Chronic Fatigue Syndrome/ Myalgic Encephalomyelopathy
... – More common within families – More likely in identical twins ...
... – More common within families – More likely in identical twins ...
Immune System
... • Identify and kill pathogens and tumor cells. • Produces white blood cells and antibodies. • Filters out organisms that cause disease. ...
... • Identify and kill pathogens and tumor cells. • Produces white blood cells and antibodies. • Filters out organisms that cause disease. ...
Fact Sheet: RHD-2 Rabbit Haemorrhagic Disease (RHD), also
... Death from RHD-2 occur later and over a longer period of time than RHD-1: typically this is 3-9 days following infection and can last up to 5 days, instead of 2-6 days infection and lasting 3-4 days as generally observed with classical RHD-1. Although this is marginal it is important to note from a ...
... Death from RHD-2 occur later and over a longer period of time than RHD-1: typically this is 3-9 days following infection and can last up to 5 days, instead of 2-6 days infection and lasting 3-4 days as generally observed with classical RHD-1. Although this is marginal it is important to note from a ...
Press Release TB status Delhi F
... One-fifth of the global burden of TB is found in India. The disease remains an enormous burden on patients, families, communities, and the nation. Premature death (more than 80%) is the main cause of the burden of tuberculosis, as measured in terms of disabilityadjusted life years (DALYs) lost. The ...
... One-fifth of the global burden of TB is found in India. The disease remains an enormous burden on patients, families, communities, and the nation. Premature death (more than 80%) is the main cause of the burden of tuberculosis, as measured in terms of disabilityadjusted life years (DALYs) lost. The ...
Infectious Diseases
... – Goes dormant and then flairs up suddenly – No cure and no vaccine, but can be treated with antiviral medicines ...
... – Goes dormant and then flairs up suddenly – No cure and no vaccine, but can be treated with antiviral medicines ...
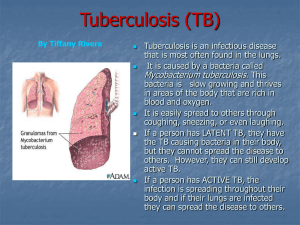
Tuberculosis
... People who live or work in residential facilities Health care professionals The elderly ...
... People who live or work in residential facilities Health care professionals The elderly ...
A1981MT33600001
... research, and actively participated in the studies described in the paper cited. I am deeply indebted to my coauthors of this paper. We were a close-knit research group put together with funds from various sources. The research reported was completed in March 1970, and at that time we had no idea th ...
... research, and actively participated in the studies described in the paper cited. I am deeply indebted to my coauthors of this paper. We were a close-knit research group put together with funds from various sources. The research reported was completed in March 1970, and at that time we had no idea th ...
Epidemic Disease Since the Black Death
... throughout the 20th century, and continue to do so to this day. There were several reasons for the decline in epidemic disease in richer countries like the United States. Better nutrition and living conditions have improved people’s ability to resist diseases. Advancements in public health, sanitati ...
... throughout the 20th century, and continue to do so to this day. There were several reasons for the decline in epidemic disease in richer countries like the United States. Better nutrition and living conditions have improved people’s ability to resist diseases. Advancements in public health, sanitati ...
CHAPTER 1 WHAT IS MICROBIOLOGY AND WHY IS IT IMPORTANT?
... – Mary, Mary, Quite Contrary – Typhoid fever – It’s For the Birds – ...
... – Mary, Mary, Quite Contrary – Typhoid fever – It’s For the Birds – ...
Key words: 1. Pathogen: A microorganism that can cause disease. 2
... Microorganism: A living thing too small to see with only your eyes. Symptom: Effects on your body from a pathogen. Communicable: Diseases can be passed on to other people Antibiotic: A type of drug that can kill bacteria. White Blood Cell: A type of cell in the immune system. Vaccine: An inactive or ...
... Microorganism: A living thing too small to see with only your eyes. Symptom: Effects on your body from a pathogen. Communicable: Diseases can be passed on to other people Antibiotic: A type of drug that can kill bacteria. White Blood Cell: A type of cell in the immune system. Vaccine: An inactive or ...
Mad Cow Disease
... • By its definition, mad cow disease, which is known to doctors, scientists, and other health professionals as bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), is a transmissible, slowly progressive, degenerative, and fatal disease affecting the central nervous system of adult cattle. (Hence the name) • To m ...
... • By its definition, mad cow disease, which is known to doctors, scientists, and other health professionals as bovine spongiform encephalopathy (BSE), is a transmissible, slowly progressive, degenerative, and fatal disease affecting the central nervous system of adult cattle. (Hence the name) • To m ...
T.R.
... It takes 6 to 9 months to entirely eliminate the mycobacteria from the body. The tuberculosis skin test (also known as the PPD test) is a test used to determine if someone has developed an immune response to the bacterium that causes TB. This response can occur if someone currently has TB or if they ...
... It takes 6 to 9 months to entirely eliminate the mycobacteria from the body. The tuberculosis skin test (also known as the PPD test) is a test used to determine if someone has developed an immune response to the bacterium that causes TB. This response can occur if someone currently has TB or if they ...
