Bloodborne Pathogens Control - Maryland State Department of
... HBV causes infection of the liver and may lead to liver failure and liver cancer. Some individuals who are infected with HBV will carry the virus for the rest of their lives. Hepatitis B carriers, or persons with chronic HBV infection, are often symptom-free. They may be unaware that they are infect ...
... HBV causes infection of the liver and may lead to liver failure and liver cancer. Some individuals who are infected with HBV will carry the virus for the rest of their lives. Hepatitis B carriers, or persons with chronic HBV infection, are often symptom-free. They may be unaware that they are infect ...
Epstein-Barr virus infection and chronic lymphocytic leukemia: a
... Lymphoma (HL), and some T/NK cell lymphoma, but also carcinomas of the nasopharynx and stomach and leiomyosarcomas arising in organ transplant patients and HIV-infected individuals [4]. EBV-induced immortalization/transformation is mediated by the activity of viral proteins that interfere with cruci ...
... Lymphoma (HL), and some T/NK cell lymphoma, but also carcinomas of the nasopharynx and stomach and leiomyosarcomas arising in organ transplant patients and HIV-infected individuals [4]. EBV-induced immortalization/transformation is mediated by the activity of viral proteins that interfere with cruci ...
AND GIDSAS
... After the virus enters the body, it requires 3-10 days incubation period before the disease appears. According to current data, infected people do not pass on the virus to others during the incubation period. They become infectious only when the first symptoms appear: cough, sneezing – which spread ...
... After the virus enters the body, it requires 3-10 days incubation period before the disease appears. According to current data, infected people do not pass on the virus to others during the incubation period. They become infectious only when the first symptoms appear: cough, sneezing – which spread ...
Infection Prevention and Control (IPC) Standard Operating
... Standard Infection Control Precautions (SICPs), Section 1 of the Health Protection Scotland (HPS) National Infection Prevention and Control Manual, must be used by all staff, in all care settings, at all times, for all patients whether infection is known to be present or not to ensure the safety of ...
... Standard Infection Control Precautions (SICPs), Section 1 of the Health Protection Scotland (HPS) National Infection Prevention and Control Manual, must be used by all staff, in all care settings, at all times, for all patients whether infection is known to be present or not to ensure the safety of ...
chapter 26
... APSGN is an antibody-antigen disease that occurs as a result of certain strains of the Group A ß-hemolytic streptococcal infection and is most commonly seen in children between the ages of 6 and 7. The exact mechanism of the pathophysiology for APSGN is not certain. It is believed that immune comple ...
... APSGN is an antibody-antigen disease that occurs as a result of certain strains of the Group A ß-hemolytic streptococcal infection and is most commonly seen in children between the ages of 6 and 7. The exact mechanism of the pathophysiology for APSGN is not certain. It is believed that immune comple ...
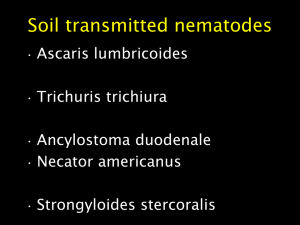
Filariasis
... circulating blood is key Where more than one species of filarial infection occurs need well stained slides for morphological identification of microfilariae Filarial infections can occur without microfilaremia ...
... circulating blood is key Where more than one species of filarial infection occurs need well stained slides for morphological identification of microfilariae Filarial infections can occur without microfilaremia ...
Hands: First line of defence
... and others from infection, dental professionals are not leaving themselves open to long term suffering and discomfort. Skin irritations and allergies are something of an occupational hazard in dentistry so it is important to reach a balance that means while hand hygiene is paramount, the dental heal ...
... and others from infection, dental professionals are not leaving themselves open to long term suffering and discomfort. Skin irritations and allergies are something of an occupational hazard in dentistry so it is important to reach a balance that means while hand hygiene is paramount, the dental heal ...
the streptococcus
... This organism causes a number of common diseases, such as pneumonia and meningitis in adults and otitis media and sinusitis in children. Habitat and transmission A normal commensal in the human upper respiratory tract; up to 4% of the population carry this bacteria in small numbers. Transmission is ...
