Introduction to Waterborne Pathogens
... Causes diarrhea (often bloody), fever, cramps 24-48 hours after infection illness lasts 5 -7 days infect only humans 18,000 cases reported annually primarily transmitted by direct contact with infected individual also transmitted by contaminated food, water, recreation low infectious dose (~10 organ ...
... Causes diarrhea (often bloody), fever, cramps 24-48 hours after infection illness lasts 5 -7 days infect only humans 18,000 cases reported annually primarily transmitted by direct contact with infected individual also transmitted by contaminated food, water, recreation low infectious dose (~10 organ ...
Viral Genomes - HCC Learning Web
... The lytic cycle is a phage replicative cycle that culminates in the death of the host cell The lytic cycle produces new phages and lyses (breaks open) the host’s cell wall, releasing the progeny viruses A phage that reproduces only by the lytic cycle is called a virulent phage ...
... The lytic cycle is a phage replicative cycle that culminates in the death of the host cell The lytic cycle produces new phages and lyses (breaks open) the host’s cell wall, releasing the progeny viruses A phage that reproduces only by the lytic cycle is called a virulent phage ...
(T/F) The outer membrane for G+ and the cell membrane for G
... Are Strep. pneumoniae sensitve to optochin? Are Viridans strep.? Strep. pneumoniae is optochin-Sensitive - Viridans streptococci is optochin-Resistant Are Strep. pyogenes Bacitracin-sensitive?> YES. both are catalase + Are Viridans strep. alpha, beta, or non-hemolytic? alpha Because of drug resistan ...
... Are Strep. pneumoniae sensitve to optochin? Are Viridans strep.? Strep. pneumoniae is optochin-Sensitive - Viridans streptococci is optochin-Resistant Are Strep. pyogenes Bacitracin-sensitive?> YES. both are catalase + Are Viridans strep. alpha, beta, or non-hemolytic? alpha Because of drug resistan ...
Document
... c Average number of plaques between duplicate wells, with the dilution (10x) used in parentheses. Please note for 0.4% and 0.5% triton treatments the initial viral suspension was diluted by an additional factor of 2 to prevent triton-killing of the cells in the assay at the 10-1 dilution. This added ...
... c Average number of plaques between duplicate wells, with the dilution (10x) used in parentheses. Please note for 0.4% and 0.5% triton treatments the initial viral suspension was diluted by an additional factor of 2 to prevent triton-killing of the cells in the assay at the 10-1 dilution. This added ...
PDF
... PEDIATRICS is the official journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics. A monthly publication, it has been published continuously since 1948. PEDIATRICS is owned, published, and trademarked by the American Academy of Pediatrics, 141 Northwest Point Boulevard, Elk Grove Village, Illinois, 60007. Co ...
... PEDIATRICS is the official journal of the American Academy of Pediatrics. A monthly publication, it has been published continuously since 1948. PEDIATRICS is owned, published, and trademarked by the American Academy of Pediatrics, 141 Northwest Point Boulevard, Elk Grove Village, Illinois, 60007. Co ...
ehv_guidelines_mar_13 - Meadows Veterinary Centre
... competitors attending equine events Although the UK has seemingly seen more problems with equine herpes virus-1 (EHV-1) infection (including neurological disease in horses in Devon, Somerset, East Anglia and Gloucestershire) since November 2012, EHV-1 is, and always has been, an ever present threat ...
... competitors attending equine events Although the UK has seemingly seen more problems with equine herpes virus-1 (EHV-1) infection (including neurological disease in horses in Devon, Somerset, East Anglia and Gloucestershire) since November 2012, EHV-1 is, and always has been, an ever present threat ...
B. Agglutination reaction
... Examination revealed low level of major classes of immunoglobulins. The direct cause of this phenomenon may be the following cell dysfunction: A. Plasmocytes B. Phagocytes C. Neutrophils D. Macrophages E. Lymphocytes 18. A patient consulted an immunologist about diarrhea, weight loss within several ...
... Examination revealed low level of major classes of immunoglobulins. The direct cause of this phenomenon may be the following cell dysfunction: A. Plasmocytes B. Phagocytes C. Neutrophils D. Macrophages E. Lymphocytes 18. A patient consulted an immunologist about diarrhea, weight loss within several ...
