Session 26 - Iowa State University
... a) How wide must this oven be so that it will contain five antinodal planes of the electric field along its width in the standing wave pattern? ...
... a) How wide must this oven be so that it will contain five antinodal planes of the electric field along its width in the standing wave pattern? ...
notes on Bohr and the hydrogen spectrum
... emit only certain frequencies. Atomic gases are the simplest cases, and here are representations of the emission and absorption spectra for mercury vapour. ...
... emit only certain frequencies. Atomic gases are the simplest cases, and here are representations of the emission and absorption spectra for mercury vapour. ...
Midterm Review Sheet
... 6. Crookes - using Crookes' tube discovered "cathode rays" as negative particles/radiation. This was the first evidence of electrons. 7. Thomson – determined: 1) that cathode rays were actually streams of negatively charged particles called electrons (could be deflected by a magnetic or electric fie ...
... 6. Crookes - using Crookes' tube discovered "cathode rays" as negative particles/radiation. This was the first evidence of electrons. 7. Thomson – determined: 1) that cathode rays were actually streams of negatively charged particles called electrons (could be deflected by a magnetic or electric fie ...
Physics 1020 Ch 10-12 Exam Answered
... calculated at the same time, since the product of both the momentum and location is greater than or equal to Planck’s constant. ...
... calculated at the same time, since the product of both the momentum and location is greater than or equal to Planck’s constant. ...
unit-4 - snist
... dimensional potential box with a width of a ‘ L’ units in which potential is constant and zero. ...
... dimensional potential box with a width of a ‘ L’ units in which potential is constant and zero. ...
Notes - Particle Theory
... • Special relativity and quantum mechanics together imply the existence of anti-particles – special relativity treats negative and positive energies the same, implies the existence of an infinite tower of negative energy states (rather than a ground state) – we make sense of this by assuming all neg ...
... • Special relativity and quantum mechanics together imply the existence of anti-particles – special relativity treats negative and positive energies the same, implies the existence of an infinite tower of negative energy states (rather than a ground state) – we make sense of this by assuming all neg ...
LOYOLA COLLEGE (AUTONOMOUS), CHENNAI – 600 034
... a) Find the eigenvalue E of H = E b) Show that the above obtained eigen value in terms of the classical frequency = (1/2)(k/m) and the constant a = (/h)(km)1/2 is E = (1/2)h. ...
... a) Find the eigenvalue E of H = E b) Show that the above obtained eigen value in terms of the classical frequency = (1/2)(k/m) and the constant a = (/h)(km)1/2 is E = (1/2)h. ...
Lecture5.EMfield
... “operator”, which stands ready to “create” or “annihilate” a photon of any energy, , and momentum, k. ...
... “operator”, which stands ready to “create” or “annihilate” a photon of any energy, , and momentum, k. ...
Lecture6.QM.to.Lagrangian.Densities
... This calls for a different kind of “Lagrangian” -- not like the one used in classical or quantum mechanics. So, we have another postulate, defining what is meant by a “Lagrangian” – called a Lagrangian density. ...
... This calls for a different kind of “Lagrangian” -- not like the one used in classical or quantum mechanics. So, we have another postulate, defining what is meant by a “Lagrangian” – called a Lagrangian density. ...
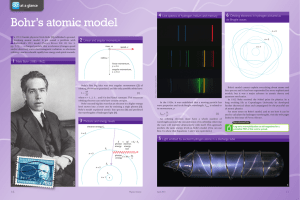
Bohr`s atomic model
... Bohr’s model cannot explain everything about atoms and line spectra and it has been superseded by more sophisticated models, but it was a major advance in atomic theory and quantum mechanics. In 1922 Bohr received the Nobel prize for physics. In a long working life at Copenhagen University he develo ...
... Bohr’s model cannot explain everything about atoms and line spectra and it has been superseded by more sophisticated models, but it was a major advance in atomic theory and quantum mechanics. In 1922 Bohr received the Nobel prize for physics. In a long working life at Copenhagen University he develo ...
Quantum Physics and Human Affairs
... with the smooth, spread-out electromagnetic wave description given above. But by 1950, physicists had found a theory that could reconcile these apparent particles of light, called "photons," with the electromagnetic wave theory of light. This "quantum field theory" states that the energy of the elec ...
... with the smooth, spread-out electromagnetic wave description given above. But by 1950, physicists had found a theory that could reconcile these apparent particles of light, called "photons," with the electromagnetic wave theory of light. This "quantum field theory" states that the energy of the elec ...
Chp 5 Guided Reading Notes and Vocabulary
... 8. Look at Figure 5.10 on page 139. The electromagnetic spectrum consists of radiation over a broad band of wavelengths. What type of radiation has the lowest frequency? The highest frequency? _______________________________________________________________________ Atomic Spectra 9. What happens when ...
... 8. Look at Figure 5.10 on page 139. The electromagnetic spectrum consists of radiation over a broad band of wavelengths. What type of radiation has the lowest frequency? The highest frequency? _______________________________________________________________________ Atomic Spectra 9. What happens when ...
Arrangement of the Electrons Chapter 4
... that are not absorbed by an atom. This is a continuous spectrum with wavelengths removed that are absorbed by the atom. These are shown as black lines for absorbed light. Continuous Spectrum: All wavelengths of a region of the spectrum are represented (i.e. visible light) ...
... that are not absorbed by an atom. This is a continuous spectrum with wavelengths removed that are absorbed by the atom. These are shown as black lines for absorbed light. Continuous Spectrum: All wavelengths of a region of the spectrum are represented (i.e. visible light) ...
Quantum Physics
... Planck's quantum theory. Explain why the classical curve is incorrect. What was Planck's key assumption in his quantum model? (What did he quantize?) CLICK FOR ANSWER ...
... Planck's quantum theory. Explain why the classical curve is incorrect. What was Planck's key assumption in his quantum model? (What did he quantize?) CLICK FOR ANSWER ...
MIT Physics Graduate General Exams
... Part I Concepts Students studying for the Fall 2003 Part I exam found it useful to first categorize each problem by the concept they thought was being tested. Such an approach simplified their subsequent attempt at solving the problem. The following is a list of all the concepts they thought could b ...
... Part I Concepts Students studying for the Fall 2003 Part I exam found it useful to first categorize each problem by the concept they thought was being tested. Such an approach simplified their subsequent attempt at solving the problem. The following is a list of all the concepts they thought could b ...
Measuring Planck`s Constant Using Light Emitting Diodes - IFSC-USP
... The results yielded should give an accurate value for Planck’s constant. This method, depending on the results, can then be used in an entry level physics lab, such as that of a high school physics lab. ...
... The results yielded should give an accurate value for Planck’s constant. This method, depending on the results, can then be used in an entry level physics lab, such as that of a high school physics lab. ...
Bohr Model and Quantum Model
... Principle Heisenberg stated that you may know the location of an electron or the velocity of electron but you may not know both simultaneously ...
... Principle Heisenberg stated that you may know the location of an electron or the velocity of electron but you may not know both simultaneously ...