hepatitis c and tuberculosis
... 3) no other apparent cause for the elevation of liver chemistry, such as excessive alcohol intake; and 1) removal of the medications re- sulted in a normalisation or at least a 50% improve- ment of the abnormal liver chemistry. ...
... 3) no other apparent cause for the elevation of liver chemistry, such as excessive alcohol intake; and 1) removal of the medications re- sulted in a normalisation or at least a 50% improve- ment of the abnormal liver chemistry. ...
Infectious Diseases
... kill helminthes are frequently very toxic to human cells. Diseases caused by helminths: • Trichinella Spiralis: occurs when improperly cooked pork from infected pigs is ingested. – Symptoms include vomiting and diarrhea and fever*** – Respiratory paralysis can occur in fatal cases of trichinella spi ...
... kill helminthes are frequently very toxic to human cells. Diseases caused by helminths: • Trichinella Spiralis: occurs when improperly cooked pork from infected pigs is ingested. – Symptoms include vomiting and diarrhea and fever*** – Respiratory paralysis can occur in fatal cases of trichinella spi ...
Cryptosporidiosis
... Cryptosporidia are commonly found in the gastrointestinal tracts of farm animals, especially lambs and calves, and occasionally in domestic pets and birds. Household tap water that has been contaminated with Cryptosporidium cysts at source is also a common source of infection, and has been linked to ...
... Cryptosporidia are commonly found in the gastrointestinal tracts of farm animals, especially lambs and calves, and occasionally in domestic pets and birds. Household tap water that has been contaminated with Cryptosporidium cysts at source is also a common source of infection, and has been linked to ...
Infectious_epidemiology
... In US, proportion of female cases has been decreasing; but it is increasing in HI (from 4% in early 2000s to 20% in late 2000s). ...
... In US, proportion of female cases has been decreasing; but it is increasing in HI (from 4% in early 2000s to 20% in late 2000s). ...
M. pneumoniae
... specific and sensitive Nucleic acid-based tests: PCR + gene sequencing of a variety of genes The traditional Weil-Felix test: not recommended for use ...
... specific and sensitive Nucleic acid-based tests: PCR + gene sequencing of a variety of genes The traditional Weil-Felix test: not recommended for use ...
Communicable_Diseases_8
... • Herpes: Herpes simplex virus infection • Two types are not restricted in distribution • Type 1: infects oral mucous membrane – Causes fever blisters, usually infected in childhood, most adults have antibodies to virus – May cause genital infections ...
... • Herpes: Herpes simplex virus infection • Two types are not restricted in distribution • Type 1: infects oral mucous membrane – Causes fever blisters, usually infected in childhood, most adults have antibodies to virus – May cause genital infections ...
Standard Precautions
... A) SOURCE OF INFECTION: An infectious agent can be transmitted by a patient, visitor, or a hospital employee with an illness, or who carriers an infectious agent. Infection can also be transmitted by inanimate objects in the environment that have become contaminated, such as food and life support ma ...
... A) SOURCE OF INFECTION: An infectious agent can be transmitted by a patient, visitor, or a hospital employee with an illness, or who carriers an infectious agent. Infection can also be transmitted by inanimate objects in the environment that have become contaminated, such as food and life support ma ...
Pharyngeal Gonorrhea - San Francisco City Clinic
... 4.8% and a 4.1% prevalence of urethral chlamydia and urethral gonorrhea infection, respectively, in men who have sex with men (MSM) attending a municipal sexually transmitted disease (STD) clinic in San Francisco, California, whose only reported sexual exposure in the previous 3 months was receiving ...
... 4.8% and a 4.1% prevalence of urethral chlamydia and urethral gonorrhea infection, respectively, in men who have sex with men (MSM) attending a municipal sexually transmitted disease (STD) clinic in San Francisco, California, whose only reported sexual exposure in the previous 3 months was receiving ...
File - Working Toward Zero HAIs
... experts and urge residents to get vaccinated amid worry that cases of the highly contagious disease could spike much higher. It's the first state to declare a whooping cough, or pertussis, epidemic since 2010, when California had more than 9,000 cases, including 10 deaths. Washington has had 10 time ...
... experts and urge residents to get vaccinated amid worry that cases of the highly contagious disease could spike much higher. It's the first state to declare a whooping cough, or pertussis, epidemic since 2010, when California had more than 9,000 cases, including 10 deaths. Washington has had 10 time ...
Patient Management With Previous Positive TB Tests or Treatment
... pulmonary nodules, calcified hilar lymph nodes, and apical pleural capping) are not at increased risk for TB disease ...
