In the name of God
... • Systemic symptoms predominate( fever, chills, shaking chills, headaches, myalgia, malaise, anorexia, In more severe cases, prostration) • The systemic symptoms usually persist for 3 days. Respiratory symptoms (dry cough, severe pharyngeal pain, nasal obstruction and discharge) are also usually pre ...
... • Systemic symptoms predominate( fever, chills, shaking chills, headaches, myalgia, malaise, anorexia, In more severe cases, prostration) • The systemic symptoms usually persist for 3 days. Respiratory symptoms (dry cough, severe pharyngeal pain, nasal obstruction and discharge) are also usually pre ...
5. Describe assessment, treatment & teaching for STDS
... Caused by Gardenella Vaginalis S/s are grey discharge and fishy odor Treatment is Flagyl Client teaching-no alcohol when taking meds as can have a rx with vomiting, tachycardia and hypotension ...
... Caused by Gardenella Vaginalis S/s are grey discharge and fishy odor Treatment is Flagyl Client teaching-no alcohol when taking meds as can have a rx with vomiting, tachycardia and hypotension ...
infectious diseases info sheet
... Coughing and sneezing. Also direct contact with the nose/throat secretions of an infected person. ...
... Coughing and sneezing. Also direct contact with the nose/throat secretions of an infected person. ...
Bioterrorism - Open Source Medicine
... o Bubonic Plague: most people infected by flea bite develop this ...
... o Bubonic Plague: most people infected by flea bite develop this ...
Reporting Criteria for Erythema infectiosum (1) Definition
... Erythematous disease caused by parvovirus B19 infection (2) Clinical manifestations The disease is most frequent among young children (2-12 years of age) but can be found among infants and also among adults. The incubation period is 4-15 days. It is characterized by the sudden onset of demarcated fa ...
... Erythematous disease caused by parvovirus B19 infection (2) Clinical manifestations The disease is most frequent among young children (2-12 years of age) but can be found among infants and also among adults. The incubation period is 4-15 days. It is characterized by the sudden onset of demarcated fa ...
Infectious Diseases Assignment Sheet - Musco-Hurley
... How does our understanding of the causes of disease allow us to prevent its proliferation in crisis situations? Section I: Level Maximum 65 points 1. Listen to the lecture and take notes each day. (5 pts/day) 2. Flashcards on vocabulary terms. (10) 3. Write a paragraph on abiotic and biotic factors. ...
... How does our understanding of the causes of disease allow us to prevent its proliferation in crisis situations? Section I: Level Maximum 65 points 1. Listen to the lecture and take notes each day. (5 pts/day) 2. Flashcards on vocabulary terms. (10) 3. Write a paragraph on abiotic and biotic factors. ...
Tuberculosis Transmission and Pathogenesis Mahesh C. Patel, MD
... Published in: Amina Jindani; Caroline J. Doré; Denis A. Mitchison; Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003, 167, 1348-1354 ...
... Published in: Amina Jindani; Caroline J. Doré; Denis A. Mitchison; Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2003, 167, 1348-1354 ...
Infection
... Fever without focus: patients at risk • Newborns: Infection, diabetes insipidus • infants: bacterial infections only in 10-15% in the first year of life, younger than 3 months of age only in 5% ...
... Fever without focus: patients at risk • Newborns: Infection, diabetes insipidus • infants: bacterial infections only in 10-15% in the first year of life, younger than 3 months of age only in 5% ...
General Virology
... feverish illness and a maculopapular rash. It starts with erythema of the cheeks followed by a rash (resembling the rash of rubella) on the trunk and limbs. These symptoms ...
... feverish illness and a maculopapular rash. It starts with erythema of the cheeks followed by a rash (resembling the rash of rubella) on the trunk and limbs. These symptoms ...
Disease
... __________1. Newborn pigs need to be given an iron supplement at 3 or 4 days of age. __________2. Rabies is caused by bacteria. __________3. Warts are a virus. __________4. Pinkeye is a bacterium. __________5. Ringworm is caused by a bacteria. __________6. Roundworms are a fungus. __________7. You c ...
