The role of hyperparasitism in microbial pathogen ecology
... are fundamentally different to those in predator– prey relationships. First, the population biology and evolutionary potential of parasites differ from predators because they are smaller, often more numerous than their host, have shorter generation time than their host, and are often dependent upon ...
... are fundamentally different to those in predator– prey relationships. First, the population biology and evolutionary potential of parasites differ from predators because they are smaller, often more numerous than their host, have shorter generation time than their host, and are often dependent upon ...
Smallpox Chapter (Pink Book)
... second viremia begins about 8–10 days after infection and is followed by the first symptoms of illness (prodromal stage), fever and toxemia. The virus localizes in small blood vessels of the dermis and in the oral and pharyngeal mucosa. In the skin, this results in the characteristic maculopapular r ...
... second viremia begins about 8–10 days after infection and is followed by the first symptoms of illness (prodromal stage), fever and toxemia. The virus localizes in small blood vessels of the dermis and in the oral and pharyngeal mucosa. In the skin, this results in the characteristic maculopapular r ...
Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathy as a Zoonotic Disease
... its wool, and the areas of wool loss may sometimes be rubbed raw (scrapie acquired its name from the fact that sheep were observed to scrape themselves against fixed objects). Some sheep will pull wool from their sides or bite at their legs or exhibit a “nibble reflex” when rubbing themselves or whe ...
... its wool, and the areas of wool loss may sometimes be rubbed raw (scrapie acquired its name from the fact that sheep were observed to scrape themselves against fixed objects). Some sheep will pull wool from their sides or bite at their legs or exhibit a “nibble reflex” when rubbing themselves or whe ...
Role of tumour necrosis factor (TNF)
... TB immunity. For example, TNF increases the phagocytic ability of macrophages and enhances the killing of mycobacteria, particularly in concert with interferon γ.18 TNF may also deprive mycobacteria of their intracellular sanctuary by inducing apoptosis of permissive macrophages.19 20 On the other h ...
... TB immunity. For example, TNF increases the phagocytic ability of macrophages and enhances the killing of mycobacteria, particularly in concert with interferon γ.18 TNF may also deprive mycobacteria of their intracellular sanctuary by inducing apoptosis of permissive macrophages.19 20 On the other h ...
SARS - tfss-g4p
... for the plague to spread from Asia to the western reaches of Europe. In perspective, the SARS virus, crossed from Hong Kong to Toronto in about 15 hours • A socio-ethical issue also refers to the privacy of one’s information versus the public need to know • The social impact of releasing confidentia ...
... for the plague to spread from Asia to the western reaches of Europe. In perspective, the SARS virus, crossed from Hong Kong to Toronto in about 15 hours • A socio-ethical issue also refers to the privacy of one’s information versus the public need to know • The social impact of releasing confidentia ...
The diagnostic role of Saliva — A Review.
... correlated with serum antibody levels (15). Salivary IgA levels to HIV decline as infected patients become symptomatic. It was suggested that detection of IgA antibody to HIV in saliva may, therefore, be a prognostic indicator for the progression of HIV infection . Analysis of antibody in saliva as ...
... correlated with serum antibody levels (15). Salivary IgA levels to HIV decline as infected patients become symptomatic. It was suggested that detection of IgA antibody to HIV in saliva may, therefore, be a prognostic indicator for the progression of HIV infection . Analysis of antibody in saliva as ...
Meningococcal Conjugate Vaccines Policy Update: Booster Dose
... Asplenic people achieve significantly lower geometric mean serum bactericidal activity than do healthy people immunized with monovalent meningococcal C conjugate vaccine. In 1 study, a protective antibody concentration was not achieved in 20% of asplenic people after vaccination.20 However, the perce ...
... Asplenic people achieve significantly lower geometric mean serum bactericidal activity than do healthy people immunized with monovalent meningococcal C conjugate vaccine. In 1 study, a protective antibody concentration was not achieved in 20% of asplenic people after vaccination.20 However, the perce ...
Biological Feasibility of Measles Eradication
... diagnosis. The detection of measles virus-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies in a single specimen of serum or oral fluid is considered diagnostic of acute infection, as is a 4-fold or greater increase in measles virus-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies between acute and convalescent ...
... diagnosis. The detection of measles virus-specific immunoglobulin M (IgM) antibodies in a single specimen of serum or oral fluid is considered diagnostic of acute infection, as is a 4-fold or greater increase in measles virus-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies between acute and convalescent ...
Antibodies to Chlamydia trachomatis heat shock proteins in women
... The risk of infertility increases after repeated episodes of salpingitis (Weström, 1980). Infertility after salpingitis is due to occlusion of the Fallopian tubes by fibrous scarring. Such scarring may occur as the result of an immunopathological response after chronic or recurrent infection by C. ...
