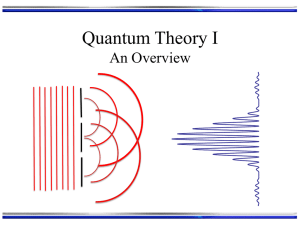
Geometry,
... form proportional to the osmotic velocity in the Nelson stochastic mechanics and using the variational principle with appropriate change of variables. The possibility to treat gradS and ps as two parts of the momentum of quantum ensemble particles is considered from the view point of uncertainty rel ...
... form proportional to the osmotic velocity in the Nelson stochastic mechanics and using the variational principle with appropriate change of variables. The possibility to treat gradS and ps as two parts of the momentum of quantum ensemble particles is considered from the view point of uncertainty rel ...
SCHRODINGER`S CAT-IN-THE-BOX WITH THE COPENHAGEN
... adequate knowledge of a system of interacting objects without active interference in it . This theory holds that energy exists in units that cannot be divided. Max Planck ushered in quantum theory into the epistemological corpus when he offered a solution to the problem of black body radiation in 19 ...
... adequate knowledge of a system of interacting objects without active interference in it . This theory holds that energy exists in units that cannot be divided. Max Planck ushered in quantum theory into the epistemological corpus when he offered a solution to the problem of black body radiation in 19 ...
Kepler`s elliptic orbits in wave mechanics, and problems with the de
... construct wave-packets that can represent electrons revolving in very Bohr orbits. ...
... construct wave-packets that can represent electrons revolving in very Bohr orbits. ...
THE ATOM
... The Bohr Model A. The Niels Bohr model of the atom, proposed in 1913, suggested that an electron in an atom possesses a specific energy level that is dependent on the orbit it is in. An electron in the innermost orbit has the least energy. B. Electron orbits are identified by a quantum number n, and ...
... The Bohr Model A. The Niels Bohr model of the atom, proposed in 1913, suggested that an electron in an atom possesses a specific energy level that is dependent on the orbit it is in. An electron in the innermost orbit has the least energy. B. Electron orbits are identified by a quantum number n, and ...
Advanced Chemistry Midterm
... 46. What is a heterogeneous mixture? 47. What value is an element’s identity based upon? ...
... 46. What is a heterogeneous mixture? 47. What value is an element’s identity based upon? ...
7Copenhagen
... •Detect which slit the electron went through with light beam (particle behaviour) •If interference pattern appears, then we have both wave and particle behaviour •Complementarity says it must be either ...
... •Detect which slit the electron went through with light beam (particle behaviour) •If interference pattern appears, then we have both wave and particle behaviour •Complementarity says it must be either ...
PYP001-122-Final Exam Solution [Choice A is the correct
... A) Electromagnetic waves with longer wavelength carry less energy. B) The total energy of an object at rest must be zero. C) Nerves use radiant energy to communicate with the body. D) Electromagnetic waves are compressional waves. E) Useful energy is always equal to wasted energy. Q15. Which of the ...
... A) Electromagnetic waves with longer wavelength carry less energy. B) The total energy of an object at rest must be zero. C) Nerves use radiant energy to communicate with the body. D) Electromagnetic waves are compressional waves. E) Useful energy is always equal to wasted energy. Q15. Which of the ...
89mc
... 50 N. The lift goes down and then stops. The reading on the scale is A. 50 N throughout the journey. B. more than 50 N when the lift starts, and remains steady until it comes to rest. C. less than 50 N when the lift starts, and remains steady until it comes to rest. D. more than 50 N as the lift sta ...
... 50 N. The lift goes down and then stops. The reading on the scale is A. 50 N throughout the journey. B. more than 50 N when the lift starts, and remains steady until it comes to rest. C. less than 50 N when the lift starts, and remains steady until it comes to rest. D. more than 50 N as the lift sta ...
l3_bondingebands
... Key result of wave mechanics (F. Bloch, 1928): Plane wave in a periodic potential Wave momentum k only unique up to 2π/a Only certain electron energies allowed, but those can propagate (theoretically) unimpeded, as long as lattice spacing is “perfectly” maintained But, resistance introduced ...
