PowerPoint
... the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
... the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
Dr.Eman Zakaria Hegazy Quantum Mechanics and Statistical
... - We can consider the nucleus to be fixed and the electron to be revolving about it. - The force holding the electron in a circular orbit is supplied by the columbic force of attraction between the proton and the electron. ...
... - We can consider the nucleus to be fixed and the electron to be revolving about it. - The force holding the electron in a circular orbit is supplied by the columbic force of attraction between the proton and the electron. ...
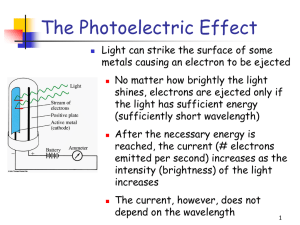
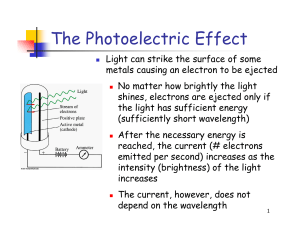
The Photoelectric Effect
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
... Bohr’s theory correctly explained the hydrogen emission spectrum The theory failed for all other elements with more than 1 electron Bohr’s theory attempted to use classical mechanics to solve a problem that could not be solved by classical mechanics ...
Quantum Chemistry - Winona State University
... Postulates of Quantum Theory • The state of a system is defined by a function (usually denoted and called the wavefunction or state function) that contains all the information that can be known about the system. • Every physical observable is represented by a linear operator called the “Hermitian ...
... Postulates of Quantum Theory • The state of a system is defined by a function (usually denoted and called the wavefunction or state function) that contains all the information that can be known about the system. • Every physical observable is represented by a linear operator called the “Hermitian ...
Orbitals and Quantum Numbers
... define an orbital in an atom, and list the limitations placed on the values each may have. ...
... define an orbital in an atom, and list the limitations placed on the values each may have. ...
Presentación de PowerPoint
... "Divergent series are on the whole devil's work, and it is a shame that one dares to found any proof on them. One can get out of them what one wants if one uses them, and it is they which have made so much unhappiness and so many paradoxes. Can one think of anything more appalling than to say that ...
... "Divergent series are on the whole devil's work, and it is a shame that one dares to found any proof on them. One can get out of them what one wants if one uses them, and it is they which have made so much unhappiness and so many paradoxes. Can one think of anything more appalling than to say that ...
Quantum Computing
... superposition. - Imagine two qubits, each in the state |0> + |1> (a superposition of the 0 and 1.) We can entangle the two qubits such that the measurement of one qubit is always correlated to the measurement of the other qubit. ...
... superposition. - Imagine two qubits, each in the state |0> + |1> (a superposition of the 0 and 1.) We can entangle the two qubits such that the measurement of one qubit is always correlated to the measurement of the other qubit. ...
Group Problems #27 - Solutions Wednesday, November 2 Problem 1
... Since this is not equal to zero, the K̂ and x̂ do not commute, and we cannot simultaneously measure the particle’s kinetic energy and position simultaneously. So if we constrain our measurement to a particular value of position (x), then we will measure a spread in kinetic energy values when we repe ...
... Since this is not equal to zero, the K̂ and x̂ do not commute, and we cannot simultaneously measure the particle’s kinetic energy and position simultaneously. So if we constrain our measurement to a particular value of position (x), then we will measure a spread in kinetic energy values when we repe ...
Integration via a Quantum Information Processor
... We start our quantum algorithm with one work qubit and log2M function qubits, where M is the number of points used in our summation, all in the state 0 . Hadamard gates are applied to each function qubit. The Hadamard gate performs the following ...
... We start our quantum algorithm with one work qubit and log2M function qubits, where M is the number of points used in our summation, all in the state 0 . Hadamard gates are applied to each function qubit. The Hadamard gate performs the following ...
rtf
... Information processing is concerned today with very large quantities of very complex data. The complexity arises from the diversity of the type of data and the relationships between data and the different types of relationships. At present semantic complexity can only be processed at the surface lev ...
... Information processing is concerned today with very large quantities of very complex data. The complexity arises from the diversity of the type of data and the relationships between data and the different types of relationships. At present semantic complexity can only be processed at the surface lev ...
PHYS13071 Assessment 2012
... in the 1920s by Neils Bohr, Erwin Schrödinger, Werner Heisenberg, Paul Dirac and others. The review essay will focus on the historical development of quantum theory. ...
... in the 1920s by Neils Bohr, Erwin Schrödinger, Werner Heisenberg, Paul Dirac and others. The review essay will focus on the historical development of quantum theory. ...
Lecture 1
... electrons didn’t behave like they were supposed to. Newton had formulated the laws according to which all particles should move and he had done it in the 17th century. Up until JJ Thomson discovered the electron in the 1890’s, those laws worked for all the particles that people could see. But electr ...
... electrons didn’t behave like they were supposed to. Newton had formulated the laws according to which all particles should move and he had done it in the 17th century. Up until JJ Thomson discovered the electron in the 1890’s, those laws worked for all the particles that people could see. But electr ...
Quantum Computers
... 2 qubits contains 4 bits of information because you need 4 coefficients of probability to determine the value they represent. ...
... 2 qubits contains 4 bits of information because you need 4 coefficients of probability to determine the value they represent. ...
Non-linear gates enabling universal quantum computation
... Quantum mechanics predicts phenomena that defies our daily experience and goes beyond our intuitive comprehension of the physical world. But despite this, quantum mechanics has much to offer. In particular, researchers are learning that quantum systems can enable to compute in a much more efficient ...
... Quantum mechanics predicts phenomena that defies our daily experience and goes beyond our intuitive comprehension of the physical world. But despite this, quantum mechanics has much to offer. In particular, researchers are learning that quantum systems can enable to compute in a much more efficient ...
chem 3374a quantum chemistry and spectroscopy
... Evaluation: Students must write at least 5 of the 6 quizzes and must sit the midterm test and the final exam. The final course grade will be a weighted average calculated as follows: five quizzes with the highest marks—25% (each quiz is 5%); the midterm test—35%; the final exam—40%. Assignments and ...
... Evaluation: Students must write at least 5 of the 6 quizzes and must sit the midterm test and the final exam. The final course grade will be a weighted average calculated as follows: five quizzes with the highest marks—25% (each quiz is 5%); the midterm test—35%; the final exam—40%. Assignments and ...
Presentation (PowerPoint File)
... 4. Stability: Long decoherence times, together with the ability to suppress decoherence through error correction and fault-tolerant computation. 5. Measurement: The ability to read out the state of the computer in a convenient product basis. ...
... 4. Stability: Long decoherence times, together with the ability to suppress decoherence through error correction and fault-tolerant computation. 5. Measurement: The ability to read out the state of the computer in a convenient product basis. ...
The fractional quantum Hall effect I
... response expression for the Hall conductance to the calculation of the Chern number of ground state wave function. The seminal experiment of Tsui et al. showed, however, that in a very clean sample, the Hall conductance develops a fractional plateau at one third of a quantum of conductance, see Fig ...
... response expression for the Hall conductance to the calculation of the Chern number of ground state wave function. The seminal experiment of Tsui et al. showed, however, that in a very clean sample, the Hall conductance develops a fractional plateau at one third of a quantum of conductance, see Fig ...