Slide ()
... Ehlers-Danlos syndrome This syndrome is actually a collection of six major genetic types with the common features of hyperextensible skin and joints, easy bruising, defective wound healing, and blood vessel fragility. Distinct abnormalities in collagen synthesis have been identified in some of the v ...
... Ehlers-Danlos syndrome This syndrome is actually a collection of six major genetic types with the common features of hyperextensible skin and joints, easy bruising, defective wound healing, and blood vessel fragility. Distinct abnormalities in collagen synthesis have been identified in some of the v ...
Human Genetics - Shelton State
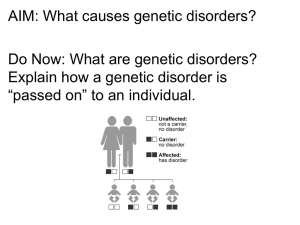
... Human Genetics Chapters 11 & 12 Genetic Disorders: Autosomal disorder= -inheritable (due to a defective gene) -not a disease/not contagious -cannot be prevented -no cure -can be treated to some degree -normal= -carrier= -affected= -recessive disorder= -dominant disorder= Recessive Disorders 1. Cysti ...
... Human Genetics Chapters 11 & 12 Genetic Disorders: Autosomal disorder= -inheritable (due to a defective gene) -not a disease/not contagious -cannot be prevented -no cure -can be treated to some degree -normal= -carrier= -affected= -recessive disorder= -dominant disorder= Recessive Disorders 1. Cysti ...
Noonan syndrome information sheet
... Disability’ 2005, which can be consulted for more detailed information.) ...
... Disability’ 2005, which can be consulted for more detailed information.) ...
ppt
... 1 in 900 people born with this Likelihood of having a child with DS increases with advancing maternal age Symptoms: mental retardation, upward slant to eyes, small mouth, abnormal ear shape, decreased muscle tone No cure ...
... 1 in 900 people born with this Likelihood of having a child with DS increases with advancing maternal age Symptoms: mental retardation, upward slant to eyes, small mouth, abnormal ear shape, decreased muscle tone No cure ...
Gene Disorders
... Gene disorder refers to the harmful effect a detrimental allele produces when it occurs at a significant frequency in a population. ...
... Gene disorder refers to the harmful effect a detrimental allele produces when it occurs at a significant frequency in a population. ...
Human Genetic Disorders
... In Turner syndrome, an error occurring very early in development results in an abnormal number and arrangement of chromosomes. Most commonly, an individual with Turner syndrome will be born with 45 chromosomes in each cell rather than 46. The missing chromosome is an X chromosome. The affected perso ...
... In Turner syndrome, an error occurring very early in development results in an abnormal number and arrangement of chromosomes. Most commonly, an individual with Turner syndrome will be born with 45 chromosomes in each cell rather than 46. The missing chromosome is an X chromosome. The affected perso ...
Genetics
... 1. Mitosis, meiosis, Barr body : Stages of mitosis, meiosis are focused under the microscope To draw the different stages of mitosis and meiosis To draw the Barr body which is focused under the microscope 2. Preparing a pedigree chart : Symbols use ...
... 1. Mitosis, meiosis, Barr body : Stages of mitosis, meiosis are focused under the microscope To draw the different stages of mitosis and meiosis To draw the Barr body which is focused under the microscope 2. Preparing a pedigree chart : Symbols use ...
Phelan-McDermid Syndrome Presenting as a Puzzling Case of
... more obvious dysmorphic features of Phelan-McDermid syndrome, but did have seizure activity and MRI findings consistent with this diagnosis. Patients with a typical symptoms or complex medical histories may often go through years of stressful, time consuming and costly testing by multiple health car ...
... more obvious dysmorphic features of Phelan-McDermid syndrome, but did have seizure activity and MRI findings consistent with this diagnosis. Patients with a typical symptoms or complex medical histories may often go through years of stressful, time consuming and costly testing by multiple health car ...
Genetic Disorder Poster Project
... Tay Sachs: baby will become blind, paralyzed & unaware. Fatal. Thalassemia: babies are listless, fussy and get sick easily. Bones become brittle and distorted. Turner Syndrome: females are short, sterile, fail to develop secondary sexual characteristics. ...