... This organism causes a number of common diseases, such as pneumonia and meningitis in adults and otitis media and sinusitis in children. Habitat and transmission A normal commensal in the human upper respiratory tract; up to 4% of the population carry this bacteria in small numbers. Transmission is ...
Vaccines on the frontline against infectious diseases
... pool of long-lasting ‘memory’ B cells against that pathogen.10 These cells reside mainly in the spleen and circulate in small numbers in blood.11 They represent a rapid response force that deal with subsequent infections. It is this memory that is the foundation of our resistance to future infection ...
... pool of long-lasting ‘memory’ B cells against that pathogen.10 These cells reside mainly in the spleen and circulate in small numbers in blood.11 They represent a rapid response force that deal with subsequent infections. It is this memory that is the foundation of our resistance to future infection ...
Diagnosis
... • By surgery: it depends on presence of complications like compression, infection bleeding (rapid increase in size and become pale and shock) • During surgery be careful to some nerves like hypoglossal never, spinal accessory nerve, mandibular branch of facial nerve ...
... • By surgery: it depends on presence of complications like compression, infection bleeding (rapid increase in size and become pale and shock) • During surgery be careful to some nerves like hypoglossal never, spinal accessory nerve, mandibular branch of facial nerve ...
One fungal infection that would prevent the treatment One bacterial
... painful. Acne can be a painful skin condition and if a facial is carried out on an acne infected face, the client will be in discomfort and possibly in pain. Skin tags; raised bits of flesh coloured or brown skin that hang off the skin, if a facial was carried out on skin with a skin tag presen ...
... painful. Acne can be a painful skin condition and if a facial is carried out on an acne infected face, the client will be in discomfort and possibly in pain. Skin tags; raised bits of flesh coloured or brown skin that hang off the skin, if a facial was carried out on skin with a skin tag presen ...
Influence of White Clover Mosaic Potexvirus
... were detected in healthy leaves, whereas viral infection led to the accumulation of high concentrations of the 9-glucosides (Fig. 1, E and F; Table II). Because this is the first time, to our knowledge, that 9-glucosides have been detected in bean, the experiment was repeated to allow confirmation o ...
... were detected in healthy leaves, whereas viral infection led to the accumulation of high concentrations of the 9-glucosides (Fig. 1, E and F; Table II). Because this is the first time, to our knowledge, that 9-glucosides have been detected in bean, the experiment was repeated to allow confirmation o ...
a cohort study investigating autoantibody levels
... 1:640, not an uncommonly high value for a person with Sjögren’s syndrome. By day 15 the titer of ANA had increased and continued to do so until peaking at day 42 before resuming to pre-infection levels. Antibodies against influenza A virus were also detected between days 15–21 post infection. These ...
... 1:640, not an uncommonly high value for a person with Sjögren’s syndrome. By day 15 the titer of ANA had increased and continued to do so until peaking at day 42 before resuming to pre-infection levels. Antibodies against influenza A virus were also detected between days 15–21 post infection. These ...
ANATOMY OF PHARYNX
... Mucous membrane Pharyngeal aponeurosis(pharyngobasilar fascia) Muscular coat Buccopharyngeal fascia ...
... Mucous membrane Pharyngeal aponeurosis(pharyngobasilar fascia) Muscular coat Buccopharyngeal fascia ...
Processing a Crime Scene
... Symptoms include itching, stinging, and burning between the toes; itching, stinging, and burning on the soles of the feet; itchy blisters; cracking and peeling skin, especially between the toes and on the soles of the feet; excessive dryness of the skin on the bottoms or sides of the feet; and/or to ...
... Symptoms include itching, stinging, and burning between the toes; itching, stinging, and burning on the soles of the feet; itchy blisters; cracking and peeling skin, especially between the toes and on the soles of the feet; excessive dryness of the skin on the bottoms or sides of the feet; and/or to ...
Z-mapp - Moodle Lille 2
... Ebola can only be spread to • Fever fatigue • Muscle pain others after symptoms • Headache begin. • Sore throat ...
... Ebola can only be spread to • Fever fatigue • Muscle pain others after symptoms • Headache begin. • Sore throat ...
Document
... the number of infected patients, and asymptomatic carriers can serve as the reservoir for spread to other patients. AST is used to identify patients who are carriers of these target pathogens so that these patients can be isolated from noncarriers and, in some situations, can undergo decolonization ...
