External-cavity diode lasers provide absolute references for WDM
... gratings and receiver filters. These diagnostic tools also can measure the wavelength of the stabilized distributed-feedback diodes and fiber-grating controlled laser-diode sources used in WDM. The most accurate measurements of these sources, however, are made by direct measurement against the WDM r ...
... gratings and receiver filters. These diagnostic tools also can measure the wavelength of the stabilized distributed-feedback diodes and fiber-grating controlled laser-diode sources used in WDM. The most accurate measurements of these sources, however, are made by direct measurement against the WDM r ...
LASER - NDLR Dspace
... The efficiency of metal machining by laser is often increased by oxygen-assisted gas cutting. This technique is based on the exploitation of exothermic chemical reactions, which are utilized in the well-established oxy-acetylene torch cutting of metals. With the latter effect, the initial melting an ...
... The efficiency of metal machining by laser is often increased by oxygen-assisted gas cutting. This technique is based on the exploitation of exothermic chemical reactions, which are utilized in the well-established oxy-acetylene torch cutting of metals. With the latter effect, the initial melting an ...
Evanescent-field optical microscopy: effects of polarization, tip
... An image of a Q 91 nm latex sphere, adsorbed to the substrate surface, scanned in constantheight mode is shown in fig. 6a. The s-polarized laser beam is propagating from left to right. The image has been differentiated in the horizontal line scan direction in order to enhance the wave pattern surrou ...
... An image of a Q 91 nm latex sphere, adsorbed to the substrate surface, scanned in constantheight mode is shown in fig. 6a. The s-polarized laser beam is propagating from left to right. The image has been differentiated in the horizontal line scan direction in order to enhance the wave pattern surrou ...
Novel 3-D microscopy techniques - Purdue University Cytometry
... Effect of increased incident power on generation of signal. Samples of acidfucsin-stained monkey kidney were imaged at a depth of 60 µm into the sample by confocal (550 µW of 532-nm light) and by multiphoton (12 mW of 1047-nm light) microscopy. Laser intensities were adjusted to produce the same mea ...
... Effect of increased incident power on generation of signal. Samples of acidfucsin-stained monkey kidney were imaged at a depth of 60 µm into the sample by confocal (550 µW of 532-nm light) and by multiphoton (12 mW of 1047-nm light) microscopy. Laser intensities were adjusted to produce the same mea ...
G020062-00 - DCC
... – (a) measuring the Q of a number of modes of sapphire samples and – (b) calculating for each mode how much energy was stored in different types of deformation ...
... – (a) measuring the Q of a number of modes of sapphire samples and – (b) calculating for each mode how much energy was stored in different types of deformation ...
Rev.Sci.Instrum.
... layer system. In favorable cases the thickness can be determined to within sub-nm accuracy. Despite the apparent similarities between these techniques as far as the parameters measured are concerned, individual features of each technique can be exploited for a given experimental task. Due to each me ...
... layer system. In favorable cases the thickness can be determined to within sub-nm accuracy. Despite the apparent similarities between these techniques as far as the parameters measured are concerned, individual features of each technique can be exploited for a given experimental task. Due to each me ...
A Ti: Sapphire Planar Waveguide Laser Grown by Pulsed Laser
... output mirror transmission varies between 3.3% and 7.5% as a function of wavelength, with a period of ~1.3 nm. If the variation in the air gap between mirror surface, and the guide exit face is also taken into consideration, then the degree of output coupling at any given wavelength may vary between ...
... output mirror transmission varies between 3.3% and 7.5% as a function of wavelength, with a period of ~1.3 nm. If the variation in the air gap between mirror surface, and the guide exit face is also taken into consideration, then the degree of output coupling at any given wavelength may vary between ...
Phys. Rev. Lett. 101, 076101 - APS Link Manager
... putational lens’’ (CL) [7–10]. Another approach is Fourier transform holography, where the scattering pattern from the sample is encoded by a reference wave. The interference pattern can then be uniquely inverted into a real space image, but the resolution is limited by the size of the reference str ...
... putational lens’’ (CL) [7–10]. Another approach is Fourier transform holography, where the scattering pattern from the sample is encoded by a reference wave. The interference pattern can then be uniquely inverted into a real space image, but the resolution is limited by the size of the reference str ...
Two-photon ablation with 1278nm laser radiation
... radiation with matter. The first can be used to accurately incise or ablate intra-cellular components, hence affecting the manner in which the cell functions [2], and the second to image deep within tissue [3]. In both cases it is important that as little absorption as possible occurs out with the f ...
