Bacteria and Viruses Powerpoint
... • HIV is a RETROVIRUS_ which is a virus that contains RNA and _REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE____. Reverse transcriptase- enzyme that copies viral RNA into DNA. HIV is an infection of the _WHITE BLOOD CELLS_____. The infected person’s white blood cells are damaged and their immune system fails which lead to ...
... • HIV is a RETROVIRUS_ which is a virus that contains RNA and _REVERSE TRANSCRIPTASE____. Reverse transcriptase- enzyme that copies viral RNA into DNA. HIV is an infection of the _WHITE BLOOD CELLS_____. The infected person’s white blood cells are damaged and their immune system fails which lead to ...
Chapter 23: Cardiovascular, Lymphatic, and Systemic Infectious
... • It is spread by contact with saliva • It is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) • Many children are infected and show no symptoms • Adolescents or young adults who are infected may develop EBV disease (a precursor of mononucleosis) • Complications include • heart defects • facial paralysis • ru ...
... • It is spread by contact with saliva • It is caused by the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) • Many children are infected and show no symptoms • Adolescents or young adults who are infected may develop EBV disease (a precursor of mononucleosis) • Complications include • heart defects • facial paralysis • ru ...
the role of mathematical modelling of hiv/aids in public health
... •no chemokines to inhibit infection, no cytokines to reduce burst size with or without killing, there is no clinical latency. •Presence of HIV-1 suppressive factors produced by CTLs control the viral load during HIV infection – thus the presence of chronic phase. •Non-lytic CTL effects are crucial t ...
... •no chemokines to inhibit infection, no cytokines to reduce burst size with or without killing, there is no clinical latency. •Presence of HIV-1 suppressive factors produced by CTLs control the viral load during HIV infection – thus the presence of chronic phase. •Non-lytic CTL effects are crucial t ...
Insights from Economic-Epidemiology
... subsidies is lowest when prevalence is highest since individuals will protect themselves regardless ...
... subsidies is lowest when prevalence is highest since individuals will protect themselves regardless ...
Toxoplasmosis
... suspected in a cat, this can be treated with a course of an appropriate antibiotic. ...
... suspected in a cat, this can be treated with a course of an appropriate antibiotic. ...
Understanding Epidemiology
... running water and liquid soap to lather hands and wrists. ◦ Scrubs all surfaces of hands and fingers for 1520 seconds. ◦ Bar soap can harbor germs that cause infection, so it is important to use liquid soap when possible. ...
... running water and liquid soap to lather hands and wrists. ◦ Scrubs all surfaces of hands and fingers for 1520 seconds. ◦ Bar soap can harbor germs that cause infection, so it is important to use liquid soap when possible. ...
HOSPITAL KUALA KUBU BHARU PHARMACY BULLETIN
... through travel to or residence in countries in and near the Arabian Peninsula. The largest known outbreak of MERS outside the Arabian Peninsula occurred in the Republic of Korea in 2015. The outbreak was associated with a traveler returning from the Arabian Peninsula. ...
... through travel to or residence in countries in and near the Arabian Peninsula. The largest known outbreak of MERS outside the Arabian Peninsula occurred in the Republic of Korea in 2015. The outbreak was associated with a traveler returning from the Arabian Peninsula. ...
Guidance on management of proven or suspected Staphylococcus
... •Look for potential source of infection: skin (cellulitis, ulcer, site of current or recent indwelling medical device, drug use by injection, surgical site infection), septic DVT, bone or joint inflammation (specifically paravertebral tenderness), prosthesis, urinary catheter, endocarditis (ausculat ...
... •Look for potential source of infection: skin (cellulitis, ulcer, site of current or recent indwelling medical device, drug use by injection, surgical site infection), septic DVT, bone or joint inflammation (specifically paravertebral tenderness), prosthesis, urinary catheter, endocarditis (ausculat ...
6Hx12:6-42 - Florida Gateway College
... there is an increased danger from infection due to diseases they may come in contact with at class or in the work place. Students with AIDS, who have defective immunity, are at risk of acquiring or experiencing serious complication of such diseases. Of particular concern is the risk of severe infect ...
... there is an increased danger from infection due to diseases they may come in contact with at class or in the work place. Students with AIDS, who have defective immunity, are at risk of acquiring or experiencing serious complication of such diseases. Of particular concern is the risk of severe infect ...
Surgical Asepsis - Philadelphia University
... specific part of the body where the microorganisms remain. ...
... specific part of the body where the microorganisms remain. ...
Treatment of Latent Tuberculosis Infection
... 2-month regimen of RIZ and PZA generally not recommended — to be used only if the potential benefits outweigh the risk of severe liver injury and death *** ** MMWR August 31, 2001; 50(34): 733-735 *** MMWR August 8, 2003; 52(31): 735-739 ...
... 2-month regimen of RIZ and PZA generally not recommended — to be used only if the potential benefits outweigh the risk of severe liver injury and death *** ** MMWR August 31, 2001; 50(34): 733-735 *** MMWR August 8, 2003; 52(31): 735-739 ...
Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure
... Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to, hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the vir ...
... Bloodborne Pathogens Exposure Procedure Background: Bloodborne pathogens are infectious microorganisms present in blood that can cause disease in humans. These pathogens include, but are not limited to, hepatitis B virus (HBV), hepatitis C virus (HCV), and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), the vir ...
Request Form Microbiology Version 5
... Doctor’s SJH Lab Code Doctor’s Signature Medical Council Registration Number Clinical Details Date Taken: ...
... Doctor’s SJH Lab Code Doctor’s Signature Medical Council Registration Number Clinical Details Date Taken: ...
