Diagnostics (HBV and HCV) - View the full AIDS 2016 programme
... •sAg negative , but HBV DNA is present in blood or liver •Other markers variably present •Past infection, good control, •low HBV DNA in blood <100 IU/ml •Mutants with altered sAg: “a” determinant or •alterations to preS causing impaired sAg secretion “a” determinant of HBsAg ...
... •sAg negative , but HBV DNA is present in blood or liver •Other markers variably present •Past infection, good control, •low HBV DNA in blood <100 IU/ml •Mutants with altered sAg: “a” determinant or •alterations to preS causing impaired sAg secretion “a” determinant of HBsAg ...
Bloodborne Pathogens
... women and 610,000 children under 15. Women are becoming increasingly affected by HIV. Approximately 50%, or 19.2 million, of the 38.6 million adults living with HIV or AIDS worldwide are ...
... women and 610,000 children under 15. Women are becoming increasingly affected by HIV. Approximately 50%, or 19.2 million, of the 38.6 million adults living with HIV or AIDS worldwide are ...
Infectious Canine Hepatitis Infectious Canine Hepatitis
... Most dogs infected with ICH will recover with good supportive care. This includes attention to nutrition, fluid intake, nursing care, and control of any secondary infections. Prognosis The more body systems that have become involved, the worse the prognosis. Transmission to Humans There is some sero ...
... Most dogs infected with ICH will recover with good supportive care. This includes attention to nutrition, fluid intake, nursing care, and control of any secondary infections. Prognosis The more body systems that have become involved, the worse the prognosis. Transmission to Humans There is some sero ...
Lung Disease - biologypost
... approx 2 million people per year die from it. • Previously known as consumption. • Pre-WW2 campaign. ...
... approx 2 million people per year die from it. • Previously known as consumption. • Pre-WW2 campaign. ...
Hepatitis B Vaccination as a Measure to
... Background. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the fifth most common cause of cancer in the world,1 is closely associated with hepatitis virus infections. 2 In Taiwan, the carrier rate of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in the general population has been as high as 15%– 20%.3 And HCC has ranked fir ...
... Background. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the fifth most common cause of cancer in the world,1 is closely associated with hepatitis virus infections. 2 In Taiwan, the carrier rate of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in the general population has been as high as 15%– 20%.3 And HCC has ranked fir ...
Gene therapy and viral vectors - Lectures For UG-5
... can be replaced with therapeutic genes, there are already many pharmaceutical options that can be used to control against unwanted replication of the virus, and the viral genome remains as an intact plasmid within the cell nucleus which protects against unwanted insertion of viral DNA into the host ...
... can be replaced with therapeutic genes, there are already many pharmaceutical options that can be used to control against unwanted replication of the virus, and the viral genome remains as an intact plasmid within the cell nucleus which protects against unwanted insertion of viral DNA into the host ...
Drug treatment for chronic hepatitis B: slide set
... Recommendations: entecavir • Entecavir is recommended as an option for the treatment of people with chronic HBeAg-positive or HBeAg-negative hepatitis B in whom antiviral treatment is indicated. ...
... Recommendations: entecavir • Entecavir is recommended as an option for the treatment of people with chronic HBeAg-positive or HBeAg-negative hepatitis B in whom antiviral treatment is indicated. ...
Treatment
... itself to stop it from replicating. • These drugs need to be used in combination with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. ...
... itself to stop it from replicating. • These drugs need to be used in combination with pegylated interferon and ribavirin. ...
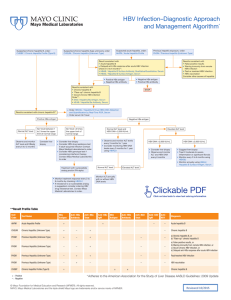
HBV Infection–Diagnostic Approach and Management Algorithm*
... ■ “Flare-up” chronic hepatitis B ■ Occult chronic HBV infection Order**: ■ EAG / Hepatitis Be Antigen, Serum ■ HEAB / Hepatitis Be Antibody, Serum ...
... ■ “Flare-up” chronic hepatitis B ■ Occult chronic HBV infection Order**: ■ EAG / Hepatitis Be Antigen, Serum ■ HEAB / Hepatitis Be Antibody, Serum ...
Lecture objectives Standard Precautions HIV/AIDS Hepatitis B
... residue in eyes/mouth/nose • Studies have shown that the concentration of Hepatitis C virus in human tear fluid is independent of the severity of hepatitis infection ...
... residue in eyes/mouth/nose • Studies have shown that the concentration of Hepatitis C virus in human tear fluid is independent of the severity of hepatitis infection ...
Section 4 Immunization
... sterility. Rubella is also known as German measles and can cause fever, rash, swelling of the neck glands and swelling and pain in the joints. When women become infected with the virus early in their pregnancy, there is a risk to the unborn child of developing congenital rubella syndrome. Hepatitis ...
... sterility. Rubella is also known as German measles and can cause fever, rash, swelling of the neck glands and swelling and pain in the joints. When women become infected with the virus early in their pregnancy, there is a risk to the unborn child of developing congenital rubella syndrome. Hepatitis ...
Infectious-and-Parasitic-disease
... Clearance of the virus occurs when cytotoxic T cells kill virus infected cells. Host develops antibodies to H and N components therefore preventing re-infection. Mutations occur in H and N, allowing new strains to emerge. Major complication is bacterial superinfection with pneumococcus, staphylococc ...