... pulmonary nodules, calcified hilar lymph nodes, and apical pleural capping) are not at increased risk for TB disease ...
Appendix 1: Written information for students
... negative), you will need to have a chest x-ray. The chest x-ray is to ensure that you do not have active TB disease in your lungs, which may be infectious to other people. If you are found to have active TB disease, you will be referred for appropriate treatment. What is latent TB infection (LTBI)? ...
... negative), you will need to have a chest x-ray. The chest x-ray is to ensure that you do not have active TB disease in your lungs, which may be infectious to other people. If you are found to have active TB disease, you will be referred for appropriate treatment. What is latent TB infection (LTBI)? ...
Healthcare Associated Infection (HAI) Surveillance and The New
... composite risk index, and a patient’s risk of developing a SSI was summarized by Culver, et al. SSI rates ranged from 1.5 SSI’s per 100 operations for patients with none of the risk factors, to a high of 13.0 for patients with all 3 risk factors present. The presence of each additional risk factor n ...
... composite risk index, and a patient’s risk of developing a SSI was summarized by Culver, et al. SSI rates ranged from 1.5 SSI’s per 100 operations for patients with none of the risk factors, to a high of 13.0 for patients with all 3 risk factors present. The presence of each additional risk factor n ...
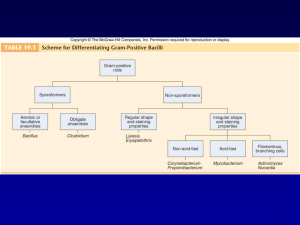
Chapter 19 - eacfaculty.org
... Mycobacterium leprae • Hansen’s bacillus • strict parasite – has not been grown on artificial media or tissue culture • slowest growing of all species • multiplies within host cells in large packets called globi • causes leprosy, a chronic disease that begins in the skin & mucous membranes & progre ...
... Mycobacterium leprae • Hansen’s bacillus • strict parasite – has not been grown on artificial media or tissue culture • slowest growing of all species • multiplies within host cells in large packets called globi • causes leprosy, a chronic disease that begins in the skin & mucous membranes & progre ...
Biology 201 Introduction and Tropical Parasites I
... Even without elephantiasis, filariasis usurps and destroys immune system - significance? ...
... Even without elephantiasis, filariasis usurps and destroys immune system - significance? ...
infectious diseasres of the nervous system
... Tissue infection of humans caused by larvae of echinoccocus granulosus (tapeworm parasite of DOG family) Brain involved in 2 % Cerebral cysts are usually single Most common in cerebral hemispheres TREAMENT: Surgical Removal without puncturing the cyst Albendazole or Mebendazole may decrease ...
... Tissue infection of humans caused by larvae of echinoccocus granulosus (tapeworm parasite of DOG family) Brain involved in 2 % Cerebral cysts are usually single Most common in cerebral hemispheres TREAMENT: Surgical Removal without puncturing the cyst Albendazole or Mebendazole may decrease ...
Veteran Fellow at Seattle Cancer Care Alliance Responsibilities
... Infection Prevention is a consultative service that works with patient care teams in both the Clinic and in collaboration with inpatient hospital settings to minimize the risk of infection to patients, visitors and staff. The Fellow will be involved in projects to document 1) the process for investi ...
... Infection Prevention is a consultative service that works with patient care teams in both the Clinic and in collaboration with inpatient hospital settings to minimize the risk of infection to patients, visitors and staff. The Fellow will be involved in projects to document 1) the process for investi ...
Causes of Disease
... syndrome) is a viral disease that destroys the body’s ability to resist other diseases by disrupting the immune system HIV, human immuno-deficiency virus) is the virus that causes AIDS ...
... syndrome) is a viral disease that destroys the body’s ability to resist other diseases by disrupting the immune system HIV, human immuno-deficiency virus) is the virus that causes AIDS ...
Infection Control Guide - Neighbourhood Houses Tasmania
... Infection is caused by pathogens ('bugs') such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa or fungi getting into or onto the body. It can take some time before the microbes multiply enough to trigger symptoms of illness, which means an infected person may unwittingly be spreading the disease during this incubati ...
... Infection is caused by pathogens ('bugs') such as bacteria, viruses, protozoa or fungi getting into or onto the body. It can take some time before the microbes multiply enough to trigger symptoms of illness, which means an infected person may unwittingly be spreading the disease during this incubati ...
