Functional Neutropenia
... These patients should receive initial oral or IV empirical antibiotic doses in a clinic or hospital setting; They may be transitioned to outpatient oral or IV treatment if they meet specific clinical criteria (Changing to the oral regimen is recommended when they become afebrile after 3 days of trea ...
... These patients should receive initial oral or IV empirical antibiotic doses in a clinic or hospital setting; They may be transitioned to outpatient oral or IV treatment if they meet specific clinical criteria (Changing to the oral regimen is recommended when they become afebrile after 3 days of trea ...
Role of Neutrophils in Dengue Patients: Clearance of Dengue Virus
... activate platelets causing platelet dysfunctions and thrombocytopenia, a hallmark of severe dengue disease. Activated platelet-neutrophil interactions have been well established, and yet its role in the pathogenic cause of dengue remains poorly understood. Forty seven acute dengue confirmed patients ...
... activate platelets causing platelet dysfunctions and thrombocytopenia, a hallmark of severe dengue disease. Activated platelet-neutrophil interactions have been well established, and yet its role in the pathogenic cause of dengue remains poorly understood. Forty seven acute dengue confirmed patients ...
PRE TEST - cloudfront.net
... 12. Sharing clothes will not put someone at risk for getting pubic lice (crabs). 13. Syphilis has various stages. 14. All STD’s can be cured with antibiotics. 15. A viral STD can be cured. 16. Chlamydia is one of the most common STD’s. 17. As long as you don’t see the Herpes blisters on a person, a ...
... 12. Sharing clothes will not put someone at risk for getting pubic lice (crabs). 13. Syphilis has various stages. 14. All STD’s can be cured with antibiotics. 15. A viral STD can be cured. 16. Chlamydia is one of the most common STD’s. 17. As long as you don’t see the Herpes blisters on a person, a ...
Outbreak Management Checklist
... Factors to be considered in the decision to convene an OCT include: (a) the type of communicable disease involved - In the case of possible healthcare associated transmission of a blood borne virus a critical incident team should be set up - see guidelines at http://www.health.qld.gov.au/chrisp/ic_g ...
... Factors to be considered in the decision to convene an OCT include: (a) the type of communicable disease involved - In the case of possible healthcare associated transmission of a blood borne virus a critical incident team should be set up - see guidelines at http://www.health.qld.gov.au/chrisp/ic_g ...
`Fusion strategy` may
... the toxins scientists call “heat-stable enterotoxins” that are generally harmful to animals and people and remain active even in at the temperature of boiling water. Zhang said heat-stable enterotoxins can’t be used directly as a vaccine component because of their toxicity and because they are poor ...
... the toxins scientists call “heat-stable enterotoxins” that are generally harmful to animals and people and remain active even in at the temperature of boiling water. Zhang said heat-stable enterotoxins can’t be used directly as a vaccine component because of their toxicity and because they are poor ...
Gompf's ID Pearls 3.0
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication, or the logo, may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Electronic or prin ...
... All rights reserved. No part of this publication, or the logo, may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopy, recording, or any information storage and retrieval system, without permission in writing from the publisher. Electronic or prin ...
bacterial_infection_of_the_kidney
... some type of energy or sound wave (procedures known as “lithotripsy”) for cases with kidney stones (known as “nephroliths”) • Infected kidney stones (nephroliths)—surgically remove, medically dissolve (for struvite kidney stones), or fragment by extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy a medical proced ...
... some type of energy or sound wave (procedures known as “lithotripsy”) for cases with kidney stones (known as “nephroliths”) • Infected kidney stones (nephroliths)—surgically remove, medically dissolve (for struvite kidney stones), or fragment by extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy a medical proced ...
Lecture 01. Infectious diseases with exanthema syndrome
... Infectious diseases with exanthema syndrome ...
... Infectious diseases with exanthema syndrome ...
Emerging and re-emerging viral diseases
... infections [16]. We have however, limited knowledge of such zoonosis and the diversity of these pathogens in their known reservoirs. Nevertheless, while there is little information on some of the domestic animals hosting a few dozen virus species, we have insufficient data on wild mammals that harbo ...
... infections [16]. We have however, limited knowledge of such zoonosis and the diversity of these pathogens in their known reservoirs. Nevertheless, while there is little information on some of the domestic animals hosting a few dozen virus species, we have insufficient data on wild mammals that harbo ...
Viral avoidance and exploitation of the ubiquitin system
... Karposi‘s sarcoma associated herpesvirus: ...
... Karposi‘s sarcoma associated herpesvirus: ...
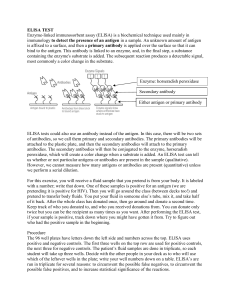
7a ELISA Test
... peroxidase, which will create a color change when a substrate is added. An ELISA test can tell us whether or not particular antigens or antibodies are present in the sample (qualitative). However, we cannot measure how many antigens or antibodies are present (quantitative) unless we perform a serial ...