... Clearance of the virus occurs when cytotoxic T cells kill virus infected cells. Host develops antibodies to H and N components therefore preventing re-infection. Mutations occur in H and N, allowing new strains to emerge. Major complication is bacterial superinfection with pneumococcus, staphylococc ...
Infection Control Policy
... appear 3 weeks after exposure. 4-6 weeks later other symptoms may appear such as rash on soles of feet and palms of the hands. This may progress into a latent phase if not treated. Testing for the exposure would include a blood test. D. Hepatitis B: Hepatitis is a term which means inflammation of th ...
... appear 3 weeks after exposure. 4-6 weeks later other symptoms may appear such as rash on soles of feet and palms of the hands. This may progress into a latent phase if not treated. Testing for the exposure would include a blood test. D. Hepatitis B: Hepatitis is a term which means inflammation of th ...
Triple vaccine for the prevention of virus infections protects against A
... D. ability to sterilise equipment made of heatsensitive materials, e.g. polystyrene E. no deleterious effects on glassware or textile fibres ...
... D. ability to sterilise equipment made of heatsensitive materials, e.g. polystyrene E. no deleterious effects on glassware or textile fibres ...
Unusual cases of hepatitis B virus transmission in the Community
... prevalence of HBV and HCV infection in barbers compared ...
... prevalence of HBV and HCV infection in barbers compared ...
UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA BLOODBORNE PATHOGEN PROGRAM
... I accept participation in the vaccination series and have not yet been vaccinated. Take a copy of this form to the Student Health Care Center (see info below) to begin the vaccination series. Jacksonville personnel go to the Employee’s Health Office, Suite 505 Tower 1, 5th floor, 8th and Jefferson S ...
... I accept participation in the vaccination series and have not yet been vaccinated. Take a copy of this form to the Student Health Care Center (see info below) to begin the vaccination series. Jacksonville personnel go to the Employee’s Health Office, Suite 505 Tower 1, 5th floor, 8th and Jefferson S ...
Hand, Foot and Mouth Disease (HFMD) FAQs
... Everyone but it usually occurs in children younger than 10 years of age. Persons taking medications or having medical conditions lowering their immune system’s ability to fight infection are also at higher risk. Not everyone who is exposed to it or infected with it becomes ill. What are the symptoms ...
... Everyone but it usually occurs in children younger than 10 years of age. Persons taking medications or having medical conditions lowering their immune system’s ability to fight infection are also at higher risk. Not everyone who is exposed to it or infected with it becomes ill. What are the symptoms ...
National Program for Viral Hepatitis prevention and control
... Hepatitis A and B vaccination and We try to apply management Programs to Prevent Perinatal HBV infection – The pregnant women should be tested for HBsAg as part of routine prenatal care – Infants born from HBsAg positive women should have medical record of hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG administration ...
... Hepatitis A and B vaccination and We try to apply management Programs to Prevent Perinatal HBV infection – The pregnant women should be tested for HBsAg as part of routine prenatal care – Infants born from HBsAg positive women should have medical record of hepatitis B vaccine and HBIG administration ...
Bloodborne Pathogens - PUR-O-ZONE
... are intended for the sole use of PUR-O-ZONE representatives and customers for educational purposes. The entire contents are copyrighted, and use by other ...
... are intended for the sole use of PUR-O-ZONE representatives and customers for educational purposes. The entire contents are copyrighted, and use by other ...
Pathogenesis of Viral Infections
... However, for certain classic viral infections, such as measles, smallpox, rabies, and influenza almost all infected individuals develop disease. It is perfectly possible to envisage viruses with a hitand-run strategy, moving quickly form one host to the next and relying on continuing circulation for ...
... However, for certain classic viral infections, such as measles, smallpox, rabies, and influenza almost all infected individuals develop disease. It is perfectly possible to envisage viruses with a hitand-run strategy, moving quickly form one host to the next and relying on continuing circulation for ...
Strep Throat Influenza
... infections, 90% occur in young adults. The virus attacks the liver and can lead to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, liver cancer, and even death. There is no cure for Hepatitis B infection; however, there is a vaccine available that is effective in preventing infection with the Hepatitis B vir ...
... infections, 90% occur in young adults. The virus attacks the liver and can lead to cirrhosis of the liver, liver failure, liver cancer, and even death. There is no cure for Hepatitis B infection; however, there is a vaccine available that is effective in preventing infection with the Hepatitis B vir ...
The Virus
... – Host ~ organism which shelters or nourishes something by providing materials necessary for viral replication ...
... – Host ~ organism which shelters or nourishes something by providing materials necessary for viral replication ...
A Guide To Biological Hazards in the Workplace
... with appropriate protective gloves, gowns, and masks. The entire program (called an Exposure Control Plan) must be in writing. And a responsible party to administer the program. [] The facility is responsible to vaccinate all workers at significant risk for hepatitis B. [] Following a significant ex ...
... with appropriate protective gloves, gowns, and masks. The entire program (called an Exposure Control Plan) must be in writing. And a responsible party to administer the program. [] The facility is responsible to vaccinate all workers at significant risk for hepatitis B. [] Following a significant ex ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.