... radiation with matter. The first can be used to accurately incise or ablate intra-cellular components, hence affecting the manner in which the cell functions [2], and the second to image deep within tissue [3]. In both cases it is important that as little absorption as possible occurs out with the f ...
An Introduction to Ultraviolet/Visible Molecular Absorption
... width is accompanied by a second-order power reduction in the radiant energy; at very narrow settings spectral detail may be lost owing to an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio. In general, it is good practice to narrow slits no more than is necessary for good resolution for the spectrum at hand. ...
... width is accompanied by a second-order power reduction in the radiant energy; at very narrow settings spectral detail may be lost owing to an increase in the signal-to-noise ratio. In general, it is good practice to narrow slits no more than is necessary for good resolution for the spectrum at hand. ...
Synchronized ti scattering microscopy
... For CRS microscopy, collinear pump- and Stokes-beams are coupled into one of two modified laser scanning upright microscopes (BX61WI/FV300, Olympus for SRS imaging and TCS-SP5, Leica for video-rate CARS imaging). We use a 60x 1.2NA water immersion objective (UPlanApo / IR, Olympus) to focus the beam ...
... For CRS microscopy, collinear pump- and Stokes-beams are coupled into one of two modified laser scanning upright microscopes (BX61WI/FV300, Olympus for SRS imaging and TCS-SP5, Leica for video-rate CARS imaging). We use a 60x 1.2NA water immersion objective (UPlanApo / IR, Olympus) to focus the beam ...
10-GHz Bandwidth RF Spectral Analyzer With MHz Resolution
... demodulated signal, corresponding to the dispersive part of the atomic response, is reproduced as the lower trace of this inset. An other important property of a spectrum analyzer is its dynamic range. It can be extracted from the experimental results reproduced in Fig. 3(b). This figure represents ...
... demodulated signal, corresponding to the dispersive part of the atomic response, is reproduced as the lower trace of this inset. An other important property of a spectrum analyzer is its dynamic range. It can be extracted from the experimental results reproduced in Fig. 3(b). This figure represents ...
Note
... • The observed profile is the convolution of the true line profile with the instrument profile • For high S/N ratio data, Fourier techniques can be used to back out the IP from a spectrum to recover some of the resolution. ...
... • The observed profile is the convolution of the true line profile with the instrument profile • For high S/N ratio data, Fourier techniques can be used to back out the IP from a spectrum to recover some of the resolution. ...
Identifying Failures and Ensuring Quality of Plastic Materials
... sample of the base material produced a spectrum characteristic of thermoplastic polyester, such as PBT. The fracture surface inclusion was excised and subsequently analyzed via FTIR. A direct comparison of the results with those obtained on the base material showed the presence of additional absorpt ...
... sample of the base material produced a spectrum characteristic of thermoplastic polyester, such as PBT. The fracture surface inclusion was excised and subsequently analyzed via FTIR. A direct comparison of the results with those obtained on the base material showed the presence of additional absorpt ...
Presentation
... Z=3 (this value defines a frequency of plasma oscillations p ): there is no additional excitations of electrons into s-band at our temperatures (Te is less than 10 eV) Important fact is: electron-electron collisions seems weakly contribute to Drude even when crystalline lattice still exists afte ...
... Z=3 (this value defines a frequency of plasma oscillations p ): there is no additional excitations of electrons into s-band at our temperatures (Te is less than 10 eV) Important fact is: electron-electron collisions seems weakly contribute to Drude even when crystalline lattice still exists afte ...
NONDESTRUCTIVE EVALUATION OF PLEXIGLAS MATERIALS USING R. Montanini
... thermography lies on the available range of frequencies for the heat flux modulation, which may be not sufficiently low to detect deeper defects in materials of very low thermal diffusivity and/or large thickness. Another approach is pulse thermography, which can be obtained by stimulating the part ...
... thermography lies on the available range of frequencies for the heat flux modulation, which may be not sufficiently low to detect deeper defects in materials of very low thermal diffusivity and/or large thickness. Another approach is pulse thermography, which can be obtained by stimulating the part ...
“Pixel” team
... Objectives should be designed to work with UV-visible light in the range 250nm750nm. Mirror objectives shall be considered to minimize chromatic aberrations over this wavelength range. Overall transmission through a 30 µm diameter pinhole at the sample position should be greater than 25% in the 40 ...