Interpretation of HBV Diagnostic Blood tests
... increased rate of spontaneous HBeAg loss. This phase may last for several weeks to several years. Patients in this phase are infectious. Phase 3: inactive-phase. This may follow seroconversion from HBeAg to HBeAb detection. HBV DNA levels are very low or undetectable and liver enzymes fall as inflam ...
... increased rate of spontaneous HBeAg loss. This phase may last for several weeks to several years. Patients in this phase are infectious. Phase 3: inactive-phase. This may follow seroconversion from HBeAg to HBeAb detection. HBV DNA levels are very low or undetectable and liver enzymes fall as inflam ...
CENTENNIAL HONORS COLLEGE Western Illinois University Undergraduate Research Day 2016
... Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is a flavivirus that is transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. Although the virus has a low mortality rate in humans, it causes several severe symptoms. In 2005, an outbreak of CHIKV was identified on the French La Reunion Island and infected more t ...
... Chikungunya virus (CHIKV) is a flavivirus that is transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. Although the virus has a low mortality rate in humans, it causes several severe symptoms. In 2005, an outbreak of CHIKV was identified on the French La Reunion Island and infected more t ...
Invasive Group A Streptococcal (iGAS) Disease
... Group A Strep is spread through direct contact with the nose or mouth secretions of an infected person, for example, through open mouth kissing, mouth-to-mouth resuscitation or through direct contact with infected sores on the skin. ...
... Group A Strep is spread through direct contact with the nose or mouth secretions of an infected person, for example, through open mouth kissing, mouth-to-mouth resuscitation or through direct contact with infected sores on the skin. ...
J C M , Apr. 2006, p. 1288–1294
... The distribution of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions among outbreak and genotype D sequences along the viral genome is shown in Fig. 4. Substitutions were not distributed at random in overlapping and nonoverlapping coding regions for the 10 genotype D sequences. Most synonymous substitutio ...
... The distribution of synonymous and nonsynonymous substitutions among outbreak and genotype D sequences along the viral genome is shown in Fig. 4. Substitutions were not distributed at random in overlapping and nonoverlapping coding regions for the 10 genotype D sequences. Most synonymous substitutio ...
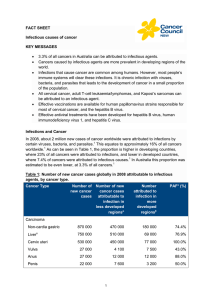
Infectious causes of cancer factsheet
... regimens and adverse side-effects, rates of antiviral therapy among this group remain low.16,17 Fortunately, safe, well-tolerated and highly effective therapies for HCV infection have become available.18,19 Human papilloma virus Human papilloma virus (HPV) is transmitted through skin-to-skin or skin ...
... regimens and adverse side-effects, rates of antiviral therapy among this group remain low.16,17 Fortunately, safe, well-tolerated and highly effective therapies for HCV infection have become available.18,19 Human papilloma virus Human papilloma virus (HPV) is transmitted through skin-to-skin or skin ...
Infectious Disease and Personal Protection Techniques for Infection
... Infectious Disease and Personal Protection Techniques for Infection Control in Dentistry Bahadır Kan1 and Mehmet Ali Altay2 ...
... Infectious Disease and Personal Protection Techniques for Infection Control in Dentistry Bahadır Kan1 and Mehmet Ali Altay2 ...
Ch 14
... › Infectious virus can be detected at all times › Disease may be present or absent during ...
... › Infectious virus can be detected at all times › Disease may be present or absent during ...
Republic of Latvia
... Issued pursuant to Section 14, Paragraph one, Clause 5 and Section 35 of the Epidemiological Safety Law 1. These Regulations determine the infectious diseases with which persons who have become ill or with which persons who have become infected, or persons in respect of whom there is a professionall ...
... Issued pursuant to Section 14, Paragraph one, Clause 5 and Section 35 of the Epidemiological Safety Law 1. These Regulations determine the infectious diseases with which persons who have become ill or with which persons who have become infected, or persons in respect of whom there is a professionall ...
Slide 1
... – All cats that go outdoors or come from unknown backgrounds should be tested for FeLV and FIV when first examined by a veterinarian ...
... – All cats that go outdoors or come from unknown backgrounds should be tested for FeLV and FIV when first examined by a veterinarian ...
Hepatitis C

Hepatitis C is an infectious disease affecting primarily the liver, caused by the hepatitis C virus (HCV). The infection is often asymptomatic, but chronic infection can lead to scarring of the liver and ultimately to cirrhosis, which is generally apparent after many years. In some cases, those with cirrhosis will go on to develop liver failure, liver cancer, or life-threatening esophageal and gastric varices.HCV is spread primarily by blood-to-blood contact associated with intravenous drug use, poorly sterilized medical equipment, and transfusions. An estimated 150–200 million people worldwide are infected with hepatitis C. The existence of hepatitis C – originally identifiable only as a type of non-A non-B hepatitis – was suggested in the 1970s and proven in 1989. Hepatitis C infects only humans and chimpanzees. It is one of five known hepatitis viruses: A, B, C, D, and E.The virus persists in the liver in about 85% of those infected. This chronic infection can be treated with medication: the standard therapy is a combination of peginterferon and ribavirin, with either boceprevir or telaprevir added in some cases. Overall, 50–80% of people treated are cured. Those who develop cirrhosis or liver cancer may require a liver transplant. Hepatitis C is the leading reason for liver transplantation, though the virus usually recurs after transplantation. No vaccine against hepatitis C is available. About 343,000 deaths due to liver cancer from hepatitis C occurred in 2013, up from 198,000 in 1990. An additional 358,000 in 2013 occurred due to cirrhosis.