Large differences between test strategies for the detection of anti
... Third, a mismatch between immunoblot and ELISA may occur during the early phase of infection. There are numerous examples – from this and other studies – in which patients with early Lyme disease were initially ELISA-positive and blot-negative [11]. In such cases, immunoblot seroconversion can only ...
... Third, a mismatch between immunoblot and ELISA may occur during the early phase of infection. There are numerous examples – from this and other studies – in which patients with early Lyme disease were initially ELISA-positive and blot-negative [11]. In such cases, immunoblot seroconversion can only ...
Vaccine Developing Countries Vaccine Manufacturers Network
... Diseases (Xiamen University). Hepatitis E is a waterborne disease, transmitted from person to person via the fecal-oral route, with epidemics reported in Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Central America. According to the WHO, one third of the global population may have been infected by the virus. ...
... Diseases (Xiamen University). Hepatitis E is a waterborne disease, transmitted from person to person via the fecal-oral route, with epidemics reported in Asia, the Middle East, Africa, and Central America. According to the WHO, one third of the global population may have been infected by the virus. ...
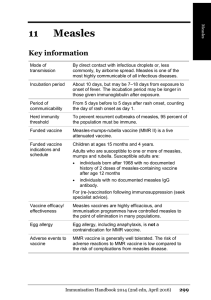
11 Measles - Ministry of Health
... vaccine). They will have therefore received the recommended two doses of measles, but only one of mumps and rubella. While the main reason for a two-dose MMR schedule is to protect against measles, two doses of all three antigens is recommended and funded. These individuals can receive a second dose ...
... vaccine). They will have therefore received the recommended two doses of measles, but only one of mumps and rubella. While the main reason for a two-dose MMR schedule is to protect against measles, two doses of all three antigens is recommended and funded. These individuals can receive a second dose ...
Bacillus anthracis (Anthrax)
... therapy should be coupled with treatment with raxibacumab, a monocolonal antibody that targets an anthrax antigen.9 Naturally occurring cutaneous anthrax is typically treated with antibiotics for 7 to 10 days. However, in an aerosol bioterrorism attack, patients with cutaneous anthrax may also have ...
... therapy should be coupled with treatment with raxibacumab, a monocolonal antibody that targets an anthrax antigen.9 Naturally occurring cutaneous anthrax is typically treated with antibiotics for 7 to 10 days. However, in an aerosol bioterrorism attack, patients with cutaneous anthrax may also have ...
What are the symptoms of Pandemic Flu and what
... Yes. This novel influenza strain did not originate in pigs but has genetic material from a number of strains including, swine, avian and human influenza. It is unfortunate and inaccurate that the label swine flu was attached to this novel Influenza virus strain. The World Health Organisation say the ...
... Yes. This novel influenza strain did not originate in pigs but has genetic material from a number of strains including, swine, avian and human influenza. It is unfortunate and inaccurate that the label swine flu was attached to this novel Influenza virus strain. The World Health Organisation say the ...
- International Journal of Infectious Diseases
... (Meningitis Vaccine Project, www.meningvax.org) promises a substantial decrease in meningococcal serogroup A epidemic ...
... (Meningitis Vaccine Project, www.meningvax.org) promises a substantial decrease in meningococcal serogroup A epidemic ...
mycobacterium tuberculosis complex
... skin lesions. Meningitis (high fever, cranial nerve deficits, and psychic changes) develops in 50% of the cases with a high mortality rate, if left untreated ...
... skin lesions. Meningitis (high fever, cranial nerve deficits, and psychic changes) develops in 50% of the cases with a high mortality rate, if left untreated ...
host susceptibility to rotavirus infection and
... Rotavirus infects mature enterocytes of the small intestine of young children and cause gastroenteritis, leading to approximately 500 000 deaths annually worldwide, 85 % of which occur in the developing world. The main objectives of the thesis were to investigate host genetic factors leading to diff ...
... Rotavirus infects mature enterocytes of the small intestine of young children and cause gastroenteritis, leading to approximately 500 000 deaths annually worldwide, 85 % of which occur in the developing world. The main objectives of the thesis were to investigate host genetic factors leading to diff ...
