File
... The manor was the heart of feudal life. It included a village or two and surrounding lands. The manor system worked by mutual obligation. Most of the population were serfs, who were bound to the land. ...
... The manor was the heart of feudal life. It included a village or two and surrounding lands. The manor system worked by mutual obligation. Most of the population were serfs, who were bound to the land. ...
Feudal Europe - TeacherV.net
... ▫ Strips a peasant could use would not be beside each other, but scattered. Lots of time could be lost in travelling from one section to another. ▫ Not an efficient way to use land, but often done so each serf would have access to water. ...
... ▫ Strips a peasant could use would not be beside each other, but scattered. Lots of time could be lost in travelling from one section to another. ▫ Not an efficient way to use land, but often done so each serf would have access to water. ...
Feudal Hierarchy - 8th Grade Social Studies Page
... • Vassals also promised to raise an army to protect the lord or lady in times of ...
... • Vassals also promised to raise an army to protect the lord or lady in times of ...
FEUDALISM
... – The manor lord also had the right to try serfs in his own courts • Legal rights of serfs – Land usually could not be taken away – Responsibilities of the serfs were fixed – The lord was obligated to protect them • Most of a manor’s land was occupied by fields for crops and pastures – Half the lan ...
... – The manor lord also had the right to try serfs in his own courts • Legal rights of serfs – Land usually could not be taken away – Responsibilities of the serfs were fixed – The lord was obligated to protect them • Most of a manor’s land was occupied by fields for crops and pastures – Half the lan ...
FEUDALISM
... – The manor lord also had the right to try serfs in his own courts • Legal rights of serfs – Land usually could not be taken away – Responsibilities of the serfs were fixed – The lord was obligated to protect them • Most of a manor’s land was occupied by fields for crops and pastures – Half the lan ...
... – The manor lord also had the right to try serfs in his own courts • Legal rights of serfs – Land usually could not be taken away – Responsibilities of the serfs were fixed – The lord was obligated to protect them • Most of a manor’s land was occupied by fields for crops and pastures – Half the lan ...
Feudalism and Manorialism
... got its name from the manor or large farming estates that fiefs were broken into. There was little to no trade during this time because it was unsafe to leave one’s manor. As a result people became self-sufficient. ...
... got its name from the manor or large farming estates that fiefs were broken into. There was little to no trade during this time because it was unsafe to leave one’s manor. As a result people became self-sufficient. ...
Module 6, Lesson 1 Feudalism Notes Presentation
... Question: How did the feudal system work? Answer: lord gave land to knight in return for protection and loyalty ...
... Question: How did the feudal system work? Answer: lord gave land to knight in return for protection and loyalty ...
Lecture Presentation - Living in Medieval Europe
... Let’s Imagine… Everyday after school, you like to go home and relax, maybe sit on the couch, watch T.V., and eat a snack before dinner time. However, right as you open a bag of chips, strangers barge in from the front door, the backyard, and through the window! They take your bag of chips, your T.V ...
... Let’s Imagine… Everyday after school, you like to go home and relax, maybe sit on the couch, watch T.V., and eat a snack before dinner time. However, right as you open a bag of chips, strangers barge in from the front door, the backyard, and through the window! They take your bag of chips, your T.V ...
Feudalism and Manorialism PPT
... system, Manorialism was the economic system of this time. Economic System- the means of producing, distributing, and consuming goods Manorialism—economic agricultural system by which the lord of the manor relied upon the labor of peasants who worked his estate or fief. ...
... system, Manorialism was the economic system of this time. Economic System- the means of producing, distributing, and consuming goods Manorialism—economic agricultural system by which the lord of the manor relied upon the labor of peasants who worked his estate or fief. ...
Chapter 24 Feudal Society
... • By 1000, the kingdoms of western Europe were divided into thousands of feudal territories. ...
... • By 1000, the kingdoms of western Europe were divided into thousands of feudal territories. ...
Feudalism and manor is the back bone of medieval Europe Why did
... ◦Due to the inability of kings and emperors to supply protection.... ...
... ◦Due to the inability of kings and emperors to supply protection.... ...
handout 17 - Spring Branch ISD
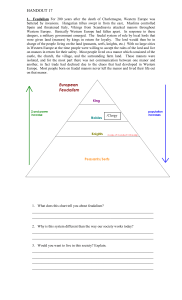
... HANDOUT 17 1. Feudalism For 200 years after the death of Charlemagne, Western Europe was battered by invasions. Hungarian tribes swept in from the east, Muslims controlled Spain and threatened Italy, Vikings from Scandinavia attacked manors throughout Western Europe. Basically Western Europe had fal ...
... HANDOUT 17 1. Feudalism For 200 years after the death of Charlemagne, Western Europe was battered by invasions. Hungarian tribes swept in from the east, Muslims controlled Spain and threatened Italy, Vikings from Scandinavia attacked manors throughout Western Europe. Basically Western Europe had fal ...