... peroxidase, which will create a color change when a substrate is added. An ELISA test can tell us whether or not particular antigens or antibodies are present in the sample (qualitative). However, we cannot measure how many antigens or antibodies are present (quantitative) unless we perform a serial ...
Small pox
... Antiviral drugs are medicines that cure or control virus infections. 4) What does the drug Cidofovir bond to in the virus it is attacking? It bonds to the DNA in the virus. Cidofovir is a modified derivative of cytosine, which bonds to the DNA through hydrogen bonding during replication. If the Cido ...
... Antiviral drugs are medicines that cure or control virus infections. 4) What does the drug Cidofovir bond to in the virus it is attacking? It bonds to the DNA in the virus. Cidofovir is a modified derivative of cytosine, which bonds to the DNA through hydrogen bonding during replication. If the Cido ...
The challenges of modelling antibody repertoire dynamics in HIV
... set-point viral load (figure 1). The virus in the acute stage of an infection caused by sexual transmission is largely homogeneous and the mutations that occur in the viral population in these early stages appear to be random [14,15]. Indeed, there is little selection pressure exerted on the virus, ...
... set-point viral load (figure 1). The virus in the acute stage of an infection caused by sexual transmission is largely homogeneous and the mutations that occur in the viral population in these early stages appear to be random [14,15]. Indeed, there is little selection pressure exerted on the virus, ...
Pigeon Fever and Strangles - Brazos Valley Equine Hospital
... both living and dead DNA and should be confirmed with culture. In a single individual case, culture is most likely adequate for diagnosis. In a herd situation, identification of animals shedding Strep equi is important to limit the outbreak. In such cases PCR is critical to identifying the asymptoma ...
... both living and dead DNA and should be confirmed with culture. In a single individual case, culture is most likely adequate for diagnosis. In a herd situation, identification of animals shedding Strep equi is important to limit the outbreak. In such cases PCR is critical to identifying the asymptoma ...
Lecture 9
... – Does not pose danger of real infection – Immuno-compromised individuals can get infection from carrier ...
... – Does not pose danger of real infection – Immuno-compromised individuals can get infection from carrier ...
Document
... Background • The frequency of mixed infection in HCV monoinfection is about 213% (Schroter et al. 2003; Qian et al. 2000) • There is a single study on viral infections with different genotypes in HIV/HCV coinfected patients and has not been evaluated the performance of the genotype during the anti- ...
... Background • The frequency of mixed infection in HCV monoinfection is about 213% (Schroter et al. 2003; Qian et al. 2000) • There is a single study on viral infections with different genotypes in HIV/HCV coinfected patients and has not been evaluated the performance of the genotype during the anti- ...
Vaccine-preventable diseases and immunisation
... usually not necessary. However, workers with significant occupational risk of exposure to hepatitis B should have a blood test four to eight weeks after completing their course of vaccination to confirm that they have adequate protection. Workers who fail to respond to hepatitis B vaccination may ga ...
... usually not necessary. However, workers with significant occupational risk of exposure to hepatitis B should have a blood test four to eight weeks after completing their course of vaccination to confirm that they have adequate protection. Workers who fail to respond to hepatitis B vaccination may ga ...
Vaccines: Essential Weapons in the Fight Against Disease
... of whom were healthy and vibrant before an infectious disease led them to their graves. Fortunately, that world no longer exists because of tremendous progress made in vaccine development and application. There are now more than two dozen vaccines that can prevent death or disability from infectious ...
... of whom were healthy and vibrant before an infectious disease led them to their graves. Fortunately, that world no longer exists because of tremendous progress made in vaccine development and application. There are now more than two dozen vaccines that can prevent death or disability from infectious ...
MUSC Student Pre-Matriculation Requirements
... coursework. Unvaccinated students should initiate the hepatitis B vaccine series prior to or during their first semester at MUSC. Previously immunized students must provide proof of the primary hepatitis B series (3 vaccines) AND a Quantitative Hepatitis B surface Antibody titer (preferably drawn 4- ...
... coursework. Unvaccinated students should initiate the hepatitis B vaccine series prior to or during their first semester at MUSC. Previously immunized students must provide proof of the primary hepatitis B series (3 vaccines) AND a Quantitative Hepatitis B surface Antibody titer (preferably drawn 4- ...
Chapter 14: Principles of Disease
... Nosocomial infections are the 8th leading cause of death in the United States! So why are hospitals such dangerous reservoirs of infection? ...
... Nosocomial infections are the 8th leading cause of death in the United States! So why are hospitals such dangerous reservoirs of infection? ...
Basic Disease Investigation in Colorado
... causing you feel so bad? Well, it's likely that your symptoms were due to one of many different types of viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi or other microbes that live in our environment. In this chapter, you will learn about the different characteristics of disease causing agents. Another term for ...
... causing you feel so bad? Well, it's likely that your symptoms were due to one of many different types of viruses, bacteria, parasites, fungi or other microbes that live in our environment. In this chapter, you will learn about the different characteristics of disease causing agents. Another term for ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.