Mycoplasma gallisepticum
... chicken embryos or chickens, is occasionally necessary to isolate the organism if these results of other tests are not conclusive; however, animal inoculation has largely been superseded by PCR. Immunological tests to detect antigens are generally not used directly on clinical samples, due to the ve ...
... chicken embryos or chickens, is occasionally necessary to isolate the organism if these results of other tests are not conclusive; however, animal inoculation has largely been superseded by PCR. Immunological tests to detect antigens are generally not used directly on clinical samples, due to the ve ...
Malaria
... surface. However, these antigens are highly polymorphic and undergo clonal antigenic variation, meaning that effective opsonisation (or prevention of iRBC sequestration in blood vessels) may only develop after many and varied malaria infections. Antigens expressed on merozoites are also polymorphic ...
... surface. However, these antigens are highly polymorphic and undergo clonal antigenic variation, meaning that effective opsonisation (or prevention of iRBC sequestration in blood vessels) may only develop after many and varied malaria infections. Antigens expressed on merozoites are also polymorphic ...
Jaundice in the newborn
... Clinical jaundice appear at SB 5 mg/dl 25% to 50% of term newborns have clinical jaundice. Jaundice may caused by serious illness or lead to keriniectrus. 75% of bilirubin comes from haemoglobin and 25% from other sources ...
... Clinical jaundice appear at SB 5 mg/dl 25% to 50% of term newborns have clinical jaundice. Jaundice may caused by serious illness or lead to keriniectrus. 75% of bilirubin comes from haemoglobin and 25% from other sources ...
E. coli infection.
... yolk sac usually is involved, Infection follows contamination of the unhealed navel with virulent strains of E. coli. Fecal contamination of eggs is considered to be the most important source of infection. Bacteria may be acquired in ovo if the hen has or salpingitis or via contamination following ...
... yolk sac usually is involved, Infection follows contamination of the unhealed navel with virulent strains of E. coli. Fecal contamination of eggs is considered to be the most important source of infection. Bacteria may be acquired in ovo if the hen has or salpingitis or via contamination following ...
Autoimmune Hepatitis
... Prednisone and azathioprine regimens have not been compared directly and there is no objective basis for preferring one to the other. ...
... Prednisone and azathioprine regimens have not been compared directly and there is no objective basis for preferring one to the other. ...
his section includes information on sexually transmitted diseases
... Transmission: fecal-oral (ingestion of fecal matter of an infected person, usually through contaminated food or water) Prevention: sanitary infrastructure, food handling regulations, hand washing; immunization Treatment: none, condition generally resolves after acute episode ...
... Transmission: fecal-oral (ingestion of fecal matter of an infected person, usually through contaminated food or water) Prevention: sanitary infrastructure, food handling regulations, hand washing; immunization Treatment: none, condition generally resolves after acute episode ...
Airborne Pathogens
... o Primary infection can remain undetected and the individual may not develop any symptoms of TB. o Usually within 2-10 weeks, an infection can be detected by the TB skin test. o Those with significant skin test reaction but NO symptoms are considered to have TB infection. oThey can NOT spread TB, BU ...
... o Primary infection can remain undetected and the individual may not develop any symptoms of TB. o Usually within 2-10 weeks, an infection can be detected by the TB skin test. o Those with significant skin test reaction but NO symptoms are considered to have TB infection. oThey can NOT spread TB, BU ...
Slide 1
... One of the healthcare workers was a 45-year-old man who got sick on May 2, and is currently in critical condition. The other employee is a 43-year-old woman who got ill on May 8, and is listed in stable condition. The latest confirmed cases provide more evidence of human-to-human transmission of the ...
... One of the healthcare workers was a 45-year-old man who got sick on May 2, and is currently in critical condition. The other employee is a 43-year-old woman who got ill on May 8, and is listed in stable condition. The latest confirmed cases provide more evidence of human-to-human transmission of the ...
Click here for handout
... stiffness, tenosynovitis and Raynaud phenomena. • Severe complications such as meningoencephalitis, cardiopulmonary decompensation, acute renal failure and death have been described with greater frequency among patients older than 65 years and those with underlying chronic medical problems. ...
... stiffness, tenosynovitis and Raynaud phenomena. • Severe complications such as meningoencephalitis, cardiopulmonary decompensation, acute renal failure and death have been described with greater frequency among patients older than 65 years and those with underlying chronic medical problems. ...
