* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rubella Clinical Signs and Symptoms
Lyme disease wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Meningococcal disease wikipedia , lookup
Neonatal infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Rocky Mountain spotted fever wikipedia , lookup
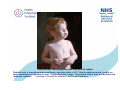
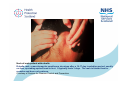
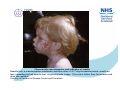
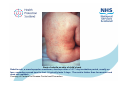
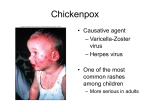
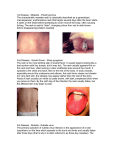
Rubella Clinical Signs and Symptoms Rubella Rubella (German measles) is an infectious acute viral disease resulting from infection with rubella virus. Rubella is transmitted via respiratory droplets, or direct contact with nasal/throat secretions, from infected individuals. The incubation period is 12-23 days, usually14 days until appearance of rash. Individuals may be infectious 7 days before to 14 days after rash onset. Rubella The EU clinical case definition for rubella is: Clinical picture compatible with rubella, e.g. acute onset of generalized maculopapular rash and arthralgia/arthritis, lymphadenopathy, or conjunctivitis. Rubella Clinical course of infection Rubella is generally a mild illness Rubella rash, a maculopapular exanthema, develops after a 14-17 day incubation period, usually on face, spreading spread head to foot. It typically lasts 3 days. The rash is fainter than for measles and does not coalesce. A prodromal illness of fever, malaise, lymphadenopathy, and upper respiratory symptoms may precede rash, in older children and adults, but is usually absent in younger children. Arthralgia and Arthritis occur frequently in adult women (70%). Up to 50% of rubella cases may be sub-clinical or assymptomatic. Rubella complications • Encephalitis (1 in 6000) • Immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP; Condition affecting blood clotting) (1 in 3000) Birth defects • Major birth defects, affecting all vital organs, highly likely if rubella acquired in early pregnancy. • These include learning difficulties, cataracts, deafness, cardiac abnormalities, retardation of intrauterine growth and inflammation of lesions of brain, liver, lungs and bone marrow. • Maternal rubella in first 10 weeks pregnancy result in fetal damage for up to 90% infants, and multiple defects common (Congenital Rubella Syndrome). Risk of damage declines to 10-20% by 16 weeks. Rubella between 16-20 weeks carries minimal risk of deafness only. Characteristic maculopapular rash indicative of rubella Rubella rash, a maculopapular exanthema, develops after a 14-17 day incubation period, usually on face, spreading spread head to foot. It typically lasts 3 days. The rash is fainter than for measles and does not coalesce. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Patient with face rash due to rubella Rubella rash, a maculopapular exanthema, develops after a 14-17 day incubation period, usually on face, spreading spread head to foot. It typically lasts 3 days. The rash is fainter than for measles and does not coalesce. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Neck of male patient with rubella Rubella rash, a maculopapular exanthema, develops after a 14-17 day incubation period, usually on face, spreading spread head to foot. It typically lasts 3 days. The rash is fainter than for measles and does not coalesce. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Characteristic maculopapular rash indicative of rubella Rubella rash, a maculopapular exanthema, develops after a 14-17 day incubation period, usually on face, spreading spread head to foot. It typically lasts 3 days. The rash is fainter than for measles and does not coalesce. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Rash of rubella on skin of child's back Rubella rash, a maculopapular exanthema, develops after a 14-17 day incubation period, usually on face, spreading spread head to foot. It typically lasts 3 days. The rash is fainter than for measles and does not coalesce. Courtesy of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention