Winning WW II
... a) Russia would enter war against Japan after Germany was defeated. b) United Nations would be created. c) Russia would regain all territories lost to Japan in 1905 d) Russia would be given three votes in the United Nations Assembly. e) Free elections would be held in European nations formerly occup ...
... a) Russia would enter war against Japan after Germany was defeated. b) United Nations would be created. c) Russia would regain all territories lost to Japan in 1905 d) Russia would be given three votes in the United Nations Assembly. e) Free elections would be held in European nations formerly occup ...
File
... live or enough money to rebuild. Americans wanted to help all the people who were affected by the war even the people they fought against. ...
... live or enough money to rebuild. Americans wanted to help all the people who were affected by the war even the people they fought against. ...
The Cold War
... • Atomic/Nuclear Arms race (aka the Space Race) • The Cold War was “fought” between the USA and the USSR and later, Communist China • U.S. Pressure for German re-armament • Soviet desire for “Satellites” or, “Buffer ...
... • Atomic/Nuclear Arms race (aka the Space Race) • The Cold War was “fought” between the USA and the USSR and later, Communist China • U.S. Pressure for German re-armament • Soviet desire for “Satellites” or, “Buffer ...
World War II
... Allies agreed to an invasion of the Western Europe in 1944. Stalin reaffirmed the Soviet commitment to enter the war against Japan Stalin insisted on Soviet control of Eastern Europe and the carving up of Germany Churchill demanded free governments in Eastern Europe and a strong Germany after the wa ...
... Allies agreed to an invasion of the Western Europe in 1944. Stalin reaffirmed the Soviet commitment to enter the war against Japan Stalin insisted on Soviet control of Eastern Europe and the carving up of Germany Churchill demanded free governments in Eastern Europe and a strong Germany after the wa ...
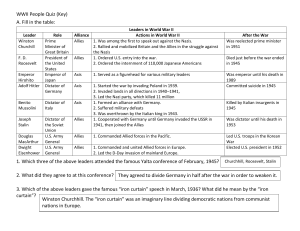
WWII Leaders Quiz Key
... 1. Cooperated with Germany until Germany invaded the USSR in 1941, then joined the Allies ...
... 1. Cooperated with Germany until Germany invaded the USSR in 1941, then joined the Allies ...
Growth of Tension: Origins of the Cold War
... • Helping liberated countries establish provisional governments ...
... • Helping liberated countries establish provisional governments ...
From the USSR to Russia
... Khalkin Gol • August 23-30, 1939 • Soviet forces under General Zhukov surround and annihilate Japanese force in Mongolia. • Japan signs treaty with USSR, turns to the Pacific • Stalin gains time for war with Germany, does not have to fight on two fronts • USSR declares war on Japan August 8, 1945, o ...
... Khalkin Gol • August 23-30, 1939 • Soviet forces under General Zhukov surround and annihilate Japanese force in Mongolia. • Japan signs treaty with USSR, turns to the Pacific • Stalin gains time for war with Germany, does not have to fight on two fronts • USSR declares war on Japan August 8, 1945, o ...
WWII Lesson 6 - Outcomes of World War II
... Tokyo Trials – Gen. MacArthur brought 25 Japanese leaders to trial for crimes against Chinese – 7 sentenced to death & 16 to life in prison ...
... Tokyo Trials – Gen. MacArthur brought 25 Japanese leaders to trial for crimes against Chinese – 7 sentenced to death & 16 to life in prison ...
World War II - Reading Community Schools
... Germany would be divided into four zones to be governed by the USSR, Britain, U.S. and France Stalin agreed to hold free elections in Europe ...
... Germany would be divided into four zones to be governed by the USSR, Britain, U.S. and France Stalin agreed to hold free elections in Europe ...
WARM UP Who was present at the Yalta Conference?
... the spread of communism. • Open to all European nations which would allow for free democratic elections. • USSR and its satellite nations did not participate. • 16 nations participated ...
... the spread of communism. • Open to all European nations which would allow for free democratic elections. • USSR and its satellite nations did not participate. • 16 nations participated ...
Rise of the Modern State System
... the United States and the Soviet Union. • A new kind of arms race began, new alliances were formed. • North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – the alliance of Western Europe and North America. • However, it is interesting to note that the post war period also saw the creation of the United Nation ...
... the United States and the Soviet Union. • A new kind of arms race began, new alliances were formed. • North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) – the alliance of Western Europe and North America. • However, it is interesting to note that the post war period also saw the creation of the United Nation ...
CHAPTER 1: FROM WORLD WAR TO COLD WAR
... defeat fascism. Churchill deemed it a “deal with the devil.” If history had taken a different turn, the United States could have aligned with Hitler against Stalin. This unlikely alliance was forced when Hitler reneged on the Molotov-Rippendorp Pact—the non-aggression agreement signed by Germany and ...
... defeat fascism. Churchill deemed it a “deal with the devil.” If history had taken a different turn, the United States could have aligned with Hitler against Stalin. This unlikely alliance was forced when Hitler reneged on the Molotov-Rippendorp Pact—the non-aggression agreement signed by Germany and ...
Origins of the Cold War
... After World War II, hopes for peace were high United Nations was established as a peacekeeping body in ...
... After World War II, hopes for peace were high United Nations was established as a peacekeeping body in ...
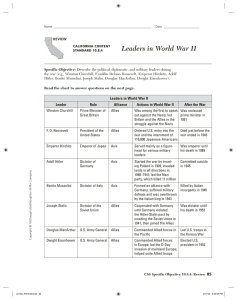
WWII - ERA CONFERENCES
... Stalin agreed to declare war on Japan 90 days after peace with Germany. Potsdam Conference – July 1945 Allied meeting at the Cecilienhof Palace in Potsdam, just outside of Berlin. US President Harry Truman, Churchill and Stalin met to discuss the punishment of Nazi officials and the end of the war a ...
... Stalin agreed to declare war on Japan 90 days after peace with Germany. Potsdam Conference – July 1945 Allied meeting at the Cecilienhof Palace in Potsdam, just outside of Berlin. US President Harry Truman, Churchill and Stalin met to discuss the punishment of Nazi officials and the end of the war a ...
End of WWII in Europe US
... centers were built all over the United States. • By avoiding the physical destruction of war, the U.S. economy dominated the world ...
... centers were built all over the United States. • By avoiding the physical destruction of war, the U.S. economy dominated the world ...
USA` isolationism ( beginning of the XX century)
... In return, Stalin promised to permit free elections in Poland. This agreement invited stinging criticisms of Churchill back in Britain, where he was accused in parliament of ‘selling out’ the Poles. The violation of Polish sovereignty had triggered Britain’s declaration of war on Germany – and now C ...
... In return, Stalin promised to permit free elections in Poland. This agreement invited stinging criticisms of Churchill back in Britain, where he was accused in parliament of ‘selling out’ the Poles. The violation of Polish sovereignty had triggered Britain’s declaration of war on Germany – and now C ...
Origins of the Cold War Debate De
... Wartime Conferences • Potsdam, July 1945 • JAPAN: Stalin wanted to take part in Japan's defeat (benefits), but Truman wanted Japanese quick surrender so that Russia would get nothing out of it; he had the atomic bomb and was prepared to use it. • GERMANY: Zone divisions were confirmed; there were d ...
... Wartime Conferences • Potsdam, July 1945 • JAPAN: Stalin wanted to take part in Japan's defeat (benefits), but Truman wanted Japanese quick surrender so that Russia would get nothing out of it; he had the atomic bomb and was prepared to use it. • GERMANY: Zone divisions were confirmed; there were d ...
U5D6- Roots of the Cold War
... Both countries also disagreed at the Yalta conference on how post-war Europe should be structured. Stalin wanted a divided Germany to keep it weak and for the Soviet Union to occupy Eastern Europe. ▪ These Eastern European nations would become satellite states, or ‘spheres of influence’. The U.S ...
... Both countries also disagreed at the Yalta conference on how post-war Europe should be structured. Stalin wanted a divided Germany to keep it weak and for the Soviet Union to occupy Eastern Europe. ▪ These Eastern European nations would become satellite states, or ‘spheres of influence’. The U.S ...
22.1 Notes - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... • To a degree, these problems were the result of decisions they had made during the war • February 1945- Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin had met at the Black Sea resort town of Yalta • Three leaders agreed to divide Austria into zones of military occupation • Berlin would lie entirely within the So ...
... • To a degree, these problems were the result of decisions they had made during the war • February 1945- Churchill, Roosevelt, and Stalin had met at the Black Sea resort town of Yalta • Three leaders agreed to divide Austria into zones of military occupation • Berlin would lie entirely within the So ...
The Cold War
... • International organization established to maintain peace after the war The Set-up • General Assembly – where all members meet to discuss issues and vote • Security Council – 11 member body with the real power to investigate & settle disputes • Five permanent members: Soviet Union, United States, G ...
... • International organization established to maintain peace after the war The Set-up • General Assembly – where all members meet to discuss issues and vote • Security Council – 11 member body with the real power to investigate & settle disputes • Five permanent members: Soviet Union, United States, G ...
Section 3 - Mr. Cosbey
... • There they planned war strategy in an atmosphere of distrust. • Stalin wanted control of Eastern Europe to protect the Soviet Union form future aggression. • Churchill and Roosevelt wanted self-determination for the people of Eastern Europe, but they needed Stalin’s help to win the war. • The thre ...
... • There they planned war strategy in an atmosphere of distrust. • Stalin wanted control of Eastern Europe to protect the Soviet Union form future aggression. • Churchill and Roosevelt wanted self-determination for the people of Eastern Europe, but they needed Stalin’s help to win the war. • The thre ...
Yalta Conference
_(B&W).jpg?width=300)
The Yalta Conference, sometimes called the Crimea Conference and codenamed the Argonaut Conference, held from February 4 to 11, 1945, was the World War II meeting of the heads of government of the United States, the United Kingdom and the Soviet Union, represented by President Franklin D. Roosevelt, Prime Minister Winston Churchill and Premier Joseph Stalin, respectively, for the purpose of discussing Europe's post-war reorganization. The conference convened in the Livadia Palace near Yalta in Crimea.The meeting was intended mainly to discuss the re-establishment of the nations of war-torn Europe. Within a few years, with the Cold War dividing the continent, Yalta became a subject of intense controversy. To some extent, it has remained controversial.Yalta was the second of three wartime conferences among the Big Three. It had been preceded by the Tehran Conference in 1943, and was followed by the Potsdam Conference in July 1945, which was attended by Stalin, Churchill (who was replaced halfway through by the newly elected British Prime Minister Clement Attlee) and Harry S. Truman, Roosevelt's successor.