
Chapter 5: Electrons in Atoms
... fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. We are certain about being uncertain Bumping into an electron while trying to determine its position and movement transfers energy and disrupts the electron ...
... fundamentally impossible to know precisely both the velocity and position of a particle at the same time. We are certain about being uncertain Bumping into an electron while trying to determine its position and movement transfers energy and disrupts the electron ...
Department of Physical Sciences (Physics)
... (i) Explain what is meant by the Photoelectric Effect. [2 marks] (ii) Describe briefly the apparatus used to study this effect and discuss the main experimental observations making reference to appropriate graphs of the results. Use these graphs to explain what is meant by: (a) prompt emission (b) t ...
... (i) Explain what is meant by the Photoelectric Effect. [2 marks] (ii) Describe briefly the apparatus used to study this effect and discuss the main experimental observations making reference to appropriate graphs of the results. Use these graphs to explain what is meant by: (a) prompt emission (b) t ...
Academic Chemistry Atomic History Study Guide 1. Identify and
... would destroy the atom. __________ _____________ proposed a new model of the atom that allowed electrons to circle the nucleus but only on specified paths (orbits) which for some reason were stable. The study of the motion of electrons lead to the development of a new branch of physics called ______ ...
... would destroy the atom. __________ _____________ proposed a new model of the atom that allowed electrons to circle the nucleus but only on specified paths (orbits) which for some reason were stable. The study of the motion of electrons lead to the development of a new branch of physics called ______ ...
The end
... momentum are conserved, demonstrate that we have: ' e 1 cos . b/ In a Compton collision with an electron, a photon of violet light ( = 400 nm) is backward scattered through an angle 180o. - How much energy is transferred to the electron in this collision? - Compare the result with the ...
... momentum are conserved, demonstrate that we have: ' e 1 cos . b/ In a Compton collision with an electron, a photon of violet light ( = 400 nm) is backward scattered through an angle 180o. - How much energy is transferred to the electron in this collision? - Compare the result with the ...
Physics116_L35
... 12. A proton and an electron are both accelerated to the same final kinetic energy. If λp is the de Broglie wavelength of the proton and λe is the de Broglie wavelength of the electron, then ...
... 12. A proton and an electron are both accelerated to the same final kinetic energy. If λp is the de Broglie wavelength of the proton and λe is the de Broglie wavelength of the electron, then ...
Course Structure
... 1. Phenomena and experiment that led us to beleive that a new understanding of nature quite distinct from what we knew in classical physics is required. In this part we will collect main features and central points that need to be included in the new understanding. Emphasis is on getting to the hear ...
... 1. Phenomena and experiment that led us to beleive that a new understanding of nature quite distinct from what we knew in classical physics is required. In this part we will collect main features and central points that need to be included in the new understanding. Emphasis is on getting to the hear ...
Course Outline Template Word Document - Physics for All
... COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is intended to be a first introduction to quantum phenomena in nature. Quatum Mechanics forms the basis of our description of nature at small scales and a clear understanding of it is required to understand phenomena ranging from atoms and chemical bonding to semicondu ...
... COURSE DESCRIPTION This course is intended to be a first introduction to quantum phenomena in nature. Quatum Mechanics forms the basis of our description of nature at small scales and a clear understanding of it is required to understand phenomena ranging from atoms and chemical bonding to semicondu ...
Document
... Many physicists’ work contributed to the discovery of the photoelectric effect What is it? • The ability of light to dislodge electrons from a metallic surface • The electrons can be detected and the resulting signals amplified • Lots of applications in visual imaging ...
... Many physicists’ work contributed to the discovery of the photoelectric effect What is it? • The ability of light to dislodge electrons from a metallic surface • The electrons can be detected and the resulting signals amplified • Lots of applications in visual imaging ...
REVIEW OF WAVE MECHANICS
... (This result is an example of the application of the Ehrenfest Theorem). In particular it shows how F=ma is recovered from the quantum mechanical equations when the spatial extent of a wave function is much less than the scale on which the potential energy varies. Thus it appears that quantum mechan ...
... (This result is an example of the application of the Ehrenfest Theorem). In particular it shows how F=ma is recovered from the quantum mechanical equations when the spatial extent of a wave function is much less than the scale on which the potential energy varies. Thus it appears that quantum mechan ...
Localized Wave Function of the 2D Topological Insulator in a
... We investigate the edge state of the Quantum Spin Hall effects which appears in a honeycomb lattice described by the Kane-Mele (KM) model[1]. It is well know that the KM model with a finite spin-orbit interaction is suggested for a 2D topological insulator[2] which shows an insulating gap in a bulk ...