... Key result of wave mechanics (F. Bloch, 1928): Plane wave in a periodic potential Wave momentum k only unique up to 2π/a Only certain electron energies allowed, but those can propagate (theoretically) unimpeded, as long as lattice spacing is “perfectly” maintained But, resistance introduced ...
Ψ (x,t) = | Ψ (x,t) - University of Notre Dame
... Within the box, the energy is constant – hence ω and k are constant – and also the wavelength λ, and the momentum p Boundary conditions: The wave-function must go to zero outside the box, at very large positive and very large negative x-values Follow Bohr and De Broglie’s ideas and fix the number of ...
... Within the box, the energy is constant – hence ω and k are constant – and also the wavelength λ, and the momentum p Boundary conditions: The wave-function must go to zero outside the box, at very large positive and very large negative x-values Follow Bohr and De Broglie’s ideas and fix the number of ...
Early Quantum Theory and Models of the Atom
... and give off a photon in the process • This is the origin of the emission spectra of excited gases • The vertical arrows represent the transitions or jumps that correspond to the various observed spectral lines ...
... and give off a photon in the process • This is the origin of the emission spectra of excited gases • The vertical arrows represent the transitions or jumps that correspond to the various observed spectral lines ...
Statistical laws
... of statistical physics §1 Statistical laws of macroscopic matter Statistical laws In classic physics, the motion of a single particle will obey Newton’s law. If the initial position and velocity are known, we can predict its position at any time by solving the Newton equation of motions. A macro ...
... of statistical physics §1 Statistical laws of macroscopic matter Statistical laws In classic physics, the motion of a single particle will obey Newton’s law. If the initial position and velocity are known, we can predict its position at any time by solving the Newton equation of motions. A macro ...
E n hf - Michael Ruiz
... This is the result we simply wrote down earlier. A superposition of two identical sine waves reflecting off the waves produces a pattern we call a “standing wave.” These standing waves form the harmonics. Note that k in our “wave function” can’t just be anything. The waves must be “fitted” to lengt ...
... This is the result we simply wrote down earlier. A superposition of two identical sine waves reflecting off the waves produces a pattern we call a “standing wave.” These standing waves form the harmonics. Note that k in our “wave function” can’t just be anything. The waves must be “fitted” to lengt ...
Simulation programs for teaching quantum mechanics
... with this behaviour from a previous example. Next one sees two “bubbles” coming up immediately behind the slit, which is more or less what one would expect. But after a while a third bubble appears in the middle, which together with the other two develops into the well-known interference pattern at ...
... with this behaviour from a previous example. Next one sees two “bubbles” coming up immediately behind the slit, which is more or less what one would expect. But after a while a third bubble appears in the middle, which together with the other two develops into the well-known interference pattern at ...
The Quantum Theory of Atoms and Molecules
... 1. It fails to provide any understanding of why certain spectral lines are brighter than others. There is no mechanism for the calculation of transition probabilities. ...
... 1. It fails to provide any understanding of why certain spectral lines are brighter than others. There is no mechanism for the calculation of transition probabilities. ...
Modules to examine on the Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms website
... Modules to examine on the Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms website: (click to go directly to the different modules) EM Waves Evidence for EM Waves Catch the Wave Stadium Wave Electric Force Quantum Atom Spectral Lines Edvidence for Spectra Absorption Spectra Bohr's Atom Vibrating Charges rev. Adv B ...
... Modules to examine on the Arrangement of Electrons in Atoms website: (click to go directly to the different modules) EM Waves Evidence for EM Waves Catch the Wave Stadium Wave Electric Force Quantum Atom Spectral Lines Edvidence for Spectra Absorption Spectra Bohr's Atom Vibrating Charges rev. Adv B ...
The mathematical formulations of quantum mechanics are those
... quantization. Although the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom could be explained in this way, the spectrum of the helium atom (classically an unsolvable 3-body problem) could not be predicted. The mathematical status of quantum theory remained uncertain for some time. In 1923 de Broglie proposed that ...
... quantization. Although the Bohr model of the hydrogen atom could be explained in this way, the spectrum of the helium atom (classically an unsolvable 3-body problem) could not be predicted. The mathematical status of quantum theory remained uncertain for some time. In 1923 de Broglie proposed that ...