Chapter 13 - eacfaculty.org
... Living Cells Examples: Botulin Toxin, Hemolysins (Strep and Staph) ...
... Living Cells Examples: Botulin Toxin, Hemolysins (Strep and Staph) ...
What could have caused this?
... might produce unusual order enoughsymptoms vaccines to protect such as these. Here, every U.S. citizen. the eyes are filled with blood, and blood reputation, blisters form in the Smallpox has a fearsome mouth and in inside the body. having killed more people history than How disease. can we protect ...
... might produce unusual order enoughsymptoms vaccines to protect such as these. Here, every U.S. citizen. the eyes are filled with blood, and blood reputation, blisters form in the Smallpox has a fearsome mouth and in inside the body. having killed more people history than How disease. can we protect ...
5.1.4 Infectious Disease Outbreak
... To ensure the accurate, coordinated and timely provision of information to relevant stakeholders, the prison’s Health Service Provider (HSP) must inform the prison General Manager immediately, of a suspected or confirmed case of infectious disease. ...
... To ensure the accurate, coordinated and timely provision of information to relevant stakeholders, the prison’s Health Service Provider (HSP) must inform the prison General Manager immediately, of a suspected or confirmed case of infectious disease. ...
Laboratory Diagnosis, Prevention and Treatment of Bacte rial Infection
... antitoxin. It is raised in the horse .It is most important to give an intented recipient of equine serum a prior test dose to exclude hypersensitivity subjects who may have been sensitized by a previous dose of equine serum. Pooled immunoglobulin: It contains the normal repertoire of antibodies for ...
... antitoxin. It is raised in the horse .It is most important to give an intented recipient of equine serum a prior test dose to exclude hypersensitivity subjects who may have been sensitized by a previous dose of equine serum. Pooled immunoglobulin: It contains the normal repertoire of antibodies for ...
Rotavirus
... •Has been at the root of several epidemics or outbreaks of gastroenteritis across North America in hospital emergency rooms, schools and even on cruise ships •There is a group of similar or related viruses that are referred to as Norwalk-like viruses or agents. •Can infect people of any age and usua ...
... •Has been at the root of several epidemics or outbreaks of gastroenteritis across North America in hospital emergency rooms, schools and even on cruise ships •There is a group of similar or related viruses that are referred to as Norwalk-like viruses or agents. •Can infect people of any age and usua ...
Tuberculosis Fact Sheet for DOs
... beginning of your employment, so that your previous skin-test status will be known if you are ever identified as having been exposed to TB. People infected with TB, but who have no signs and symptoms of disease in their lungs, are not contagious. ...
... beginning of your employment, so that your previous skin-test status will be known if you are ever identified as having been exposed to TB. People infected with TB, but who have no signs and symptoms of disease in their lungs, are not contagious. ...
Comparison of the Effects of Diseases and the Side Effects of Vaccines
... Caused by toxin of bacteria in soil; causes painful muscle spasms, convulsions, lockjaw. ...
... Caused by toxin of bacteria in soil; causes painful muscle spasms, convulsions, lockjaw. ...
A. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek B. Edward Jenner C. Francesco Redi
... ____ A process where one microorganism inhibits or prevents the growth of another. ____ A symbiosis where both groups benefit. 18. Which of the following is not one of Koch’s postulates? 1pt (a) The same pathogen must be present in every case of the disease. (b) The pathogen must be isolated and gro ...
... ____ A process where one microorganism inhibits or prevents the growth of another. ____ A symbiosis where both groups benefit. 18. Which of the following is not one of Koch’s postulates? 1pt (a) The same pathogen must be present in every case of the disease. (b) The pathogen must be isolated and gro ...
Viral Diseases Chart
... malady when Australian physicians ingested bacteria to develop symptoms Camplyobactor: common culprit; substantial loss of fluids & salts necessary to maintain normal bodily health; young & old vulnerable: thirst, dry skin, light-headedness, crying without tears, dry diapers, & reduced activity; com ...
... malady when Australian physicians ingested bacteria to develop symptoms Camplyobactor: common culprit; substantial loss of fluids & salts necessary to maintain normal bodily health; young & old vulnerable: thirst, dry skin, light-headedness, crying without tears, dry diapers, & reduced activity; com ...
Fall exam 2 MSII CLIs - LSH Student Resources
... • Neutropenia and central venous catheters Spread and multiplication: • Main host defense in T-cell mediated immunity (protects against mucosal surfaces) • Neutrophils protect from spread through mucosa and subsequent dissemination Damage: • Mucosal candidiasis – adherent white plaques on oropharyng ...
... • Neutropenia and central venous catheters Spread and multiplication: • Main host defense in T-cell mediated immunity (protects against mucosal surfaces) • Neutrophils protect from spread through mucosa and subsequent dissemination Damage: • Mucosal candidiasis – adherent white plaques on oropharyng ...
Infectious disease
... • LARGE SLOW MOVING • RESIDE IN BONE MARROW, LIVER, SPLEEN, AND BLOOD • KILL ORGANISMS SURVIVING THE NEUTROPHILS ...
... • LARGE SLOW MOVING • RESIDE IN BONE MARROW, LIVER, SPLEEN, AND BLOOD • KILL ORGANISMS SURVIVING THE NEUTROPHILS ...