Sore Mouth (Orf Virus) - Boston Public Health Commission
... Sore mouth (also known as “scabby mouth”, contagious ecthyma, or orf) is caused by a germ (virus) passed to people from sheep and goats. This disease can cause sores on people’s hands, but not sores around the mouth like it does in animals. It cannot spread from person to person. How is it transmitt ...
... Sore mouth (also known as “scabby mouth”, contagious ecthyma, or orf) is caused by a germ (virus) passed to people from sheep and goats. This disease can cause sores on people’s hands, but not sores around the mouth like it does in animals. It cannot spread from person to person. How is it transmitt ...
Full Text PDF - Jaypee Journals
... Ebola is introduced into the human population through close personal contact with the blood, body secretions or organs of infected animals. It then spreads in the community through person-to-person transmission with infection resulting from direct contact (through broken skin or mucous membranes) wi ...
... Ebola is introduced into the human population through close personal contact with the blood, body secretions or organs of infected animals. It then spreads in the community through person-to-person transmission with infection resulting from direct contact (through broken skin or mucous membranes) wi ...
Clinical features
... coalesce to produce a flushed appearance. The onset of rash is often accompanied by low-grade fever. Although the rash usually lasts 3 to 5 days (hence the term “3-day measles”), the associated fever rarely persists for more than 24 hours. Postnatal rubella usually resolves without complication. How ...
... coalesce to produce a flushed appearance. The onset of rash is often accompanied by low-grade fever. Although the rash usually lasts 3 to 5 days (hence the term “3-day measles”), the associated fever rarely persists for more than 24 hours. Postnatal rubella usually resolves without complication. How ...
Chronic Hepatitis B and Hepatitis C Infection Surveillance
... sexual contact, needle sharing, accidental needle stick, sharing items that may be contaminated with blood such as razors or toothbrushes, unprotected contact with other body fluids (e.g., drainage from open skin wounds), or contact with HBV-contaminated surfaces. Thus, in addition to sexual contact ...
... sexual contact, needle sharing, accidental needle stick, sharing items that may be contaminated with blood such as razors or toothbrushes, unprotected contact with other body fluids (e.g., drainage from open skin wounds), or contact with HBV-contaminated surfaces. Thus, in addition to sexual contact ...
Infection-Preventionist-HRJD.136
... Preventionist will work collaboratively with the Director of Plant Operations, project manager and/or other departments for risk assessment, planning and monitoring. Hospital Policies and Procedures for the assessment and management of construction, renovation, and maintenance activity will be used ...
... Preventionist will work collaboratively with the Director of Plant Operations, project manager and/or other departments for risk assessment, planning and monitoring. Hospital Policies and Procedures for the assessment and management of construction, renovation, and maintenance activity will be used ...
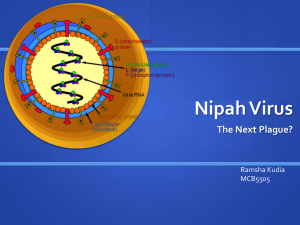
Nipah Virus
... goats, sheep, cats and dogs) were first reported during the initial Malaysian outbreak in 1999 ...
... goats, sheep, cats and dogs) were first reported during the initial Malaysian outbreak in 1999 ...
Nsg_Fund_3.01_Infection_Control_Student_Notes
... Must be worn during procedures or situations where there will be exposure to body fluids, blood, draining wounds, or mucous membranes. ...
... Must be worn during procedures or situations where there will be exposure to body fluids, blood, draining wounds, or mucous membranes. ...
recommended puppy - SouthCare Animal Medical Center
... Rabies Vaccine: Washington State Law requires all dogs and cats be vaccinated against Rabies because it is a deadly disease that is transmissible to humans. In Washington, this vaccine is administered as a single vaccine which lasts 1 year the first time they are vaccinated and lasts 3 years thereaf ...
... Rabies Vaccine: Washington State Law requires all dogs and cats be vaccinated against Rabies because it is a deadly disease that is transmissible to humans. In Washington, this vaccine is administered as a single vaccine which lasts 1 year the first time they are vaccinated and lasts 3 years thereaf ...
Infectious Disease
... • Describe the different types of infection control practices and justify which type is most appropriately implemented for different outbreak conditions. • Demonstrate effective communication skills with patients and the community as a whole. • Describe appropriate approaches to prevent or reduce th ...
... • Describe the different types of infection control practices and justify which type is most appropriately implemented for different outbreak conditions. • Demonstrate effective communication skills with patients and the community as a whole. • Describe appropriate approaches to prevent or reduce th ...
PDF | 267 KB - Hannover Re
... conditions an epidemic usually ends when all possible victims have been infected and either have become immune or, in the most lethal examples, have died. Epidemics can be classified as being ‘common source’ outbreaks where those who get infected do so because they have been exposed to an infectious ...
... conditions an epidemic usually ends when all possible victims have been infected and either have become immune or, in the most lethal examples, have died. Epidemics can be classified as being ‘common source’ outbreaks where those who get infected do so because they have been exposed to an infectious ...
BSL 2 - UniMAP Portal
... – Procedures that produce aerosols have higher risk – Procedures using needles or other sharps have higher risk – Handling blood, serum or tissue samples may have lower risk – Purified cultures or cell concentrates may have higher risk – Larger volumes (10 L) have higher risk ...
... – Procedures that produce aerosols have higher risk – Procedures using needles or other sharps have higher risk – Handling blood, serum or tissue samples may have lower risk – Purified cultures or cell concentrates may have higher risk – Larger volumes (10 L) have higher risk ...
Estimating the prevalence of infectious bursal disease
... PCR is accepted to be the most sensitive test for detection of IBD virus (Moody et al, 2000). Despite this, there are no quantitative estimates available for this parameter. Based on the qualitative information available and discussions with microbiological experts the sensitivity of the RT-PCR test ...
... PCR is accepted to be the most sensitive test for detection of IBD virus (Moody et al, 2000). Despite this, there are no quantitative estimates available for this parameter. Based on the qualitative information available and discussions with microbiological experts the sensitivity of the RT-PCR test ...
HIV for the oral surgeon
... Window period of 3 to 6 weeks from acute infection to development of antibodies HIV PCR can detect virus around 5 days from infection ...
... Window period of 3 to 6 weeks from acute infection to development of antibodies HIV PCR can detect virus around 5 days from infection ...
SPLENOMEGALY
... VCA-IgG and VCA-IgM tests are useful in diagnosing patients who have highly suggestive clinical features but negative heterophile antibody test results ...
... VCA-IgG and VCA-IgM tests are useful in diagnosing patients who have highly suggestive clinical features but negative heterophile antibody test results ...
What is MRSA? - Santa Fe Institute
... • People have no idea whether or not they are colonized, and most colonized people will not develop an infection. Colonization may last a few days or months. • Direct physical contact (such as hugging, holding hands, child care or contact sports) with a colonized or infected person can spread MRSA. ...
... • People have no idea whether or not they are colonized, and most colonized people will not develop an infection. Colonization may last a few days or months. • Direct physical contact (such as hugging, holding hands, child care or contact sports) with a colonized or infected person can spread MRSA. ...
Skin and Soft Tissue Infections (SSTIs)
... investigations and need not be hospitalized. However, patients with symptoms and signs of systemic toxicity, such as tachycardia and hypotension, should undergo the following tests: Blood culture and drug susceptibility ...
... investigations and need not be hospitalized. However, patients with symptoms and signs of systemic toxicity, such as tachycardia and hypotension, should undergo the following tests: Blood culture and drug susceptibility ...
Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will go on to develop liver failure, liver cancer, or life-threatening esophageal and gastric varices.HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with intravenous drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, and transfusions. An estimated 150–200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. The existence of hepatitis C – originally identifiable only as a type of non-A non-B hepatitis – was suggested in the 1970s and proven in 1989. Hepatitis C infects only humans and chimpanzees. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The virus persists in the liver in about 85% of those infected. This chronic infection can be treated with medication: the standard therapy is a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin, with either boceprevir or telaprevir added in some cases. Overall, 50–80% of people treated are cured. Those who develop cirrhosis or liver cancer may require a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is the leading reason for liver transplantation, though the virus usually recurs after transplantation. No vaccine against hepatitis C is available. About 343,000 deaths due to liver cancer from hepatitis C occurred in 2013, up from 198,000 in 1990. An additional 358,000 in 2013 occurred due to cirrhosis.