... __________1. Newborn pigs need to be given an iron supplement at 3 or 4 days of age. __________2. Rabies is caused by bacteria. __________3. Warts are a virus. __________4. Pinkeye is a bacterium. __________5. Ringworm is caused by a bacteria. __________6. Roundworms are a fungus. __________7. You c ...
Sexually Transmitted Diseases Sexually Transmitted
... Bacterial STD that affects mucous membranes. Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported infectious disease in the U.S. More than 700,000 Americans are infected with gonorrhea each year, but only half of these are reported. Many males are asymptomatic and females show only mild symptoms. ...
... Bacterial STD that affects mucous membranes. Gonorrhea is the second most commonly reported infectious disease in the U.S. More than 700,000 Americans are infected with gonorrhea each year, but only half of these are reported. Many males are asymptomatic and females show only mild symptoms. ...
Asepsis & antisepsis in surgery
... Pre and Postop care are essential parts of surgical treatment Good History, physical examination and selected investigations are the key Complications do occur, but many are ...
... Pre and Postop care are essential parts of surgical treatment Good History, physical examination and selected investigations are the key Complications do occur, but many are ...
herpes simplex virus
... Encephalitis: Serious infections of the CNS, affecting both children and adolescents. It may occur due to primary or latent infection with HSV1 virus. HSV encephalitis affects one temporal lobe, leading to focal neurologic signs and edema. The disease can be fatal (mortality rate of 70%), if left u ...
... Encephalitis: Serious infections of the CNS, affecting both children and adolescents. It may occur due to primary or latent infection with HSV1 virus. HSV encephalitis affects one temporal lobe, leading to focal neurologic signs and edema. The disease can be fatal (mortality rate of 70%), if left u ...
disease - West Ada
... Mothers can transmit diseases to an infant in the womb or as the baby passes through the vagina during birth ...
... Mothers can transmit diseases to an infant in the womb or as the baby passes through the vagina during birth ...
Streptoccocal Respiratory Infection
... often develops gradually.. several weeks mild respiratory symptoms, dry irritating prolonged cough..nasal congestion.. with/without fever..Few weeks..No blood sepsis. C. pneumoniae infections in adults.. often asymptomatic, mild, May include sore throat, headache, fever, dry cough. Clusters of i ...
... often develops gradually.. several weeks mild respiratory symptoms, dry irritating prolonged cough..nasal congestion.. with/without fever..Few weeks..No blood sepsis. C. pneumoniae infections in adults.. often asymptomatic, mild, May include sore throat, headache, fever, dry cough. Clusters of i ...
RSV - NSW Health
... contaminated items. A person is usually infectious for up to 10 days after symptoms begin. ...
... contaminated items. A person is usually infectious for up to 10 days after symptoms begin. ...
Duke in Darwin
... Symptoms 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected tick (incubation period from 2-14 days) Most between 5 & 7 days after exposure Onset often sudden Early symptoms: fever, headache, malaise, myalgias, arthralgias, & nausea, +/- vomiting Abdominal pain that can be severe Other symptoms: cough, b ...
... Symptoms 2 to 14 days after being bitten by an infected tick (incubation period from 2-14 days) Most between 5 & 7 days after exposure Onset often sudden Early symptoms: fever, headache, malaise, myalgias, arthralgias, & nausea, +/- vomiting Abdominal pain that can be severe Other symptoms: cough, b ...
Pediatric Pathogens and Impact on the Adult Population
... collection, and prior antibiotics contribute to high rate false negatives ...
... collection, and prior antibiotics contribute to high rate false negatives ...
Slide ()
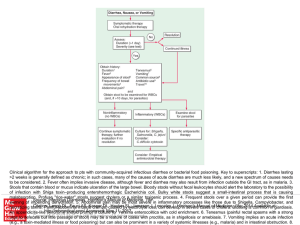
... Clinical algorithm for the approach to pts with community-acquired infectious diarrhea or bacterial food poisoning. Key to superscripts: 1. Diarrhea lasting >2 weeks is generally defined as chronic; in such cases, many of the causes of acute diarrhea are much less likely, and a new spectrum of cause ...