... the number of infected patients, and asymptomatic carriers can serve as the reservoir for spread to other patients. AST is used to identify patients who are carriers of these target pathogens so that these patients can be isolated from noncarriers and, in some situations, can undergo decolonization ...
14239-51880-2-ED - Saudi Medical Journal
... Trichosporon spp. with the lungs being the most commonly affected organs. The lower respiratory tract was involved as a single site or as one of multiple organ involvement. Following Rhizopus spp., the most prevalent isolated non-Aspergillus molds were Scedosporium spp., Paecilomyces spp., and Geosm ...
... Trichosporon spp. with the lungs being the most commonly affected organs. The lower respiratory tract was involved as a single site or as one of multiple organ involvement. Following Rhizopus spp., the most prevalent isolated non-Aspergillus molds were Scedosporium spp., Paecilomyces spp., and Geosm ...
Human immunodeficiency virus infection in Saudi
... were tested for confirmation using the strip immunoblot assay, which is intended for use in the confirmation of specimens found to be repeatedly reactive using a MEIA. Anti-HIV reactivity in a specimen was determined by comparing the intensity of each antigen band to the intensity of the human immun ...
... were tested for confirmation using the strip immunoblot assay, which is intended for use in the confirmation of specimens found to be repeatedly reactive using a MEIA. Anti-HIV reactivity in a specimen was determined by comparing the intensity of each antigen band to the intensity of the human immun ...
Bonewit-West: Clinical Procedures for Medical Assistants, 8th
... 2. Not all invading pathogens are able to cause disease 3. Body attempts to stop the invasion a. Uses second line of defense mechanisms Inflammation: - Purpose of inflammation ...
... 2. Not all invading pathogens are able to cause disease 3. Body attempts to stop the invasion a. Uses second line of defense mechanisms Inflammation: - Purpose of inflammation ...
Reporting Incidence of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome
... H5N1 and other avian flus were already a concern, and these reports led WHO to activate its Global Pandemic Preparedness Plan. This warns governments of likely cross-border spread of highly infectious diseases and includes procedures for requesting and receiving assistance from WHO or a member state ...
... H5N1 and other avian flus were already a concern, and these reports led WHO to activate its Global Pandemic Preparedness Plan. This warns governments of likely cross-border spread of highly infectious diseases and includes procedures for requesting and receiving assistance from WHO or a member state ...
Chagas Disease, Human African Trypanosomiasis, and Hookworms
... prevalent in infected children and are associated with a worse prognosis Approximately 2-8% of infected children die from acute Chagas disease In most people, the acute symptoms resolve within 2-4 months ...
... prevalent in infected children and are associated with a worse prognosis Approximately 2-8% of infected children die from acute Chagas disease In most people, the acute symptoms resolve within 2-4 months ...
MICR 454L - Cal State LA - Instructional Web Server
... Three groups which share a common structure and mode of replication, but differ serologically based on M and NP antigens ...
... Three groups which share a common structure and mode of replication, but differ serologically based on M and NP antigens ...
Role of Neutrophils in Dengue Patients: Clearance of Dengue Virus
... activate platelets causing platelet dysfunctions and thrombocytopenia, a hallmark of severe dengue disease. Activated platelet-neutrophil interactions have been well established, and yet its role in the pathogenic cause of dengue remains poorly understood. Forty seven acute dengue confirmed patients ...
... activate platelets causing platelet dysfunctions and thrombocytopenia, a hallmark of severe dengue disease. Activated platelet-neutrophil interactions have been well established, and yet its role in the pathogenic cause of dengue remains poorly understood. Forty seven acute dengue confirmed patients ...
Infection Control and Preventions
... Precautions are used for those infections that are transmitted through the air after being expelled. The particles are so small that they attach to moisture in the air. Diseases consist of: Tuberculosis, Chickenpox and Measles. Prevention: standard, wear respiratory protection, patient may be in ...
... Precautions are used for those infections that are transmitted through the air after being expelled. The particles are so small that they attach to moisture in the air. Diseases consist of: Tuberculosis, Chickenpox and Measles. Prevention: standard, wear respiratory protection, patient may be in ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.