... Tay Sachs: baby will become blind, paralyzed & unaware. Fatal. Thalassemia: babies are listless, fussy and get sick easily. Bones become brittle and distorted. Turner Syndrome: females are short, sterile, fail to develop secondary sexual characteristics. ...
ONE GENE, TWO DISEASES: SCN5A AND ITS ROLE IN LONG QT
... Sudden cardiac death (SCD) is one of the leading causes of mortality globally and accounted for 24.1% of deaths in Singapore in 2008. Cardiac arrhythmias such as the Long QT (LQTS) and Brugada syndrome cause deaths in young individuals with structurally normal hearts. Cardiac arrhythmias include the ...
... Sudden cardiac death (SCD) is one of the leading causes of mortality globally and accounted for 24.1% of deaths in Singapore in 2008. Cardiac arrhythmias such as the Long QT (LQTS) and Brugada syndrome cause deaths in young individuals with structurally normal hearts. Cardiac arrhythmias include the ...
MCB Lecture 1 – Molecular Diagnostics
... What is the typical size of fragments that PCR can amplify? o >1kb How many cycles must you perform via PCR before you get the first exact sample that you want to amplify? o 4 Cycles If you have a single base difference in sequence that does not affect a restriction site, how do you detect it? o Use ...
... What is the typical size of fragments that PCR can amplify? o >1kb How many cycles must you perform via PCR before you get the first exact sample that you want to amplify? o 4 Cycles If you have a single base difference in sequence that does not affect a restriction site, how do you detect it? o Use ...
Chromosome Mutation - Hicksville Public Schools
... 1. Achondroplasia - most common genetic cause of dwarfism 2. Albinism - little or no production of melanin in hair, skin, and iris of the eyes 3. Bloom Syndrome - high frequency of breaks and rearrangements in the chromosomes 4. Cystic Fibrosis - autosomal recessive disorder secreting mucus and swe ...
... 1. Achondroplasia - most common genetic cause of dwarfism 2. Albinism - little or no production of melanin in hair, skin, and iris of the eyes 3. Bloom Syndrome - high frequency of breaks and rearrangements in the chromosomes 4. Cystic Fibrosis - autosomal recessive disorder secreting mucus and swe ...
Neonatology Genetics Topics - East Bay Newborn Specialists
... genes on the maternal copy are imprinted (inactive) • 25% of cases, a patient has 2 copies of chromosome 15 inherited from their mother (uniparental disomy) • Angelman - caused by deletion in maternal 15 or by paternal uniparental disomy ...
... genes on the maternal copy are imprinted (inactive) • 25% of cases, a patient has 2 copies of chromosome 15 inherited from their mother (uniparental disomy) • Angelman - caused by deletion in maternal 15 or by paternal uniparental disomy ...
Chromosomal Genetics and Pathology (Dr
... unequal recombination b/w OR clusters on chrom. 8 (short arm) results in three recurrent chromosomal rearrangements: inverted duplication (distinct phenotype), supranumery chromosome (minor anomalies), 8p23 interstitial deletion (heart defect) these recombination events are associated with a mat ...
... unequal recombination b/w OR clusters on chrom. 8 (short arm) results in three recurrent chromosomal rearrangements: inverted duplication (distinct phenotype), supranumery chromosome (minor anomalies), 8p23 interstitial deletion (heart defect) these recombination events are associated with a mat ...
Ellis-van Creveld Syndrome - National Foundation for Ectodermal
... teeth fall out or are extracted by a dentist, they are not replaced by other teeth. Other abnormalities in the mouth include serrated (washboard-like) ridges of the gums. Congenital heart disease is the most life-threatening feature of this syndrome and is found in about half of all patients with th ...
... teeth fall out or are extracted by a dentist, they are not replaced by other teeth. Other abnormalities in the mouth include serrated (washboard-like) ridges of the gums. Congenital heart disease is the most life-threatening feature of this syndrome and is found in about half of all patients with th ...
