Fleas
... Parasites are animals that benefit at the expense of another organism (called the host), usually of a different species. The association may also lead to the injury of the host. ...
... Parasites are animals that benefit at the expense of another organism (called the host), usually of a different species. The association may also lead to the injury of the host. ...
History and definitions of HAI
... infections already present on admission, unless a change in pathogen or symptoms strongly suggests the acquisition of a new infection; Infections in infants that have been acquired transplacentally (eg, herpes simplex, toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, or syphilis) and become evident ≥48 hour ...
... infections already present on admission, unless a change in pathogen or symptoms strongly suggests the acquisition of a new infection; Infections in infants that have been acquired transplacentally (eg, herpes simplex, toxoplasmosis, rubella, cytomegalovirus, or syphilis) and become evident ≥48 hour ...
Read Article - Arizona Dental Association
... elaborate on some diseases listed as they relate to dentistry since it is important to know when to restrict employees from work. The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) is the infectious disease physicians’ association, and their opinions hold great weight in the infection control ...
... elaborate on some diseases listed as they relate to dentistry since it is important to know when to restrict employees from work. The Society for Healthcare Epidemiology of America (SHEA) is the infectious disease physicians’ association, and their opinions hold great weight in the infection control ...
Infection Control - Nicole
... Remember the underpinning knowledge of infection control: Common infections are caused my 4 microorganisms (virus, bacteria, fungus, parasites). Infection is most often transmitted by hands. Therefore the importance of correct hand hygiene and protective clothing as essential component in reducing c ...
... Remember the underpinning knowledge of infection control: Common infections are caused my 4 microorganisms (virus, bacteria, fungus, parasites). Infection is most often transmitted by hands. Therefore the importance of correct hand hygiene and protective clothing as essential component in reducing c ...
AASLD poster 2014 - TARA
... • Recent studies show that at least 2 per 1000 people in the greater Dublin area have been diagnosed with HIV infection. • Prevalence rates for Hepatitis C infection in Ireland have varied in previous studies from 0.5-1.2%. • True Hepatitis B prevalence rate in Ireland is unknown, • Given the recent ...
... • Recent studies show that at least 2 per 1000 people in the greater Dublin area have been diagnosed with HIV infection. • Prevalence rates for Hepatitis C infection in Ireland have varied in previous studies from 0.5-1.2%. • True Hepatitis B prevalence rate in Ireland is unknown, • Given the recent ...
Protection - HEROIN IMPACT RESPONSE
... Northern Kentucky (NKY PAR), Transitions Inc., Northern Kentucky Drug Strike Force, and other community and faith-based partners. In 2015-16, we will continue distribution of Naloxone within the community through fixed locations and the mobile unit. We will also protect law officers from inadvertent ...
... Northern Kentucky (NKY PAR), Transitions Inc., Northern Kentucky Drug Strike Force, and other community and faith-based partners. In 2015-16, we will continue distribution of Naloxone within the community through fixed locations and the mobile unit. We will also protect law officers from inadvertent ...
Infections in Rural and Remote Australia Program
... Outline and describe the various methods used in the microbiology laboratory to confirm an infection (i.e., microscopy, culture, biochemical, antigen detection, serology and molecular). Describe the general methods of antimicrobial sensitivity testing (including manual, semi-automated and automated ...
... Outline and describe the various methods used in the microbiology laboratory to confirm an infection (i.e., microscopy, culture, biochemical, antigen detection, serology and molecular). Describe the general methods of antimicrobial sensitivity testing (including manual, semi-automated and automated ...
Slide 1
... Emerging infectious diseases Have not occurred in humans before, Have occurred previously but affected only small numbers, Or have occurred throughout human history, but only recently recognized as disease due to infectious agent Re-emerging infectious diseases Once were major health problems ...
... Emerging infectious diseases Have not occurred in humans before, Have occurred previously but affected only small numbers, Or have occurred throughout human history, but only recently recognized as disease due to infectious agent Re-emerging infectious diseases Once were major health problems ...