Biological Weapons: A Module for Nursing Professionals
... Ingestion of contaminated food or water ...
... Ingestion of contaminated food or water ...
Chapter 27 Nervous System Infections
... • Neisseria meningitidis differs from the other causes in that it is often responsible for epidemics of meningitis. ...
... • Neisseria meningitidis differs from the other causes in that it is often responsible for epidemics of meningitis. ...
Anthrax - Schools
... redness, itching, swelling and lumps at the injection site • 35% experience muscle or joint aches, chills, fever, headaches, nausea, loss of appetite, feeling on unease • Serious reactions requiring hospitalization are rare, occurring about once per 50,000 doses. • Severe allergic reactions can occu ...
... redness, itching, swelling and lumps at the injection site • 35% experience muscle or joint aches, chills, fever, headaches, nausea, loss of appetite, feeling on unease • Serious reactions requiring hospitalization are rare, occurring about once per 50,000 doses. • Severe allergic reactions can occu ...
6. BRIEF RESUME OF THE INTENDED WORK 6.1 Need for Study In
... Catheter Related Blood Stream Infection (CRBSI) is an infection of recent times.2 Both infectious and non-infectious complications have been reported following Central Venous Catheterisation. Of all the “Device related nosocomial infections”, CRBSI forms a major part.3 Healthcare associated septicae ...
... Catheter Related Blood Stream Infection (CRBSI) is an infection of recent times.2 Both infectious and non-infectious complications have been reported following Central Venous Catheterisation. Of all the “Device related nosocomial infections”, CRBSI forms a major part.3 Healthcare associated septicae ...
Facts about ebola
... contact with infected blood, sweat, secretions, tissues, organs or other bodily fluids of dead or living persons. It can also be contracted through unprotected sexual contact with patients who have recently recovered from the disease. It can take between 2 and 21 days from the point of contact with ...
... contact with infected blood, sweat, secretions, tissues, organs or other bodily fluids of dead or living persons. It can also be contracted through unprotected sexual contact with patients who have recently recovered from the disease. It can take between 2 and 21 days from the point of contact with ...
Module 5: Stewardship in intra
... Patients to be treated non-operatively for low-risk infections should be on a low-risk regimen with plans for early PO conversion ...
... Patients to be treated non-operatively for low-risk infections should be on a low-risk regimen with plans for early PO conversion ...
SHINGLES (Herpes Zoster)
... Shingles, or herpes zoster, is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. It occurs only in persons who have had chickenpox in the past. It is a reactivation of a dormant (inactive) varicella infection in the dorsal root ganglia (nerve fibers). This means that someone who has had and recovered ...
... Shingles, or herpes zoster, is caused by the same virus that causes chickenpox. It occurs only in persons who have had chickenpox in the past. It is a reactivation of a dormant (inactive) varicella infection in the dorsal root ganglia (nerve fibers). This means that someone who has had and recovered ...
SOURCES OF ERROR IN SEROLOGIC AND IMMUNOLOGIC LAB
... Serum specimens are lipemic, hemolyzed, or heavily contaminated with bacteria. | If the reaction time is longer than 2 minutes, a falsepositive result may also be produced from a drying effect. effect False-negative results may be observed in: | Undiluted serum specimens p because of high g levels o ...
... Serum specimens are lipemic, hemolyzed, or heavily contaminated with bacteria. | If the reaction time is longer than 2 minutes, a falsepositive result may also be produced from a drying effect. effect False-negative results may be observed in: | Undiluted serum specimens p because of high g levels o ...
Appendix D
... 16.1b. To make sure all the reagents are functioning properly, positive and negative controls are run along with your blood sample. A positive control contains antibodies specific to hepatitis C antigen so a positive color reaction will be produced. A negative control lacks hepatitis C antibodies, s ...
... 16.1b. To make sure all the reagents are functioning properly, positive and negative controls are run along with your blood sample. A positive control contains antibodies specific to hepatitis C antigen so a positive color reaction will be produced. A negative control lacks hepatitis C antibodies, s ...
