CHEMISTRY 113 EXAM 3(A)
... B. gamma C. infrared D. radio waves 2. The photoelectric effect is: A. reflection of light by metal surface B. ejection of electrons by a metal when struck by light C. acceleration of electrons in vacuum by the electric field D. effect of the electric field on the emission of light 3. The frequency ...
... B. gamma C. infrared D. radio waves 2. The photoelectric effect is: A. reflection of light by metal surface B. ejection of electrons by a metal when struck by light C. acceleration of electrons in vacuum by the electric field D. effect of the electric field on the emission of light 3. The frequency ...
Problem set 8
... Problem set 8 Due by beginning of class on Monday March 14, 2011 Time independent Schrödinger Eqn: Particle on a circle ...
... Problem set 8 Due by beginning of class on Monday March 14, 2011 Time independent Schrödinger Eqn: Particle on a circle ...
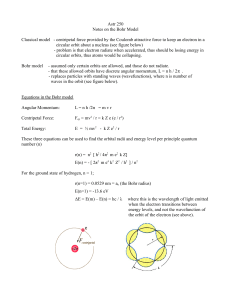
Astr 250 Notes on the Bohr Model Classical model
... Astr 250 Notes on the Bohr Model Classical model - centripetal force provided by the Coulomb attractive force to keep an electron in a circular orbit about a nucleus (see figure below) - problem is that electron radiate when accelerated, thus should be losing energy in circular orbits, thus atoms wo ...
... Astr 250 Notes on the Bohr Model Classical model - centripetal force provided by the Coulomb attractive force to keep an electron in a circular orbit about a nucleus (see figure below) - problem is that electron radiate when accelerated, thus should be losing energy in circular orbits, thus atoms wo ...
in nm 1240 E in eV - Little Shop of Physics
... how many does the filament temperature increase? b. By what factor does the total radiation from the filament increase due to this temperature change? 54. || The star Sirius is much hotter than the sun, with a peak wavelength of 290 nm compared to the sun’s 500 nm. It is also larger, with a diameter ...
... how many does the filament temperature increase? b. By what factor does the total radiation from the filament increase due to this temperature change? 54. || The star Sirius is much hotter than the sun, with a peak wavelength of 290 nm compared to the sun’s 500 nm. It is also larger, with a diameter ...
PHY4604–Introduction to Quantum Mechanics Fall 2004 Practice
... (d) How large would a constant magnetic field have to be to split two H-atom states which are degenerate in zero field by an amount so as to maximally absorb light of wavelength λ? e H = −µ · B = S · B m e e = = Sz Bz = h̄ms Bz , m m where the last step where the operator is replaced by its eigenval ...
... (d) How large would a constant magnetic field have to be to split two H-atom states which are degenerate in zero field by an amount so as to maximally absorb light of wavelength λ? e H = −µ · B = S · B m e e = = Sz Bz = h̄ms Bz , m m where the last step where the operator is replaced by its eigenval ...
Wave-Particle Duality
... behaviors are seen in light quanta, and in 1916 that the emission of light is done at random times and in random directions. This was the introduction of ontological chance (Zufall) into physics, over a decade before Heisenberg announced in his “uncertainty principle” paper of 1927 that quantum mech ...
... behaviors are seen in light quanta, and in 1916 that the emission of light is done at random times and in random directions. This was the introduction of ontological chance (Zufall) into physics, over a decade before Heisenberg announced in his “uncertainty principle” paper of 1927 that quantum mech ...
Quantum Mechanics Problem Set
... (b) De Broglie states that electrons demonstrate the properties of both particles and waves and that each moving particle has a wave associated with it. A wave function is the mathematical description of the matter wave of an electron. (c) Although we cannot predict he exact location of an electron ...
... (b) De Broglie states that electrons demonstrate the properties of both particles and waves and that each moving particle has a wave associated with it. A wave function is the mathematical description of the matter wave of an electron. (c) Although we cannot predict he exact location of an electron ...
File
... The double-slit interference experiment Originally performed by Young (1801) with light. Subsequently also performed with many types of matter particle (see references). ...
... The double-slit interference experiment Originally performed by Young (1801) with light. Subsequently also performed with many types of matter particle (see references). ...
Quantum physics
... • Why rate of emission of electrons << rate of incidence of photons {for f>f0}: • Not every photon would collide with an electron; most are reflected by the metal or miss hitting any electron. • On the way out to the metal surface, an electron may lose its kinetic energy to ions and other electrons ...
... • Why rate of emission of electrons << rate of incidence of photons {for f>f0}: • Not every photon would collide with an electron; most are reflected by the metal or miss hitting any electron. • On the way out to the metal surface, an electron may lose its kinetic energy to ions and other electrons ...
Lecture 3: Electronic Band Theory: A Many
... For many materials it is reasonable to assume the electron wavefunctions only have support at the ions, vanishing away. This means the wave function lives on a lattice, not in the continuum. In other words, our wave function looks like ψ(nx , ny ) instead of ψ(x, y). The consequence of this is that ...