... The risk of infertility increases after repeated episodes of salpingitis (Weström, 1980). Infertility after salpingitis is due to occlusion of the Fallopian tubes by fibrous scarring. Such scarring may occur as the result of an immunopathological response after chronic or recurrent infection by C. ...
Bacteria – host interplay in Staphylococcus aureus infections
... Infectious diseases plagued humankind all through the history [1]. Only during the last decades and in the western countries, infectious diseases ceased to be the main cause of death, replaced by cancer and cardiovascular diseases [2]. However, infections still remain amongst the leading causes of d ...
... Infectious diseases plagued humankind all through the history [1]. Only during the last decades and in the western countries, infectious diseases ceased to be the main cause of death, replaced by cancer and cardiovascular diseases [2]. However, infections still remain amongst the leading causes of d ...
Employee Power Point presentation template
... Experts believe another pandemic is inevitable - but they are unable to predict when it will occur. ...
... Experts believe another pandemic is inevitable - but they are unable to predict when it will occur. ...
Vaccine Epidemiology - Hospital Industry Data Institute
... to measure vaccine effectiveness is the “indirect cohort” or “quasi-cohort” study, in which different responses in the same vaccinated population are examined [8]. For example, an analysis of the vaccine effectiveness of pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine examined all invasive pneumococcal disease ...
... to measure vaccine effectiveness is the “indirect cohort” or “quasi-cohort” study, in which different responses in the same vaccinated population are examined [8]. For example, an analysis of the vaccine effectiveness of pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine examined all invasive pneumococcal disease ...
Epidemiology of Seafood-Associated Infections in the United States
... endemic and epidemic forms. Most cases occur among children aged ⬍10 years. Humans are the primary reservoir of Shigella. Transmission occurs through direct or indirect contact with feces of infected persons. Shigella infection is highly communicable, because ingestion of as few as 10 viable organis ...
... endemic and epidemic forms. Most cases occur among children aged ⬍10 years. Humans are the primary reservoir of Shigella. Transmission occurs through direct or indirect contact with feces of infected persons. Shigella infection is highly communicable, because ingestion of as few as 10 viable organis ...
Principal Investigator/Program Director (Last, First, Middle): Halonen
... and phosphatases that are differentially regulated during parasite infection and explore how these host cell changes are altered by the parasites of distinct virulent phenotypes. Model of Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in Human Neuronal Cells P.I.: Sandra K. Halonen Agency: NIH-NIMH Type: R01 (Anticipated S ...
... and phosphatases that are differentially regulated during parasite infection and explore how these host cell changes are altered by the parasites of distinct virulent phenotypes. Model of Cerebral Toxoplasmosis in Human Neuronal Cells P.I.: Sandra K. Halonen Agency: NIH-NIMH Type: R01 (Anticipated S ...
Experimental Transmission of Infectious Pancreatic Necrosis Virus
... disinfected and then rinsed in ASW, and each mussel was placed in individual tanks containing clean 0.5 liter of ASW and algae. At 24-h intervals of depuration, feces and pseudofeces (collectively referred to as fecal matter) and 5-ml water samples were collected from each tank, and the mussels were ...
... disinfected and then rinsed in ASW, and each mussel was placed in individual tanks containing clean 0.5 liter of ASW and algae. At 24-h intervals of depuration, feces and pseudofeces (collectively referred to as fecal matter) and 5-ml water samples were collected from each tank, and the mussels were ...
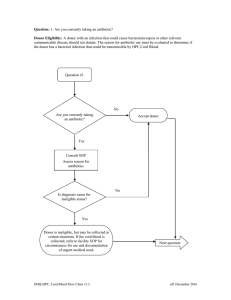
Cord Blood Flowchart
... Question: 14. In the past 12 months have you had sexual contact with anyone who has ever used needles to take drugs or steroids, or anything not prescribed by their doctor? Donor Eligibility: Persons who have had sexual contact with persons who have used needles to take drugs, steroids, or anything ...
... Question: 14. In the past 12 months have you had sexual contact with anyone who has ever used needles to take drugs or steroids, or anything not prescribed by their doctor? Donor Eligibility: Persons who have had sexual contact with persons who have used needles to take drugs, steroids, or anything ...
Bacillus anthracis and anthrax
... In humans, anthrax is fairly rare; the risk of infection is about 1/100,000. The most common form of the disease in humans is cutaneous anthrax, which is usually acquired via injured skin or mucous membranes. A minor scratch or abrasion, usually on an exposed area of the face or neck or arms, is ino ...