Homework #332 Plant Pathology - Colorado State University
... 3. What is the difference between biotic and abiotic causal agents? Biotic causal agents are infectious, transmissible and display a random symptomatic pattern. Abiotic causal agents are non-infectious, non-transmissible, and display a uniform symptomatic pattern. 4. Leaf spots are a symptom of only ...
... 3. What is the difference between biotic and abiotic causal agents? Biotic causal agents are infectious, transmissible and display a random symptomatic pattern. Abiotic causal agents are non-infectious, non-transmissible, and display a uniform symptomatic pattern. 4. Leaf spots are a symptom of only ...
Practice Guidelines for Treatment of Children with LTBI
... If TB cultures available on source case for child’s infection, confirm sensitivity to INH Call and reschedule patients who miss follow up appointments For questions or problems call your local or state health department or a pediatric TB or infectious disease specialist for assistance. Completion of ...
... If TB cultures available on source case for child’s infection, confirm sensitivity to INH Call and reschedule patients who miss follow up appointments For questions or problems call your local or state health department or a pediatric TB or infectious disease specialist for assistance. Completion of ...
Health Advisory: NTM Infections Following hCG Injections
... multi-state outbreak of skin and soft tissue infections associated with hCG injections. MDH has notified CDC of a cluster of skin and soft tissue infections in 4 patients who had self-administered injections of hCG obtained from weight loss clinics. CDC had also received notification from another st ...
... multi-state outbreak of skin and soft tissue infections associated with hCG injections. MDH has notified CDC of a cluster of skin and soft tissue infections in 4 patients who had self-administered injections of hCG obtained from weight loss clinics. CDC had also received notification from another st ...
Infection Prevention - Medical Center Hospital
... • Encourage personnel to wash hands frequently using soap and water for 15-20 seconds. • Substitute alcohol-based hand sanitizer when clean water and soap are unavailable. • Promote appropriate respiratory etiquette: Cover coughs and sneezes with tissue. Throw away tissues immediately and WASH YOUR ...
... • Encourage personnel to wash hands frequently using soap and water for 15-20 seconds. • Substitute alcohol-based hand sanitizer when clean water and soap are unavailable. • Promote appropriate respiratory etiquette: Cover coughs and sneezes with tissue. Throw away tissues immediately and WASH YOUR ...
HIV/AIDS
... Pandemic: infectious disease that is spreading through human populations worldwide estimated that there are 33.3 million people worldwide infected 2.6 million new HIV infections per year 1.8 million annual deaths due to AIDS 76% of those deaths occurred in sub-Saharan Africa. attacks every ...
... Pandemic: infectious disease that is spreading through human populations worldwide estimated that there are 33.3 million people worldwide infected 2.6 million new HIV infections per year 1.8 million annual deaths due to AIDS 76% of those deaths occurred in sub-Saharan Africa. attacks every ...
Bloodborne Pathogens/TB
... In 2005 AIDS claimed 2.4-3.3 million lives of which, more than 570,000 were children. It is one of the most destructive pandemics in recorded history. ...
... In 2005 AIDS claimed 2.4-3.3 million lives of which, more than 570,000 were children. It is one of the most destructive pandemics in recorded history. ...
Oesophagostomum
.jpg?width=300)
Oesophagostomum is a genus of free-living nematodes of the family Strongyloidae. These worms occur in Africa, Brazil, China, Indonesia and the Philippines. The majority of human infection with Oesophagostomum is localized to northern Togo and Ghana. Because the eggs may be indistinguishable from those of the hookworms (which are widely distributed and can also rarely cause helminthomas), the species causing human helminthomas are rarely identified with accuracy. Oesophagostomum, especially O. bifurcum, are common parasites of livestock and animals like goats, pigs and non-human primates, although it seems that humans are increasingly becoming favorable hosts as well. The disease they cause, oesophagostomiasis, is known for the nodule formation it causes in the intestines of its infected hosts, which can lead to more serious problems such as dysentery. Although the routes of human infection have yet to be elucidated sufficiently, it is believed that transmission occurs through oral-fecal means, with infected humans unknowingly ingesting soil containing the infectious filariform larvae.Oesophagostomum infection is largely localized to northern Togo and Ghana in western Africa where it is a serious public health problem. Because it is so localized, research on intervention measures and the implementation of effective public health interventions have been lacking. In recent years, however, there have been advances in the diagnosis of Oesophagostomum infection with PCR assays and ultrasound and recent interventions involving mass treatment with albendazole shows promise for controlling and possibly eliminating Oesophagostomum infection in northern Togo and Ghana.