Definition - WordPress.com
... Describe the symptoms and what it might be like to have the disease: Some symptoms would include; fever, headache, body aches, fatigue (sleepiness), skin rash (occasionally), swollen lymph glands (occasionally), stiff neck, lack of coordination, and eye pain. If a person had this disease they would ...
... Describe the symptoms and what it might be like to have the disease: Some symptoms would include; fever, headache, body aches, fatigue (sleepiness), skin rash (occasionally), swollen lymph glands (occasionally), stiff neck, lack of coordination, and eye pain. If a person had this disease they would ...
2010 Dr. Juliet Pulliam and the Clinic on the Meaningful Modeling of
... Place: Worldwide Time: On or after March 15, 2009 ...
... Place: Worldwide Time: On or after March 15, 2009 ...
STI info! HW: QUIZ NEXT CLASS! 1,3,5 * Tues jan 24 2,4,6 * mon
... Parasites…treated with special lotions/creams, washing all clothing/bedding! Spread through close physical contact, using bedding/towels, etc. of infected person. Symptoms: itching, lice in hair, pin-sized blood spots on underwear (both males and females) Complications are severe itching, infections ...
... Parasites…treated with special lotions/creams, washing all clothing/bedding! Spread through close physical contact, using bedding/towels, etc. of infected person. Symptoms: itching, lice in hair, pin-sized blood spots on underwear (both males and females) Complications are severe itching, infections ...
ID Fellows Case Conference - City-Wide Infectious Diseases Case
... Pt was started on high dose acyclovir at 10mg/kg IV q8H He was treated for 12 days IV and then transitioned to PO valacyclovir Lesions have scabbed over, Na is corrected, no further abdominal pain. Still with fevers and mild elevation of transaminases. ...
... Pt was started on high dose acyclovir at 10mg/kg IV q8H He was treated for 12 days IV and then transitioned to PO valacyclovir Lesions have scabbed over, Na is corrected, no further abdominal pain. Still with fevers and mild elevation of transaminases. ...
List 5 ways can students minimize the spread of pathogens at school?
... spread from person to person through coughing or sneezing. Symptoms may not occur for years after the initial infection. A bacterial disease may be treated with an antibiotic (an tih by AHT ik), a drug that inhibits or kills bacteria. Viral diseases include the common cold, influenza, pneumonia, and ...
... spread from person to person through coughing or sneezing. Symptoms may not occur for years after the initial infection. A bacterial disease may be treated with an antibiotic (an tih by AHT ik), a drug that inhibits or kills bacteria. Viral diseases include the common cold, influenza, pneumonia, and ...
An acute bacterial disease, characterized by sudden onset of fever
... An acute bacterial disease, characterized by sudden onset of fever, intense headache, nausea and often vomiting, stiff neck and photophobia. A petechial rash with pink macules or occasionally vesicles may be observed . Case fatality rates formerly exceeded 50%. Sequelae including mental reta ...
... An acute bacterial disease, characterized by sudden onset of fever, intense headache, nausea and often vomiting, stiff neck and photophobia. A petechial rash with pink macules or occasionally vesicles may be observed . Case fatality rates formerly exceeded 50%. Sequelae including mental reta ...
Roseola
... the rash appears. The risk to the child increases with exposure to a day care centre or to public places. There is no known way to prevent its spread. ...
... the rash appears. The risk to the child increases with exposure to a day care centre or to public places. There is no known way to prevent its spread. ...
Viruses and Bacteria
... Replication of Viruses • Cannot multiply outside cells • Uses cell organelles to multiply • Process is called lytic cycle ...
... Replication of Viruses • Cannot multiply outside cells • Uses cell organelles to multiply • Process is called lytic cycle ...
Medical Virology Lower Respiratory Tract Infections
... In humans, the transmission of coronaviruses between an infected individual and others can occur via respiratory secretions. This can happen either directly through droplets from coughing or sneezing, or indirectly through touching contaminated objects or surfaces as well as close contact, such a ...
... In humans, the transmission of coronaviruses between an infected individual and others can occur via respiratory secretions. This can happen either directly through droplets from coughing or sneezing, or indirectly through touching contaminated objects or surfaces as well as close contact, such a ...
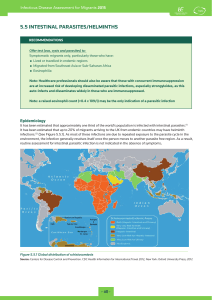
5.5 INTESTINAL PARASITES/HELMINTHS
... Note: Healthcare professionals should also be aware that those with concurrent immunosuppression are at increased risk of developing disseminated parasitic infections, especially strongyloides, as this auto-infects and disseminates widely in those who are immunosuppressed. Note: a raised eosinophil ...
... Note: Healthcare professionals should also be aware that those with concurrent immunosuppression are at increased risk of developing disseminated parasitic infections, especially strongyloides, as this auto-infects and disseminates widely in those who are immunosuppressed. Note: a raised eosinophil ...
Problem One
... problem that PRRS virus crops up among their sites with a high enough frequency to reduce their ability to make their predicted profit, but not on a chronic basis. They typically have attempted to develop closed, confinement herds at all their operations with all in, all out management practiced. Th ...
... problem that PRRS virus crops up among their sites with a high enough frequency to reduce their ability to make their predicted profit, but not on a chronic basis. They typically have attempted to develop closed, confinement herds at all their operations with all in, all out management practiced. Th ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.