Causes and Spread of Infection – Unit Information
... Infection finds way into the body through 1. Down the respiratory tract (nose, windpipe, lungs) into the lungs. Coughs, cold, influenza and other common airborne infections are contracted in this fashion. 2. Breaks in the skin. One of the many functions of the skin is to act as a barrier against inf ...
... Infection finds way into the body through 1. Down the respiratory tract (nose, windpipe, lungs) into the lungs. Coughs, cold, influenza and other common airborne infections are contracted in this fashion. 2. Breaks in the skin. One of the many functions of the skin is to act as a barrier against inf ...
References - New England TB Consortium
... Screen patients for risk factors for M. tuberculosis and test for LTBI before initiating immunosuppressive therapies, including TNF-α antagonists. Risk factors include 1) history of a positive TB skin test (TST), 2) birth in country where TB is endemic (4) or 3) history of any of the following: a) e ...
... Screen patients for risk factors for M. tuberculosis and test for LTBI before initiating immunosuppressive therapies, including TNF-α antagonists. Risk factors include 1) history of a positive TB skin test (TST), 2) birth in country where TB is endemic (4) or 3) history of any of the following: a) e ...
Heart Water
... Heartwater is an infectious, noncontagious, tick-borne disease of domestic and wild ruminantsand usually an acute disease and is commonly fatal within a week of onset of clinical signs.It occurs where its tick vectors are present.The disease is widespread in most of Africa and is present onseveral i ...
... Heartwater is an infectious, noncontagious, tick-borne disease of domestic and wild ruminantsand usually an acute disease and is commonly fatal within a week of onset of clinical signs.It occurs where its tick vectors are present.The disease is widespread in most of Africa and is present onseveral i ...
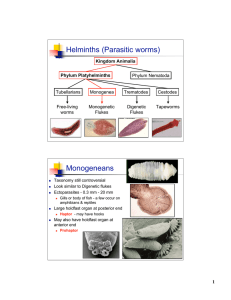
Helminths (Parasitic worms) Monogeneans
... Parasites are relatively common in the US. Up to 17% of Montana cattle are infected, but human disease in the US is rare. Pasture rotation is an important control mechanism to ...
... Parasites are relatively common in the US. Up to 17% of Montana cattle are infected, but human disease in the US is rare. Pasture rotation is an important control mechanism to ...
leptospira
... efflux or mutational gain of function in the genes encoding these proteins contribute to antibiotic resistance in a number of bacterial species . ...
... efflux or mutational gain of function in the genes encoding these proteins contribute to antibiotic resistance in a number of bacterial species . ...
NHSN Definitions CLABSI
... Criterion 1: Patient has a recognized pathogen cultured from one or more blood cultures and organism cultured from blood is not related to an infection at another site. Criterion 2: Patient has at least one of the following signs or symptoms: fever (>380 C), chills, or hypotension and signs and symp ...
... Criterion 1: Patient has a recognized pathogen cultured from one or more blood cultures and organism cultured from blood is not related to an infection at another site. Criterion 2: Patient has at least one of the following signs or symptoms: fever (>380 C), chills, or hypotension and signs and symp ...
File - PCHS Health Science Education
... Symptoms Severity Transmission How to protect yourself and your patient ...
... Symptoms Severity Transmission How to protect yourself and your patient ...
Diapositiva 1
... causes a broad spread of infectious agents, even when both infectiousness and infectivity are limited. These management-induced outbreaks are quite common with respect to viral infections like PRRSv and PCV-2. Also Streptococcus suis easily spread between litters, when litters are mixed, although th ...
... causes a broad spread of infectious agents, even when both infectiousness and infectivity are limited. These management-induced outbreaks are quite common with respect to viral infections like PRRSv and PCV-2. Also Streptococcus suis easily spread between litters, when litters are mixed, although th ...
virginia mason medical center
... 7. Which of the following changes is a developmental change? a. A change in a person’s weight b. A change in the person’s place of residence c. A change in a person’s height d. A change in the person’s social behavior 8. You are caring for Mrs. Burrell, who lives in a long-term care facility. Which ...