... Objectives should be designed to work with UV-visible light in the range 250nm750nm. Mirror objectives shall be considered to minimize chromatic aberrations over this wavelength range. Overall transmission through a 30 µm diameter pinhole at the sample position should be greater than 25% in the 40 ...
Microscopes
... Kohler illumination Basic format for all transmitted light systems Ensures that: ...
... Kohler illumination Basic format for all transmitted light systems Ensures that: ...
CALCULATION OF THE FOCAL LENGTH OF A THERMAL LENS
... This work allows us to clarify the meaning of w1 in (28). It is the radius of the waist of the field distribution in the cell, see (14) and (15). In [l] w. is used, and it is not clear whether this is the radius of the beam on the cell or of the of waist in the cavity, because it is alternatively ca ...
... This work allows us to clarify the meaning of w1 in (28). It is the radius of the waist of the field distribution in the cell, see (14) and (15). In [l] w. is used, and it is not clear whether this is the radius of the beam on the cell or of the of waist in the cavity, because it is alternatively ca ...
File
... College of Nanoscale Science and Engineering, SUNY Polytechnic Institute, State University of New York, Albany, NY, USA Improving spatial resolution has been a major goal of scanning electron microscope (SEM) development since the first commercial instrument was introduced in the mid-1960s. An area ...
... College of Nanoscale Science and Engineering, SUNY Polytechnic Institute, State University of New York, Albany, NY, USA Improving spatial resolution has been a major goal of scanning electron microscope (SEM) development since the first commercial instrument was introduced in the mid-1960s. An area ...
Ay 105 Lab Experiment #8: Infrared Array Camera
... to zero incident radiation. This is like a “bias” or reference frame, but in this case really a combination of bias, dark current, and thermal background signal. It turns out that finding a source of zero radiation is not easy in the thermal infrared. Think about the problem at hand for a moment. On ...
... to zero incident radiation. This is like a “bias” or reference frame, but in this case really a combination of bias, dark current, and thermal background signal. It turns out that finding a source of zero radiation is not easy in the thermal infrared. Think about the problem at hand for a moment. On ...
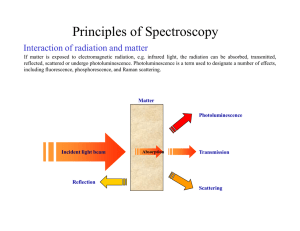
Principles of Spectroscopy
... Origin of the interferogram Spectrometers are equipped with a broadband light source, which yields a continuous, infinite number, of wavelengths, as shown in the figure on the left. The interferogram is the continuous sum, i.e. the integral, of all the interference patterns produced by each wavelen ...
... Origin of the interferogram Spectrometers are equipped with a broadband light source, which yields a continuous, infinite number, of wavelengths, as shown in the figure on the left. The interferogram is the continuous sum, i.e. the integral, of all the interference patterns produced by each wavelen ...
39 Raman Scattering Spectroscopy Raman - Rose
... Raman spectroscopy can be used to assess secondary structure, because different secondary structural elements have characteristic Raman bands. In addition, as with most spectroscopic techniques, Raman is sensitive to changes in the bonding patterns of a molecule. Thus, Raman can be used to study hyd ...
... Raman spectroscopy can be used to assess secondary structure, because different secondary structural elements have characteristic Raman bands. In addition, as with most spectroscopic techniques, Raman is sensitive to changes in the bonding patterns of a molecule. Thus, Raman can be used to study hyd ...
AFM-IR

AFM-IR refers to atomic force microscope (AFM) based infrared (IR) spectroscopy. AFM-IR is a technique for chemical analysis of samples at nanoscale spatial resolution. AFM-IR is related to techniques including Tip-Enhanced Raman Spectroscopy (TERS) and scanning near-field optical microscopy (SNOM) and other methods of vibrational analysis with scanning probe microscopy. The AFM-IR technique uses a sharp tip of an AFM probe to measure the absorption of infrared light by a sample. Recording the amount of IR absorption as a function of wavelength or wavenumber creates nanoscale IR absorption spectra, which can be used to chemically characterize and even identify unknown materials. Recording the IR absorption as a function of position can be used to create chemical composition maps that show the spatial distribution of different chemical components. AFM-IR can overcome the diffraction limit that limits the spatial resolution of conventional infrared microscopy and microspectroscopy to the scale of several microns. AFM-IR can achieve spatial resolution down to around 20 nm, limited in some case only by the sharpness of the AFM probe tip and sensitivity down to the scale of molecular monolayers.