... For many materials it is reasonable to assume the electron wavefunctions only have support at the ions, vanishing away. This means the wave function lives on a lattice, not in the continuum. In other words, our wave function looks like ψ(nx , ny ) instead of ψ(x, y). The consequence of this is that ...
L 35 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics
... and the Bohr Atom • Niels Bohr, a Danish physicist, used the quantum concept to explain the nature of the atom. • Recall that the orbiting electrons, according to classical ideas, should very quickly radiate away all of its energy • If this were so, then we would observe that atoms emit light over a ...
... and the Bohr Atom • Niels Bohr, a Danish physicist, used the quantum concept to explain the nature of the atom. • Recall that the orbiting electrons, according to classical ideas, should very quickly radiate away all of its energy • If this were so, then we would observe that atoms emit light over a ...
The Photoelectric Effect, work function
... relativity). R. Millikan was finally able to prove it in 1916, by cutting metal surfaces in a vacuum – eliminating the oxide layers on the metal. Classical wave theory:1 Energy of a wave goes as the square of the amplitude, so a more intense wave has more energy. This jiggles the electrons more, s ...
... relativity). R. Millikan was finally able to prove it in 1916, by cutting metal surfaces in a vacuum – eliminating the oxide layers on the metal. Classical wave theory:1 Energy of a wave goes as the square of the amplitude, so a more intense wave has more energy. This jiggles the electrons more, s ...
slides in pdf format
... • Theory: de Broglie (1924) proposes matter waves • assumes all “particles” (e.g. electrons) also have a wave associated with them with wavelength determined by its momentum, λ = h/p. • Bohr’s quantization follows because the electron in an atom is described by a “standing electron wave”. • Experime ...
... • Theory: de Broglie (1924) proposes matter waves • assumes all “particles” (e.g. electrons) also have a wave associated with them with wavelength determined by its momentum, λ = h/p. • Bohr’s quantization follows because the electron in an atom is described by a “standing electron wave”. • Experime ...
Document
... •the actual position of electrons can't really be specified •best we can do is say where they PROBABLY are •they are likely to be in cloud-like zones (called orbitals, not orbits) of varied shape •electrons with more energy can assume orbitals of increasingly bizzarre shape. These shapes sort of "fa ...
... •the actual position of electrons can't really be specified •best we can do is say where they PROBABLY are •they are likely to be in cloud-like zones (called orbitals, not orbits) of varied shape •electrons with more energy can assume orbitals of increasingly bizzarre shape. These shapes sort of "fa ...
L35 - University of Iowa Physics
... that mass is not a constant, but depends on speed As speed increases, so does mass Speed can never exceed the speed of light, c ...
... that mass is not a constant, but depends on speed As speed increases, so does mass Speed can never exceed the speed of light, c ...
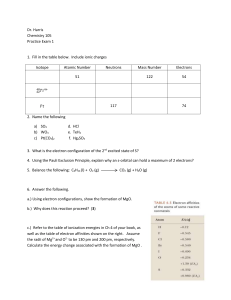
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... 14. A laser emits 200mJ of energy per hour. Given that the wavelength of the photons in the beam is 300 nm, and assuming that the emission rate is constant, how many photons are emitted per minute? ...
... 14. A laser emits 200mJ of energy per hour. Given that the wavelength of the photons in the beam is 300 nm, and assuming that the emission rate is constant, how many photons are emitted per minute? ...
Walker3_Lecture_Ch30
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
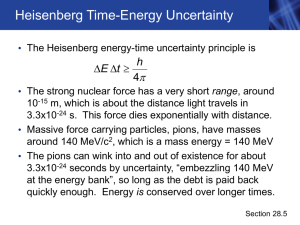
Chapter 28 - Purdue Physics
... around 140 MeV/c2, which is a mass energy = 140 MeV • The pions can wink into and out of existence for about 3.3x10-24 seconds by uncertainty, “embezzling 140 MeV at the energy bank”, so long as the debt is paid back quickly enough. Energy is conserved over longer times. Section 28.5 ...
... around 140 MeV/c2, which is a mass energy = 140 MeV • The pions can wink into and out of existence for about 3.3x10-24 seconds by uncertainty, “embezzling 140 MeV at the energy bank”, so long as the debt is paid back quickly enough. Energy is conserved over longer times. Section 28.5 ...
PHYS 113: Quantum Mechanics Waves and Interference In much of
... What does this mean? It means that if you were to look in such a box, you might find (with equal probability) the electron to be “near” one of three spots. There are certain places (where the probability is 0, for example), where you’d never find it. One caveat: once you look at the electron or obse ...
... What does this mean? It means that if you were to look in such a box, you might find (with equal probability) the electron to be “near” one of three spots. There are certain places (where the probability is 0, for example), where you’d never find it. One caveat: once you look at the electron or obse ...










![L 35 Modern Physics [1] - University of Iowa Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000679677_1-b925cf8c8f031b0f2b0c09a806312d20-300x300.png)
![L 35 Modern Physics [1] Modern Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001558975_1-84d6e03bc786b63795533f59711ce2f4-300x300.png)





![L 35 Modern Physics [1] - University of Iowa Physics](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001147028_1-f00aa7577568b42bc32948cbade9023a-300x300.png)