... Clinical algorithm for the approach to pts with community-acquired infectious diarrhea or bacterial food poisoning. Key to superscripts: 1. Diarrhea lasting >2 weeks is generally defined as chronic; in such cases, many of the causes of acute diarrhea are much less likely, and a new spectrum of cause ...
Hemorrhagic fever in hantavirus infection: Histopathologic
... We consider that the results presented in this paper provide important elements sufficient for pathologists presuming the presence of Hantavirus infection in the biopsy and autopsy specimens. Our results reveal that endothelium dysfunction is either the cause or the consequence of two different clin ...
... We consider that the results presented in this paper provide important elements sufficient for pathologists presuming the presence of Hantavirus infection in the biopsy and autopsy specimens. Our results reveal that endothelium dysfunction is either the cause or the consequence of two different clin ...
Case Study, Porth Chapter 16, Mechanisms of Infectious Disease
... Chapter 19, Disorders of the Immune Response Ahmed has worked as a phlebotomist in the local hospital for the past 7 years. Last year, he began to complain of watery eyes, nasal congestion, and wheezing whenever he went to work. He suspected he was allergic to something at the hospital because his s ...
... Chapter 19, Disorders of the Immune Response Ahmed has worked as a phlebotomist in the local hospital for the past 7 years. Last year, he began to complain of watery eyes, nasal congestion, and wheezing whenever he went to work. He suspected he was allergic to something at the hospital because his s ...
myoclonus - Pediatric Neurology Briefs
... cytotoxic T lymphocytes and other mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Rasmussen's encephalitis (RE) is reviewed at the University of Vienna, Austria, and the University of Bonn, Germany. The densities of T cells, microglial nodules and glial fibrillary acidic protein positive astrocytes in surgically ...
... cytotoxic T lymphocytes and other mechanisms in the pathogenesis of Rasmussen's encephalitis (RE) is reviewed at the University of Vienna, Austria, and the University of Bonn, Germany. The densities of T cells, microglial nodules and glial fibrillary acidic protein positive astrocytes in surgically ...
Chickenpox

Chickenpox, also known as varicella, is a highly contagious disease caused by the initial infection with varicella zoster virus (VZV). The disease results in a characteristic skin rash that forms small, itchy blisters, which eventually scab over. It usually starts on the face, chest, and back and then spreads to the rest of the body. Other symptoms may include fever, feeling tired, and headaches. Symptoms usually last five to ten days. Complications may occasionally include pneumonia, inflammation of the brain, or bacterial infections of the skin among others. The disease is often more severe in adults than children. Symptoms begin ten to twenty one days after exposure to the virus.Chickenpox is an airborne disease which spreads easily through the coughs and sneezes of an infected person. It may be spread from one to two days before the rash appears until all lesions have crusted over. It may also spread through contact with the blisters. Those with shingles may spread chickenpox to those who are not immune through contact with the blisters. The disease can usually be diagnosed based on the presenting symptom; however, in unusual cases may be confirmed by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) testing of the blister fluid or scabs. Testing for antibodies may be done to determine if a person is or is not immune. People usually only get the disease once.The varicella vaccine has resulted in a decrease in the number of cases and complications from the disease. It protects about 70 to 90 percent of people from disease with a greater benefit for severe disease. Routine immunization of children is recommended in many countries. Immunization within three days of exposure may improve outcomes in children. Treatment of those infected may include calamine lotion to help with itching, keeping the fingernails short to decrease injury from scratching, and the use of paracetamol (acetaminophen) to help with fevers. For those at increased risk of complications antiviral medication such as aciclovir are recommended.Chickenpox occurs in all parts of the world. Before routine immunization the number of cases occurring each year was similar to the number of people born. Since immunization the number of infections in the United States has decreased nearly 90%. In 2013 chickenpox resulted in 7,000 deaths globally – down from 8,900 in 1990. Death occurs in about 1 per 60,000 cases. Chickenpox was not separated from smallpox until the late 19th century. In 1888 its connection to shingles was determined. The first documented use of the term chicken pox was in 1658. Various explanations have been suggested for the use of ""chicken"" in the name, one being the relative mildness of the disease.