packaged into vesicles that are digested to prevent enzymes from leaking out and damaging other cells ...
... • Apoptosis – A response that is a programmed or controlled cell suicide • A cell is chopped and packaged into vesicles that are digested to prevent enzymes from leaking out and damaging other cells ...
AP BIO Chp 11 Cell to Cell Communication
... receptor protein in some way The signal usually starts a signaling cascade, a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions, known as a signal transduction pathway Multi-step pathways can amplify a signal ...
... receptor protein in some way The signal usually starts a signaling cascade, a series of enzyme catalyzed reactions, known as a signal transduction pathway Multi-step pathways can amplify a signal ...
G-protein linked receptor
... Extracellular ligand-binding domain (N-terminal) Cytoplasmic “effector” domain Activated receptor acts as GEF to activate “heterotrimeric G-protein” ...
... Extracellular ligand-binding domain (N-terminal) Cytoplasmic “effector” domain Activated receptor acts as GEF to activate “heterotrimeric G-protein” ...
Chapter 16
... Nearly all RTKs signal via Ras/MAP kinase pathways. They also may signal via other pathways. For example, the insulin receptor uses the Ras/MAP kinase pathway to regulate gene expression and the PI-3 kinase pathway to regulate enzyme activity (e.g., glycogen synthase). RTK-Ras/MAP kinase signaling c ...
... Nearly all RTKs signal via Ras/MAP kinase pathways. They also may signal via other pathways. For example, the insulin receptor uses the Ras/MAP kinase pathway to regulate gene expression and the PI-3 kinase pathway to regulate enzyme activity (e.g., glycogen synthase). RTK-Ras/MAP kinase signaling c ...
Toll-like receptor

Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single, membrane-spanning, non-catalytic receptors usually expressed in sentinel cells such as macrophages and dendritic cells, that recognize structurally conserved molecules derived from microbes. Once these microbes have breached physical barriers such as the skin or intestinal tract mucosa, they are recognized by TLRs, which activate immune cell responses. The TLRs include TLR1, TLR2, TLR3, TLR4, TLR5, TLR6, TLR7, TLR8, TLR9, TLR10, TLR11, TLR12, and TLR13, though the latter three are not found in humans.They received their name from their similarity to the protein coded by the toll gene identified in Drosophila in 1985 by Christiane Nüsslein-Volhard. The researchers were so surprised that they spontaneously shouted out in German, ""Das ist ja toll!"" which translates as ""That's great!""