Health and Wellness
... Metastasis is the spread of cancer cells from the primary tumor to other parts of the body, usually through the lymphatic system or blood to areas such as the lungs and liver. Classification of Tumors Tumors can be categorized by origin and their cell features. The suffix of the tumor will indicate ...
... Metastasis is the spread of cancer cells from the primary tumor to other parts of the body, usually through the lymphatic system or blood to areas such as the lungs and liver. Classification of Tumors Tumors can be categorized by origin and their cell features. The suffix of the tumor will indicate ...
Test Word Lists
... Plasma Cell-assist in the development of antibodies in the humoral immunity Antigen-any substance that can stimulate the formation of an antibody Macrophage-a waundering phagocytic cell in the blood. Infectivity-capacity of an agent to enter and multiply in a susceptible host. Antigenicity (Immunoge ...
... Plasma Cell-assist in the development of antibodies in the humoral immunity Antigen-any substance that can stimulate the formation of an antibody Macrophage-a waundering phagocytic cell in the blood. Infectivity-capacity of an agent to enter and multiply in a susceptible host. Antigenicity (Immunoge ...
HLSC 3623 Human Diseases
... Plasma Cell-assist in the development of antibodies in the humoral immunity Antigen-any substance that can stimulate the formation of an antibody Macrophage-a waundering phagocytic cell in the blood. Infectivity-capacity of an agent to enter and multiply in a susceptible host. Antigenicity (Immunoge ...
... Plasma Cell-assist in the development of antibodies in the humoral immunity Antigen-any substance that can stimulate the formation of an antibody Macrophage-a waundering phagocytic cell in the blood. Infectivity-capacity of an agent to enter and multiply in a susceptible host. Antigenicity (Immunoge ...
Infectious Disease
... • Viral infections – no cure, symptoms are treated, must run its course. • Fungal infections – OTC antifungal, oral meds in severe cases. • Protozoan infections – prescription meds. • Parasitic infections – medicated shampoos (lice), prescription meds. ...
... • Viral infections – no cure, symptoms are treated, must run its course. • Fungal infections – OTC antifungal, oral meds in severe cases. • Protozoan infections – prescription meds. • Parasitic infections – medicated shampoos (lice), prescription meds. ...
FS_Live_Poultry_Newcastle_disease_FVSU.pdf
... and will cause a selflimiting conjunctivitis, most commonly seen in poultry workers. ...
... and will cause a selflimiting conjunctivitis, most commonly seen in poultry workers. ...
4. Other Infectious Microbes
... Symptoms show when there is a lack of bacteria in the body. (When you are on antibiotics) ...
... Symptoms show when there is a lack of bacteria in the body. (When you are on antibiotics) ...
hales_ith15e_powerpoint_lectures_chapter16
... Treatment Combination of therapies can relieve symptoms ...
... Treatment Combination of therapies can relieve symptoms ...
Signs and Symptoms of HIV DiseaseThree stages
... Signs and Symptoms of HIV Disease HIV (HUMAN IMMUMODIFICIENCY VIRUS) Three stages: (All test positive) ASYMPTOMATIC STAGE No physically apparent symptoms HAZARDS: unknowing infection to others Activation of condition through vaccines SYMPTOMATIC STAGE Some symptoms, less severe than the classic AIDS ...
... Signs and Symptoms of HIV Disease HIV (HUMAN IMMUMODIFICIENCY VIRUS) Three stages: (All test positive) ASYMPTOMATIC STAGE No physically apparent symptoms HAZARDS: unknowing infection to others Activation of condition through vaccines SYMPTOMATIC STAGE Some symptoms, less severe than the classic AIDS ...
African trypanosomiasis

African trypanosomiasis or sleeping sickness is a parasitic disease of humans and other animals. It is caused by protozoa of the species Trypanosoma brucei. There are two types that infect humans, Trypanosoma brucei gambiense (T.b.g) and Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense (T.b.r.). T.b.g causes over 98% of reported cases. Both are usually transmitted by the bite of an infected tsetse fly and are most common in rural areas.Initially, in the first stage of the disease, there are fevers, headaches, itchiness, and joint pains. This begins one to three weeks after the bite. Weeks to months later the second stage begins with confusion, poor coordination, numbness and trouble sleeping. Diagnosis is via finding the parasite in a blood smear or in the fluid of a lymph node. A lumbar puncture is often needed to tell the difference between first and second stage disease.Prevention of severe disease involves screening the population at risk with blood tests for T.b.g. Treatment is easier when the disease is detected early and before neurological symptoms occur. Treatment of the first stage is with the medications pentamidine or suramin. Treatment of the second stage involves: eflornithine or a combination of nifurtimox and eflornithine for T.b.g. While melarsoprol works for both it is typically only used for T.b.r. due to serious side effects.The disease occurs regularly in some regions of sub-Saharan Africa with the population at risk being about 70 million in 36 countries. As of 2010 it caused around 9,000 deaths per year, down from 34,000 in 1990. An estimated 30,000 people are currently infected with 7000 new infections in 2012. More than 80% of these cases are in the Democratic Republic of the Congo. Three major outbreaks have occurred in recent history: one from 1896 to 1906 primarily in Uganda and the Congo Basin and two in 1920 and 1970 in several African countries. Other animals, such as cows, may carry the disease and become infected.