... In humans, anthrax is fairly rare; the risk of infection is about 1/100,000. The most common form of the disease in humans is cutaneous anthrax, which is usually acquired via injured skin or mucous membranes. A minor scratch or abrasion, usually on an exposed area of the face or neck or arms, is ino ...
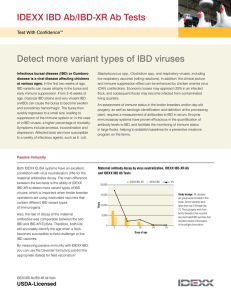
IBD Ab/IBD-XR Ab Tests Information Sheet
... Staphylococcus spp., Clostridium spp., and respiratory viruses, including live respiratory vaccines (rolling reactions). In addition, the clinical picture and immune suppression effect can be enhanced by chicken anemia virus (CAV) coinfections. Economic losses may approach 20% in an infected flock, ...
... Staphylococcus spp., Clostridium spp., and respiratory viruses, including live respiratory vaccines (rolling reactions). In addition, the clinical picture and immune suppression effect can be enhanced by chicken anemia virus (CAV) coinfections. Economic losses may approach 20% in an infected flock, ...
standard operating procedure for transport of biological specimens
... materials are infectious substances, biological products, cultures, genetically modified organism (GMO) or exempt substances. The requirements of various regulatory bodies are based on the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods Model Regulations which are adopted by Inter ...
... materials are infectious substances, biological products, cultures, genetically modified organism (GMO) or exempt substances. The requirements of various regulatory bodies are based on the United Nations Recommendations on the Transport of Dangerous Goods Model Regulations which are adopted by Inter ...
Rubella Clinical Signs and Symptoms
... Rubella Rubella (German measles) is an infectious acute viral disease resulting from infection with rubella virus. Rubella is transmitted via respiratory droplets, or direct contact with nasal/throat secretions, from infected individuals. The incubation period is 12-23 days, usually14 days until ap ...
... Rubella Rubella (German measles) is an infectious acute viral disease resulting from infection with rubella virus. Rubella is transmitted via respiratory droplets, or direct contact with nasal/throat secretions, from infected individuals. The incubation period is 12-23 days, usually14 days until ap ...
Wednesday evening poster session – 5
... Chagas parasite strain TcI predominates in the main insect vector, Triatoma dimidiata, from Mexico through Central America Exploitation of ecological traps for mosquito control Fine-scale spatial variation in host resistance, parasite infectivity, and disease Disease dynamics on wildlife contact net ...
... Chagas parasite strain TcI predominates in the main insect vector, Triatoma dimidiata, from Mexico through Central America Exploitation of ecological traps for mosquito control Fine-scale spatial variation in host resistance, parasite infectivity, and disease Disease dynamics on wildlife contact net ...
mumps - Mitch Horn
... to those who are non-immune. A case is infectious from 2 days before onset of rash until all lesions are crusted and no new lesions are appearing (5-7 days after onset of rash). If possible postpone hospital visits during this time. The incubation period (time from exposure to the infection until de ...
... to those who are non-immune. A case is infectious from 2 days before onset of rash until all lesions are crusted and no new lesions are appearing (5-7 days after onset of rash). If possible postpone hospital visits during this time. The incubation period (time from exposure to the infection until de ...
$doc.title
... compared the genetic diversification of three important genes of the virus, gag that encodes the viral structural proteins, and two pol genes, the protease that is essential for the maturation and ...
... compared the genetic diversification of three important genes of the virus, gag that encodes the viral structural proteins, and two pol genes, the protease that is essential for the maturation and ...
Infectious Diseases : a Clinical Short Course
... high school and college athletes. Extensively drugresistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) has resulted in near 100% mortality in an outbreak in South Africa. Newly discovered infectious diseases such as SARS, Avian Influenza, Ehrlichia, Lyme Disease, and West Nile Encephalitis are emerging as threats to our ...
... high school and college athletes. Extensively drugresistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB) has resulted in near 100% mortality in an outbreak in South Africa. Newly discovered infectious diseases such as SARS, Avian Influenza, Ehrlichia, Lyme Disease, and West Nile Encephalitis are emerging as threats to our ...
Morning Report
... 54 y/o AAM with hx of syphillis, htn, OSA and Langerhans Cell Sarcoma with spinal cord compression s/p steroids and XRT now c/o pain and difficulty upon swallowing. Pt was originally admitted on 11/18 to MICU for spinal chord compression, treated with decadron (11/18 to 12/05) and transferred to GME ...
... 54 y/o AAM with hx of syphillis, htn, OSA and Langerhans Cell Sarcoma with spinal cord compression s/p steroids and XRT now c/o pain and difficulty upon swallowing. Pt was originally admitted on 11/18 to MICU for spinal chord compression, treated with decadron (11/18 to 12/05) and transferred to GME ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.