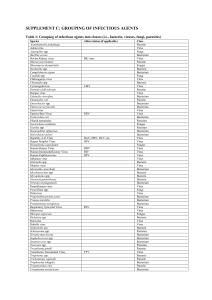
SUPPLEMENT C: GROUPING OF INFECTIOUS AGENTS Table 4
... Note: Viruses act intracellularly and are able to utilise the information system of the host cells and act on the DNA, RNA, or protein level. Interpretation of the results in Figure 8 suggests that viruses are the most versatile agents as they were capable of causing disease in every organ system in ...
... Note: Viruses act intracellularly and are able to utilise the information system of the host cells and act on the DNA, RNA, or protein level. Interpretation of the results in Figure 8 suggests that viruses are the most versatile agents as they were capable of causing disease in every organ system in ...
Lesson 2: An STI`s Tale
... from Luke? Since most people who have STIs don’t know they have an infection, how can people protect themselves? The virus took pleasure in the knowledge that there might be copies of itself running around in Luke’s two unprotected partners, but how might Luke have felt if he discovered herpes was t ...
... from Luke? Since most people who have STIs don’t know they have an infection, how can people protect themselves? The virus took pleasure in the knowledge that there might be copies of itself running around in Luke’s two unprotected partners, but how might Luke have felt if he discovered herpes was t ...
Peste des petits ruminants virus detected in tissues from an Asiatic
... isolates. In general, six of the seven residues in the H gene are presumed to be important for measles virus hemagglutininsignalling lymphocyte activation molecule (SLAM) receptor interactions [6]. Along with the isolate from our study, these residues are conserved within the Nigerian and other PPRV ...
... isolates. In general, six of the seven residues in the H gene are presumed to be important for measles virus hemagglutininsignalling lymphocyte activation molecule (SLAM) receptor interactions [6]. Along with the isolate from our study, these residues are conserved within the Nigerian and other PPRV ...
Transmission of Diseases via Animals and Insects Zoonotic infections
... • More than 2 million cases of campylobacter infection occur each year in the United States, and C. jejuni is now the leading cause of bacterial gastroenteritis. • Campylobacter infections are contagious, especially among members of the same family and kids in childcare or preschools. Infectio ...
... • More than 2 million cases of campylobacter infection occur each year in the United States, and C. jejuni is now the leading cause of bacterial gastroenteritis. • Campylobacter infections are contagious, especially among members of the same family and kids in childcare or preschools. Infectio ...
AIDS pathogenesis: a tale of two monkeys
... SIV-infected RMs has profound theoretical implications, as it indicates that natural SIV hosts have evolved to a non-pathogenic type of infection independent of immune control of virus replication. From a more practical point of view, this observation emphasizes the tremendous challenge of artificial ...
... SIV-infected RMs has profound theoretical implications, as it indicates that natural SIV hosts have evolved to a non-pathogenic type of infection independent of immune control of virus replication. From a more practical point of view, this observation emphasizes the tremendous challenge of artificial ...
Clase 6 de Octubre
... Shortly after birth the newborn is colonized by microbial flora. a | Neonatal skin is colonized by Grampositive bacteria (for example, coagulase-negative staphylococci) that often gain access to the skin through hair follicles and induce a benign rash known as erythema toxicum. At sites of eythema t ...
... Shortly after birth the newborn is colonized by microbial flora. a | Neonatal skin is colonized by Grampositive bacteria (for example, coagulase-negative staphylococci) that often gain access to the skin through hair follicles and induce a benign rash known as erythema toxicum. At sites of eythema t ...
Avian influenza Fact sheet Updated April 2011 Key facts
... influenza, which is around two to three days. Current data for H5N1 infection indicate an incubation period ranging from two to eight days and possibly as long as 17 days. WHO currently recommends that an incubation period of seven days be used for field investigations and the monitoring of patient ...
... influenza, which is around two to three days. Current data for H5N1 infection indicate an incubation period ranging from two to eight days and possibly as long as 17 days. WHO currently recommends that an incubation period of seven days be used for field investigations and the monitoring of patient ...
Principles of Prevention
... reproduce only by taking over other cells and becoming part of them. ...
... reproduce only by taking over other cells and becoming part of them. ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.