* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
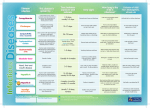
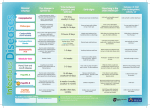
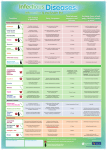
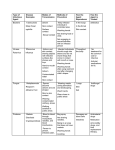
Download infectious diseases info sheet
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Neglected tropical diseases wikipedia , lookup
Kawasaki disease wikipedia , lookup
Hospital-acquired infection wikipedia , lookup
Infection control wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Rheumatic fever wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Whooping cough wikipedia , lookup
Germ theory of disease wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Globalization and disease wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Transmission (medicine) wikipedia , lookup
Childhood immunizations in the United States wikipedia , lookup