... 7. Which of the following changes is a developmental change? a. A change in a person’s weight b. A change in the person’s place of residence c. A change in a person’s height d. A change in the person’s social behavior 8. You are caring for Mrs. Burrell, who lives in a long-term care facility. Which ...
HIV-1 containing the I50V mutation to amprenavir. Thus, if N88S can
... amprenavir. Thus, if N88S can be maintained, future treatment options for this patient, who harbors I50V-containing virus, may include amprenavir, perhaps in combination with ritonavir. Although the change was less dramatic, N88S also lowered the level of resistance to lopinavir imparted by I50V. Th ...
... amprenavir. Thus, if N88S can be maintained, future treatment options for this patient, who harbors I50V-containing virus, may include amprenavir, perhaps in combination with ritonavir. Although the change was less dramatic, N88S also lowered the level of resistance to lopinavir imparted by I50V. Th ...
Pet-Related Infections - American Academy of Family Physicians
... during the first trimester, can cause serious congenital infection. It can also cause severe disease in immunocompromised persons. Toxocariasis. Roundworm infection (toxocariasis) caused by the ascarid Toxocara canis (dogs) and Toxocara cati (cats) is one of the most common zoonotic infections assoc ...
... during the first trimester, can cause serious congenital infection. It can also cause severe disease in immunocompromised persons. Toxocariasis. Roundworm infection (toxocariasis) caused by the ascarid Toxocara canis (dogs) and Toxocara cati (cats) is one of the most common zoonotic infections assoc ...
Freeman 1e: How we got there
... whooping cough. From an average of less than 2000 pertussis cases per year in the 1970s, the number of cases has now risen to over 8000 per year. Inadequately immunized children are at high risk for acquiring pertussis. ...
... whooping cough. From an average of less than 2000 pertussis cases per year in the 1970s, the number of cases has now risen to over 8000 per year. Inadequately immunized children are at high risk for acquiring pertussis. ...
Must be present!
... •Slightly less severity of disease •Less known to public therefore less likely to cause panic •Slightly less risk to National Security ...
... •Slightly less severity of disease •Less known to public therefore less likely to cause panic •Slightly less risk to National Security ...
Case report Triple infection with HIV-1, HTLV
... well as a temporary increase in the number of T-helper 1 CD4+ cells causing an ineffective immune response to S. stercoralis. This masked the severity of immunosuppression induced by HIV, and the high CD4+ T-cell counts were misleading to the responsible clinicians. ...
... well as a temporary increase in the number of T-helper 1 CD4+ cells causing an ineffective immune response to S. stercoralis. This masked the severity of immunosuppression induced by HIV, and the high CD4+ T-cell counts were misleading to the responsible clinicians. ...
Oesophagostomum
.jpg?width=300)
Oesophagostomum is a genus of free-living nematodes of the family Strongyloidae. These worms occur in Africa, Brazil, China, Indonesia and the Philippines. The majority of human infection with Oesophagostomum is localized to northern Togo and Ghana. Because the eggs may be indistinguishable from those of the hookworms (which are widely distributed and can also rarely cause helminthomas), the species causing human helminthomas are rarely identified with accuracy. Oesophagostomum, especially O. bifurcum, are common parasites of livestock and animals like goats, pigs and non-human primates, although it seems that humans are increasingly becoming favorable hosts as well. The disease they cause, oesophagostomiasis, is known for the nodule formation it causes in the intestines of its infected hosts, which can lead to more serious problems such as dysentery. Although the routes of human infection have yet to be elucidated sufficiently, it is believed that transmission occurs through oral-fecal means, with infected humans unknowingly ingesting soil containing the infectious filariform larvae.Oesophagostomum infection is largely localized to northern Togo and Ghana in western Africa where it is a serious public health problem. Because it is so localized, research on intervention measures and the implementation of effective public health interventions have been lacking. In recent years, however, there have been advances in the diagnosis of Oesophagostomum infection with PCR assays and ultrasound and recent interventions involving mass treatment with albendazole shows promise for controlling and possibly eliminating Oesophagostomum infection in northern Togo and Ghana.