Feudalism
... the lord and the serfs (peasants tied to land)? Serfs worked the land for the lord in exchange for housing, land and protection Serfs also had to pay several different kinds of taxes to the lord Serfs provided lord with share of crops and provide labor to the lord ...
... the lord and the serfs (peasants tied to land)? Serfs worked the land for the lord in exchange for housing, land and protection Serfs also had to pay several different kinds of taxes to the lord Serfs provided lord with share of crops and provide labor to the lord ...
Feudalism in Medieval Europe
... TO THE CREATION OF A POLITICAL AND SOCIAL SYSTEM throughout Europe KNOWN AS FEUDALISM. This system created a way for kings and nobles to hold onto their land during this time of constant warfare. Don’t forget: land = power!! ...
... TO THE CREATION OF A POLITICAL AND SOCIAL SYSTEM throughout Europe KNOWN AS FEUDALISM. This system created a way for kings and nobles to hold onto their land during this time of constant warfare. Don’t forget: land = power!! ...
Feudalism in Europe - school search home
... i person who received land Irom a lord, in •xchange for land, or a fief, a vassal promised" to lelp his lord in battle. Under feudalism, society in western Enrope vas divided into three groups. Those who fought vere the nobles and knights. Those who prayed ,vere the officials of the Church. Those w ...
... i person who received land Irom a lord, in •xchange for land, or a fief, a vassal promised" to lelp his lord in battle. Under feudalism, society in western Enrope vas divided into three groups. Those who fought vere the nobles and knights. Those who prayed ,vere the officials of the Church. Those w ...
1. Kings and nobles didn`t know how to protect their land, and they
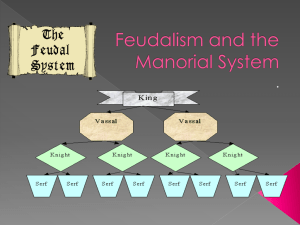
... land that was given to knights the feudal system or otherwise became fiefs. Fiefs that accepted known as the structure of feudalism. land were called vassals. And the lord was who the land was accepted from. 3. When one of the fiefs or vassals This oath included feudal went into a battle they had to ...
... land that was given to knights the feudal system or otherwise became fiefs. Fiefs that accepted known as the structure of feudalism. land were called vassals. And the lord was who the land was accepted from. 3. When one of the fiefs or vassals This oath included feudal went into a battle they had to ...
Feudalism Pyramid of Power Manoralism
... • Person could be both lord, vassal • Some knights with large fiefs gave small pieces of land to other knights ...
... • Person could be both lord, vassal • Some knights with large fiefs gave small pieces of land to other knights ...
Feudalism and Manorialism Power Point
... Vassals could further divide the land and grant it to others such as knights, who would fight for them in war A vassal could also be a lord ...
... Vassals could further divide the land and grant it to others such as knights, who would fight for them in war A vassal could also be a lord ...
Constructing the Pyramid Feudal Power
... 3) Lesser nobles (knights) gave _________ _________ in return for land 4) _______ were bound to the land. They worked in return for ____________. 5) __________ were skilled workers. They paid rent to the ______ and were free to move if they wanted to. ...
... 3) Lesser nobles (knights) gave _________ _________ in return for land 4) _______ were bound to the land. They worked in return for ____________. 5) __________ were skilled workers. They paid rent to the ______ and were free to move if they wanted to. ...
Feudalism in Europe
... exchange for land, or a fief, a vassal promised to help his lord in battle. Under feudalism, society in western Europe was divided into three groups. Those who fought were the nobles and knights. Those who prayed were the officials of the Church. Those who worked were the peasants. Peasants were by ...
... exchange for land, or a fief, a vassal promised to help his lord in battle. Under feudalism, society in western Europe was divided into three groups. Those who fought were the nobles and knights. Those who prayed were the officials of the Church. Those who worked were the peasants. Peasants were by ...
Feudalism Notes - Prep World History I
... military or economic or both; the vassal was required to provide some form of service to the lord, which could also be military or economic or both. For example, the king granted lands known as fiefs (and the peasants that went with them) to his nobles in exchange for their loyalty, military service ...
... military or economic or both; the vassal was required to provide some form of service to the lord, which could also be military or economic or both. For example, the king granted lands known as fiefs (and the peasants that went with them) to his nobles in exchange for their loyalty, military service ...
Manorial System
... 3) Lesser nobles (knights) gave _________ _________ in return for land 4) _______ were bound to the land. They worked in return for ____________. 5) __________ were skilled workers. They paid rent to the ______ and were free to move if they wanted to. ...
... 3) Lesser nobles (knights) gave _________ _________ in return for land 4) _______ were bound to the land. They worked in return for ____________. 5) __________ were skilled workers. They paid rent to the ______ and were free to move if they wanted to. ...