Product Adopter Categories
... • Learning: a relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience. • Interplay of drives, stimuli, cues, responses, and reinforcement. • Strongly influenced by the consequences of an individual’s behavior – Behaviors with satisfying results tend to be repeated. – Behaviors with unsatisfying re ...
... • Learning: a relatively permanent change in behavior due to experience. • Interplay of drives, stimuli, cues, responses, and reinforcement. • Strongly influenced by the consequences of an individual’s behavior – Behaviors with satisfying results tend to be repeated. – Behaviors with unsatisfying re ...
cognitive learning
... to get food. When placed on opposite side instead of turning right, rat moved towards food. So, rat formed a cognitive map to get food and reinforcement was not a precondition for learning to take place. ...
... to get food. When placed on opposite side instead of turning right, rat moved towards food. So, rat formed a cognitive map to get food and reinforcement was not a precondition for learning to take place. ...
Conformity and obedience
... adopt the behaviours, attitudes and values of other members of a reference group ◦ Minority influence: a form of social influence where a persuasive minority exerts pressure to change the attitudes, beliefs or behaviours of the majority. ...
... adopt the behaviours, attitudes and values of other members of a reference group ◦ Minority influence: a form of social influence where a persuasive minority exerts pressure to change the attitudes, beliefs or behaviours of the majority. ...
In-groups
... Social Comparison • Comparing oneself to another person (out-group member) to enhance one’s self-esteem Reason For Discrimination • The need to maintain a positive selfesteem (through the process of a downward comparison of an outgroup member) engenders negative stereotypes and prejudice → discrimin ...
... Social Comparison • Comparing oneself to another person (out-group member) to enhance one’s self-esteem Reason For Discrimination • The need to maintain a positive selfesteem (through the process of a downward comparison of an outgroup member) engenders negative stereotypes and prejudice → discrimin ...
I`m a Hypocrite, but So Is Everyone Else: Group Support and the
... in-group with the confederate. Such an assumption could be reasonable, given that past research into affiliation under conditions of stress (e.g., Schachter, 1959) has demonstrated that participants prefer to wait with another person prior to an anxiety-provoking experiment—possibly for social compa ...
... in-group with the confederate. Such an assumption could be reasonable, given that past research into affiliation under conditions of stress (e.g., Schachter, 1959) has demonstrated that participants prefer to wait with another person prior to an anxiety-provoking experiment—possibly for social compa ...
Social interventions to moderate discriminatory attitudes
... social reference. Our all attitudes have their basis in social communication and learning, which we share with other members of our group or community. In some societies, attitudes are closely linked with group goals or group identity and there are pressures towards uniformity. In such cases, attitu ...
... social reference. Our all attitudes have their basis in social communication and learning, which we share with other members of our group or community. In some societies, attitudes are closely linked with group goals or group identity and there are pressures towards uniformity. In such cases, attitu ...
The Origins of Cognitive Dissonance
... explained these results in terms of relative contrast effects: Pigeons who receive a piece of food after pecking many times experience a larger shift in relative hedonic status than those who simply receive a piece of food after pecking once (Friedrich & Zentall, 2004). Thus, the results of effort-j ...
... explained these results in terms of relative contrast effects: Pigeons who receive a piece of food after pecking many times experience a larger shift in relative hedonic status than those who simply receive a piece of food after pecking once (Friedrich & Zentall, 2004). Thus, the results of effort-j ...
The Origins of Cognitive Dissonance
... explained these results in terms of relative contrast effects: Pigeons who receive a piece of food after pecking many times experience a larger shift in relative hedonic status than those who simply receive a piece of food after pecking once (Friedrich & Zentall, 2004). Thus, the results of effort-j ...
... explained these results in terms of relative contrast effects: Pigeons who receive a piece of food after pecking many times experience a larger shift in relative hedonic status than those who simply receive a piece of food after pecking once (Friedrich & Zentall, 2004). Thus, the results of effort-j ...