Chapter 16 Review
... 7. Why are sex linked traits more common in males? 8. What are polygenic traits, give two examples of these types of traits in humans. 9. Know how to use the product rule to predict probabilities of consecutive events. 10. You MUST know how to carry out all types of crosses that we have done. Mono ...
... 7. Why are sex linked traits more common in males? 8. What are polygenic traits, give two examples of these types of traits in humans. 9. Know how to use the product rule to predict probabilities of consecutive events. 10. You MUST know how to carry out all types of crosses that we have done. Mono ...
Greig Syndrome - City Tech OpenLab
... involving physical abnormalities of the fingers and toes and the craniofacial area. In most cases, GCPS is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait but the phenotype may range from mild to severe in affected individuals. Dominant genetic disorders occur when only a single copy of an abnormal gene is ...
... involving physical abnormalities of the fingers and toes and the craniofacial area. In most cases, GCPS is inherited as an autosomal dominant trait but the phenotype may range from mild to severe in affected individuals. Dominant genetic disorders occur when only a single copy of an abnormal gene is ...
Genetics - Max Appeal!
... The extent to which a person is affected is extremely variable and almost impossible to predict. There are almost 200 anomalies caused by the deletion, and each individual could be affected by many (but NOT all!) or just a few or have some minor problems, say, not being very good at maths at school. ...
... The extent to which a person is affected is extremely variable and almost impossible to predict. There are almost 200 anomalies caused by the deletion, and each individual could be affected by many (but NOT all!) or just a few or have some minor problems, say, not being very good at maths at school. ...
Jacobsen Disease
... chromosome 11 that includes band 11q24.1. • It can cause intellectual disabilities, a distinctive facial appearance, and a variety of physical problems including heart defects and a bleeding disorder. ...
... chromosome 11 that includes band 11q24.1. • It can cause intellectual disabilities, a distinctive facial appearance, and a variety of physical problems including heart defects and a bleeding disorder. ...
Happy Heart Syndrome It`s already been proven that intense
... It's already been proven that intense emotional distress -- say, after losing a loved one -- can trigger a cardiac abnormality called "broken heart syndrome." But now new research suggests sudden bursts of joy can have the same effect. The condition, known as Takotsubo syndrome (TTS), occurs when th ...
... It's already been proven that intense emotional distress -- say, after losing a loved one -- can trigger a cardiac abnormality called "broken heart syndrome." But now new research suggests sudden bursts of joy can have the same effect. The condition, known as Takotsubo syndrome (TTS), occurs when th ...
Genetics - Max Appeal!
... deletion, or it could be as few as 1:6,000. It is the most frequently occurring chromosome deletion and the second most common cause of congenital heart defects. The frequency of diagnosis has increased enormously over the past decade or so and many individuals who are now found to have the deletion ...
... deletion, or it could be as few as 1:6,000. It is the most frequently occurring chromosome deletion and the second most common cause of congenital heart defects. The frequency of diagnosis has increased enormously over the past decade or so and many individuals who are now found to have the deletion ...
DiGeorge syndrome

DiGeorge syndrome is also known as 22q11.2 deletion syndrome,DiGeorge anomaly, velocardiofacial syndrome (VCFS), Shprintzen syndrome, conotruncal anomaly face syndrome (CTAF) or Takao syndrome, Sedlackova syndrome, Cayler cardiofacial syndrome,Strong syndrome, congenital thymic aplasia, and thymic hypoplasia. This syndrome is caused by the deletion of a small piece of chromosome 22. As such, it is recommended that the name ""22q11.2 deletion syndrome (22q11.2DS)"" be used.22q11.2DS is the most common microdeletion syndrome characterized by low copy repeats and the deletion occurs near the middle of the chromosome at a location designated 22q11.2—signifying its location on the long arm of one of the pair of chromosomes 22, on region 1, band 1, sub-band 2. The inheritance pattern is autosomal dominant and it has a prevalence estimated at 1:4000. The syndrome was described in 1968 by the pediatric endocrinologist Angelo DiGeorge. 22q11 deletion is also associated with truncus arteriosus and tetralogy of Fallot.