Chlorhexidine: Expanding the Armamentarium for Infection Control
... Whether chlorhexidine baths alone can reduce MRSA infection remains unknown. However, recent evidence suggests that decontaminating ICU patients with daily chlorhexidine baths may reduce transmission of other multidrug-resistant organisms and prevent HAI. Daily bathing of ICU patients with chlorhexi ...
... Whether chlorhexidine baths alone can reduce MRSA infection remains unknown. However, recent evidence suggests that decontaminating ICU patients with daily chlorhexidine baths may reduce transmission of other multidrug-resistant organisms and prevent HAI. Daily bathing of ICU patients with chlorhexi ...
EUROLINE Myositis-Profil 3 (IgG).
... synthetases occur with differing prevalences (anti-Jo-1: 25% to 55 %, anti-PL-7: 3 % to 6 %, anti-PL-12: up to 3 %, anti-EJ: 1 % , anti-OJ: 1 %) in myositis patients and are often associated with other, simultaneously occurring autoimmune diseases (e.g. SLE, SSc or interstitial lung fibrosis). Antib ...
... synthetases occur with differing prevalences (anti-Jo-1: 25% to 55 %, anti-PL-7: 3 % to 6 %, anti-PL-12: up to 3 %, anti-EJ: 1 % , anti-OJ: 1 %) in myositis patients and are often associated with other, simultaneously occurring autoimmune diseases (e.g. SLE, SSc or interstitial lung fibrosis). Antib ...
Preventing the spread of disease in the EU_02032010
... pestilence won, and shift national resources to such chronic problems as cancer and heart disease". The last 40 years have shown that this optimism was misplaced; infectious diseases are a continuing and significant burden on the health and prosperity of the global community, not only in the develop ...
... pestilence won, and shift national resources to such chronic problems as cancer and heart disease". The last 40 years have shown that this optimism was misplaced; infectious diseases are a continuing and significant burden on the health and prosperity of the global community, not only in the develop ...
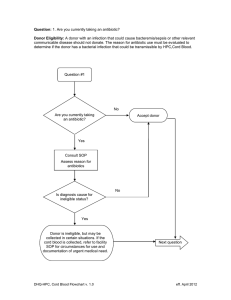
DHQ-HPC-cord-flow-chartsv1-1
... Question: 14. In the past 12 months have you had sexual contact with anyone who has ever used needles to take drugs or steroids, or anything not prescribed by their doctor? Donor Eligibility: Persons who have had sexual contact with persons who have used needles to take drugs, steroids, or anything ...
... Question: 14. In the past 12 months have you had sexual contact with anyone who has ever used needles to take drugs or steroids, or anything not prescribed by their doctor? Donor Eligibility: Persons who have had sexual contact with persons who have used needles to take drugs, steroids, or anything ...
LTBI: latent tuberculosis infection or lasting immune responses to M. tuberculosis?
... summarises knowledge and limitations of the currently available tests used in adults and children for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection. In summary, the main issue regarding testing is to restrict it to those who are known to be at higher risk of developing tuberculosis and who are will ...
... summarises knowledge and limitations of the currently available tests used in adults and children for the diagnosis of latent tuberculosis infection. In summary, the main issue regarding testing is to restrict it to those who are known to be at higher risk of developing tuberculosis and who are will ...
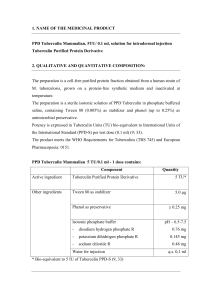
1. NAME OF THE MEDICINAL PRODUCT PPD Tuberculin
... 4.5. Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction Reactivity to the test may be depressed or suppressed for up to 6 weeks in individuals who have had viral infections (rubella, influenza, mumps and probably others) or in those who are receiving corticosteroids or immunosu ...
... 4.5. Interaction with other medicinal products and other forms of interaction Reactivity to the test may be depressed or suppressed for up to 6 weeks in individuals who have had viral infections (rubella, influenza, mumps and probably others) or in those who are receiving corticosteroids or immunosu ...
the Amaral PPT-slides here
... Martins M, Viveiros M, Ramos J, Couto I, Molnar J, Boeree M, Amaral L. SILA 421, an inhibitor of efflux pumps of cancer cells, enhances the killing of intracellular extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB). Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;33:479-82 ...