The Origins of Cognitive Dissonance
... explained these results in terms of relative contrast effects: Pigeons who receive a piece of food after pecking many times experience a larger shift in relative hedonic status than those who simply receive a piece of food after pecking once (Friedrich & Zentall, 2004). Thus, the results of effort-j ...
... explained these results in terms of relative contrast effects: Pigeons who receive a piece of food after pecking many times experience a larger shift in relative hedonic status than those who simply receive a piece of food after pecking once (Friedrich & Zentall, 2004). Thus, the results of effort-j ...
Social Psychology - Napa Valley College
... an exciting event: driving out with a new car. To have had the anticipated event thwarted (by not going ahead with the deal) would have produced dissonance and disappointment. 3. Although the final price is substantially higher than the customer thought it would be, it is probably only slightly high ...
... an exciting event: driving out with a new car. To have had the anticipated event thwarted (by not going ahead with the deal) would have produced dissonance and disappointment. 3. Although the final price is substantially higher than the customer thought it would be, it is probably only slightly high ...
psychology`s roots, big ideas and critical thinking tools
... #3 Dual Processing Theory – our mind simultaneously operates consciously and unconsciously Dual Attitude System – we have two sets of attitudes systems that influence behavior Implicit Attitudes (unconscious) often differ from our Explicit Attitudes (conscious) ...
... #3 Dual Processing Theory – our mind simultaneously operates consciously and unconsciously Dual Attitude System – we have two sets of attitudes systems that influence behavior Implicit Attitudes (unconscious) often differ from our Explicit Attitudes (conscious) ...
Slide 1
... Thinking that other people think the same way that we do. Reinforces inclinations to follow authority and submit to peer pressure. Honest people will tend to believe that those they interact with are honest as well. ...
... Thinking that other people think the same way that we do. Reinforces inclinations to follow authority and submit to peer pressure. Honest people will tend to believe that those they interact with are honest as well. ...
Social Influence
... • Generally accepted way of thinking, feeling, or behaving that is endorsed and expected because it is perceived as the right and proper thing to do (Turner, 1991 pg. 3). ...
... • Generally accepted way of thinking, feeling, or behaving that is endorsed and expected because it is perceived as the right and proper thing to do (Turner, 1991 pg. 3). ...
How We Conceptualize Our Attitudes Matters: The Effects of Valence
... attitude in terms of opposition rather than in terms of support may be sufficient to enhance the resistance of that attitude. All prior work on the power of negative information and attitudes compared people who presumably had different substantive bases for their preferences. That is, people who op ...
... attitude in terms of opposition rather than in terms of support may be sufficient to enhance the resistance of that attitude. All prior work on the power of negative information and attitudes compared people who presumably had different substantive bases for their preferences. That is, people who op ...
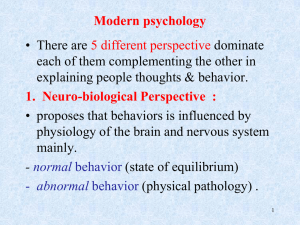
1. Neuro-biological Perspective
... scientifically testable theory of human development: • Their explanations are less convincing when applied to psychosis or organic brain disorders. • Most behaviorist research has been conducted on animals under laboratory conditions (mechanistic) . • mental illness can occur in a person in healthy ...
... scientifically testable theory of human development: • Their explanations are less convincing when applied to psychosis or organic brain disorders. • Most behaviorist research has been conducted on animals under laboratory conditions (mechanistic) . • mental illness can occur in a person in healthy ...
Introduction - Nipissing University Word
... Researching the Mind Behavior approach measures relationship between stimuli and behavior y g approach pp measures Physiological relationship between physiology and behavior Both contribute to our understanding of cognition ...
... Researching the Mind Behavior approach measures relationship between stimuli and behavior y g approach pp measures Physiological relationship between physiology and behavior Both contribute to our understanding of cognition ...
Ch. 19 S. 4
... Another form of cognitive therapy was introduced in the 1960s by psychiatrist Aaron __________. In contrast to REBT’s focus on faulty assumptions, the focus of Beck’s cognitive therapy is on __________________ illogical thought _________________. Beck has noted several types of illogical thought pro ...
... Another form of cognitive therapy was introduced in the 1960s by psychiatrist Aaron __________. In contrast to REBT’s focus on faulty assumptions, the focus of Beck’s cognitive therapy is on __________________ illogical thought _________________. Beck has noted several types of illogical thought pro ...
Contemporary Perspectives on Abnormal Behavior The Biological
... Aaron Beck, proposes that depression may result from errors in thinking or “cognitive distortions,” such as judging oneself entirely on the basis of one’s flaws or failures and interpreting events in a negative light (through blue-colored glasses, as it ...
... Aaron Beck, proposes that depression may result from errors in thinking or “cognitive distortions,” such as judging oneself entirely on the basis of one’s flaws or failures and interpreting events in a negative light (through blue-colored glasses, as it ...
Perspectives Powerpoint
... Behaviorism says we do what we do because of classical conditioning, operant conditioning or we simply learn the behavior from watching or copying it. In its extreme, they think we are simply rats in a cage pressing buttons. Many diet apps are based on behaviorist ...
... Behaviorism says we do what we do because of classical conditioning, operant conditioning or we simply learn the behavior from watching or copying it. In its extreme, they think we are simply rats in a cage pressing buttons. Many diet apps are based on behaviorist ...
SG-Ch 14 ANSWERS
... a., b., & c. In all of these situations, the counterattitudinal behaviors should not arouse much dissonance because they can be attributed to the demands of the situation. 14. b. is the answer. Dissonance theory focuses on what happens when our actions contradict our attitudes. a. Attribution theory ...
... a., b., & c. In all of these situations, the counterattitudinal behaviors should not arouse much dissonance because they can be attributed to the demands of the situation. 14. b. is the answer. Dissonance theory focuses on what happens when our actions contradict our attitudes. a. Attribution theory ...
Attitudes, Attributions and Social Cognition
... If you look carefully at advertisements, you will find that many give very little information about the objects they are promoting. For example, an advertisement for a Citroen car shows ...
... If you look carefully at advertisements, you will find that many give very little information about the objects they are promoting. For example, an advertisement for a Citroen car shows ...
Social Psychology 1
... other he proposed marriage. In both conditions, both female and male subjects viewed the woman's (identical) actions as inevitably leading to the (very different) results. ...
... other he proposed marriage. In both conditions, both female and male subjects viewed the woman's (identical) actions as inevitably leading to the (very different) results. ...
BSSCA - Ch05
... The definition of culture includes the customs, values, beliefs, and behavioral norms that are shared among a community and passed down to the next generation. Culture can play a major role in human responses, and multiple cultures may influence an individual at the same time. Culture, both singular ...
... The definition of culture includes the customs, values, beliefs, and behavioral norms that are shared among a community and passed down to the next generation. Culture can play a major role in human responses, and multiple cultures may influence an individual at the same time. Culture, both singular ...
Foundation of Behavior
... Implication for Managers Managers should be interested in employee’s attitudes because they influence behavior. Satisfied and committed employees, for instance, have lower rates of turnover and absenteeism. ...
... Implication for Managers Managers should be interested in employee’s attitudes because they influence behavior. Satisfied and committed employees, for instance, have lower rates of turnover and absenteeism. ...
Attitude change

Attitudes are associated beliefs and behaviors towards some object. They are not stable, and because of the communication and behavior of other people, are subject to change by social influences, as well as by the individual's motivation to maintain cognitive consistency when cognitive dissonance occurs--when two attitudes or attitude and behavior conflict. Attitudes and attitude objects are functions of affective and cognitive components. It has been suggested that the inter-structural composition of an associative network can be altered by the activation of a single node. Thus, by activating an affective or emotional node, attitude change may be possible, though affective and cognitive components tend to be intertwined.