... We investigate the edge state of the Quantum Spin Hall effects which appears in a honeycomb lattice described by the Kane-Mele (KM) model[1]. It is well know that the KM model with a finite spin-orbit interaction is suggested for a 2D topological insulator[2] which shows an insulating gap in a bulk ...
Honors Chemistry
... 10. What is meant by an electron having dual wave-particle nature, where were these electrons described as being located, and who suggested this theory? Sometimes light acts like a wave and some other times like a particle. To understand what light is one must take both characteristics into consider ...
... 10. What is meant by an electron having dual wave-particle nature, where were these electrons described as being located, and who suggested this theory? Sometimes light acts like a wave and some other times like a particle. To understand what light is one must take both characteristics into consider ...
CHEMISTRY CHAPTER 5 OUTLINE NOTES 5.1 – Light and
... adequately describe important aspects of lights interactions with matter. o Quantum Concept • Max Planck began searching for explanation for light emitted by heated objects and he found that matter can gain or lose energy only in small, specific amounts called quanta. ...
... adequately describe important aspects of lights interactions with matter. o Quantum Concept • Max Planck began searching for explanation for light emitted by heated objects and he found that matter can gain or lose energy only in small, specific amounts called quanta. ...
2.1 Historical Development
... independent of the intensity of the incident radiation. Furthermore the classical theory predicts that the photoelectric effect should occur for any frequency of light as long as the intensity is sufficiently high. The experimental fact, however is that there is a minimum frequency, threshold freque ...
... independent of the intensity of the incident radiation. Furthermore the classical theory predicts that the photoelectric effect should occur for any frequency of light as long as the intensity is sufficiently high. The experimental fact, however is that there is a minimum frequency, threshold freque ...
Lecture 11 Atomic Structure Earlier in the semester, you read about
... Substituting this value into Planck's equation gives: E = hν = (6.626 x 10-34 J s)(5.09 x 1014 s-1) = 3.37 x 10-19 J This means that sodium (with a line at 589 nm) can absorb (or emit) 3.37 x 10-19 joules of energy, or 6.74 x 10-19 J, or 10.11 x 10-19 J of energy, but not 5.00 x 10-19 J of energy. P ...
... Substituting this value into Planck's equation gives: E = hν = (6.626 x 10-34 J s)(5.09 x 1014 s-1) = 3.37 x 10-19 J This means that sodium (with a line at 589 nm) can absorb (or emit) 3.37 x 10-19 joules of energy, or 6.74 x 10-19 J, or 10.11 x 10-19 J of energy, but not 5.00 x 10-19 J of energy. P ...
Physics 1220/1320
... The hindsight approach for electromagnetism is to start with the Maxwell Equations: (here in their less useful integral form) ...
... The hindsight approach for electromagnetism is to start with the Maxwell Equations: (here in their less useful integral form) ...
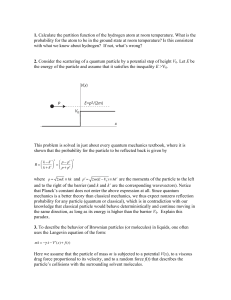
1. Calculate the partition function of the hydrogen atom at room
... where p = 2mE ≡ k and p′ = 2m(E − V0 ) ≡ k ′ are the momenta of the particle to the left and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than class ...
... where p = 2mE ≡ k and p′ = 2m(E − V0 ) ≡ k ′ are the momenta of the particle to the left and to the right of the barrier (and k and k’ are the corresponding wavevectors). Notice that Planck’s constant does not enter the above expression at all. Since quantum mechanics is a better theory than class ...
UNM Physics 262, Problem Set 12, Fall 2006
... of the hydrogen atom entirely in terms of its radius. What radius corresponds to the lowest possible energy? (c) In the lowest energy quantum mechanical con guration of the hydrogen atom, the momentum of the electron (which is entirely azimuthal) and its location along the circumference of its orbit ...
... of the hydrogen atom entirely in terms of its radius. What radius corresponds to the lowest possible energy? (c) In the lowest energy quantum mechanical con guration of the hydrogen atom, the momentum of the electron (which is entirely azimuthal) and its location along the circumference of its orbit ...
Atomic Structure - Sakshi Education
... iii. The cathode rays travel in straight line in the absence of electric or magnetic field. iv. The cathode rays are deflected towards the positively charged plate in the presence of electric field and South Pole in the magnetic field. This shows that the cathode rays consist of a stream of negative ...
... iii. The cathode rays travel in straight line in the absence of electric or magnetic field. iv. The cathode rays are deflected towards the positively charged plate in the presence of electric field and South Pole in the magnetic field. This shows that the cathode rays consist of a stream of negative ...




















![Chapter7_1 - Department of Chemistry [FSU]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/016128835_1-aea3c1aec04363d6cbf538e8faf80e45-300x300.png)