... Martins M, Viveiros M, Ramos J, Couto I, Molnar J, Boeree M, Amaral L. SILA 421, an inhibitor of efflux pumps of cancer cells, enhances the killing of intracellular extensively drug-resistant tuberculosis (XDR-TB). Int J Antimicrob Agents. 2009;33:479-82 ...
4 Risk reviews - Department of Agriculture and Water Resources
... vector-borne hazard of biosecurity concern when imported. However this policy review recommends that PAQ remains a necessary biosecurity measure, with a minimum PAQ period of 10 days to apply for both dogs and cats. Ten days in quarantine is a significant reduction from the minimum PAQ period of 30 ...
... vector-borne hazard of biosecurity concern when imported. However this policy review recommends that PAQ remains a necessary biosecurity measure, with a minimum PAQ period of 10 days to apply for both dogs and cats. Ten days in quarantine is a significant reduction from the minimum PAQ period of 30 ...
Synthetic peptides from four separate regions of the poliovirus type 1
... The ability of sera raised against VP1 to react with peptides was also assessed (Fig. 3C). Peptides 5, 7, 8, and 9 were specifically recognized, and these reactions were competitively blocked by the addition of isolated VP1. Neutralization Activity of Anti-Peptide Antisera. The ability of the anti-p ...
... The ability of sera raised against VP1 to react with peptides was also assessed (Fig. 3C). Peptides 5, 7, 8, and 9 were specifically recognized, and these reactions were competitively blocked by the addition of isolated VP1. Neutralization Activity of Anti-Peptide Antisera. The ability of the anti-p ...
SOP: Lentivirus Usage - Environmental Health and Safety
... 2.2.1 Replication-Deficient Lentiviral Vectors: Certain lentiviral vectors are designed to be less pathogenic than wild-type lentiviruses due in part to the separation of genes required for packaging of viral particles onto several plasmids, replacement of the native lentiviral envelope protein, and ...
... 2.2.1 Replication-Deficient Lentiviral Vectors: Certain lentiviral vectors are designed to be less pathogenic than wild-type lentiviruses due in part to the separation of genes required for packaging of viral particles onto several plasmids, replacement of the native lentiviral envelope protein, and ...
Australian Immunisation Handbook, 8th Edition Part 3: Vaccines
... The cutaneous form of the disease starts as a small papule, which develops into a characteristic painless skin ulcer (eschar) surrounded by significant oedema. Patients are generally toxic and there may be local lymphadenitis. Without appropriate treatment 10 to 20% percent of persons contracting cu ...
... The cutaneous form of the disease starts as a small papule, which develops into a characteristic painless skin ulcer (eschar) surrounded by significant oedema. Patients are generally toxic and there may be local lymphadenitis. Without appropriate treatment 10 to 20% percent of persons contracting cu ...
Melioidosis: an important emerging infectious disease — a military
... Air Vice-Marshal Bruce Short is the Surgeon General ADF. He is in private practice as a specialist general physician in Sydney. ...
... Air Vice-Marshal Bruce Short is the Surgeon General ADF. He is in private practice as a specialist general physician in Sydney. ...
The Role of Chlorhexidine in Vascular Access
... Milstone, Aaron M., Catherine L. Passaretti and Trish M. Perl. "Healthcare Epidemiology: Chlorhexidine: Expanding the Armamentarium for Infection Control and Prevention." Clinical Infectious Diseases 46.2 (2008): 274-81. Print. Lim, K. S. and P. A. A. Kam. "Chlorhexidine--pharmacology and Clinical A ...
... Milstone, Aaron M., Catherine L. Passaretti and Trish M. Perl. "Healthcare Epidemiology: Chlorhexidine: Expanding the Armamentarium for Infection Control and Prevention." Clinical Infectious Diseases 46.2 (2008): 274-81. Print. Lim, K. S. and P. A. A. Kam. "Chlorhexidine--pharmacology and Clinical A ...
Cytauxzoon felis infections are present in bobcats
... Cytauxzoonosis was first reported in Missouri in 1979 and the disease was only recognized in the south central and southeastern United States for the past 20 years. The geographic distribution of cytauxzoonosis in domestic cats has been recently documented to extend east and northeast of its previou ...
... Cytauxzoonosis was first reported in Missouri in 1979 and the disease was only recognized in the south central and southeastern United States for the past 20 years. The geographic distribution of cytauxzoonosis in domestic cats has been recently documented to extend east and northeast of its previou ...
serologic survey for selected infectious disease agents in raccoons
... the United States (Kaufmann, 1982). Human expansion into rural areas, outdoor recreational activities, and raccoon expansion into urban areas have increased human contact with raccoons and led to greater potential for zoonotic disease transmission. The adaptability of raccoons to human inhabited are ...
... the United States (Kaufmann, 1982). Human expansion into rural areas, outdoor recreational activities, and raccoon expansion into urban areas have increased human contact with raccoons and led to greater potential for zoonotic disease transmission. The adaptability of raccoons to human inhabited are ...
Updated disease risk assessment report
... diseases of cultured salmon in New Zealand. An outbreak of disease in salmon cultured at Waihinau Bay in early 2012 was originally thought to be solely related to suboptimal environmental conditions at that site (MPI 2013). However, subsequent testing has shown diseased fish at that location were al ...
... diseases of cultured salmon in New Zealand. An outbreak of disease in salmon cultured at Waihinau Bay in early 2012 was originally thought to be solely related to suboptimal environmental conditions at that site (MPI 2013). However, subsequent testing has shown diseased fish at that location were al ...
Hepatitis B

Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV) which affects the liver. It can cause both acute and chronic infections. Many people have no symptoms during the initial infection. Some develop a rapid onset of sickness with vomiting, yellowish skin, feeling tired, dark urine and abdominal pain. Often these symptoms last a few weeks and rarely does the initial infection result in death. It may take 30 to 180 days for symptoms to begin. In those who get infected around the time of birth 90% develop chronic hepatitis B while less than 10% of those infected after the age of five do. Most of those with chronic disease have no symptoms; however, cirrhosis and liver cancer may eventually develop. These complications results in the death of 15 to 25% of those with chronic disease.The virus is transmitted by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Infection around the time of birth or from contact with other people's blood during childhood is the most frequent method by which hepatitis B is acquired in areas where the disease is common. In areas where the disease is rare, intravenous drug use and sexual intercourse are the most frequent routes of infection. Other risk factors include working in healthcare, blood transfusions, dialysis, living with an infected person, travel in countries where the infection rate is high, and living in an institution. Tattooing and acupuncture led to a significant number of cases in the 1980s; however, this has become less common with improved sterility. The hepatitis B viruses cannot be spread by holding hands, sharing eating utensils, kissing, hugging, coughing, sneezing, or breastfeeding. The infection can be diagnosed 30 to 60 days after exposure. Diagnosis is typically by testing the blood for parts of the virus and for antibodies against the virus. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The infection has been preventable by vaccination since 1982. Vaccination is recommended by the World Health Organization in the first day of life if possible. Two or three more doses are required at a later time for full effect. This vaccine works about 95% of the time. About 180 countries gave the vaccine as part of national programs as of 2006. It is also recommended that all blood be tested for hepatitis B before transfusion and condoms be used to prevent infection. During an initial infection, care is based on the symptoms that a person has. In those who develop chronic disease antiviral medication such as tenofovir or interferon maybe useful, however these drugs are expensive. Liver transplantation is sometimes used for cirrhosis.About a third of the world population has been infected at one point in their lives, including 240 million to 350 million who have chronic infections. Over 750,000 people die of hepatitis B each year. About 300,000 of these are due to liver cancer. The disease is now only common in East Asia and sub-Saharan Africa where between 5 and 10% of adults have chronic disease. Rates in Europe and North America are less than 1%. It was originally known as serum hepatitis. Research is looking to create foods that contain HBV vaccine. The disease may affect other great apes as well.