BACTERIAL AGENTS Bacterial Infectious DiseasesAnthrax
... Mumps : characterized by painful swelling of the salivary glands and fever. Painful testicular swelling and rash may also occur. Poliomyelitis : spread from one person to other via the fecal-oral route, e.g. poor hand washing. Progressive multifocal leukencephalopathy : occurs exclusively in people ...
... Mumps : characterized by painful swelling of the salivary glands and fever. Painful testicular swelling and rash may also occur. Poliomyelitis : spread from one person to other via the fecal-oral route, e.g. poor hand washing. Progressive multifocal leukencephalopathy : occurs exclusively in people ...
Chapter Nine – Nutrition Quiz Clues
... Transmitted Infections; with Focus on Reducing Risks and Coping with Chronic Disease and Conditions Know what is the term used for disease causing agents (not virus, bacteria, or germs) ...
... Transmitted Infections; with Focus on Reducing Risks and Coping with Chronic Disease and Conditions Know what is the term used for disease causing agents (not virus, bacteria, or germs) ...
Summaries of Infectious Diseases
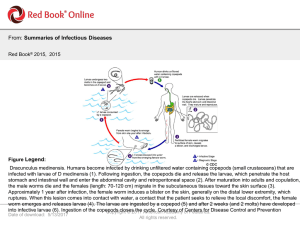
... stomach and intestinal wall and enter the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space (2). After maturation into adults and copulation, the male worms die and the females (length: 70-120 cm) migrate in the subcutaneous tissues toward the skin surface (3). Approximately 1 year after infection, the fem ...
... stomach and intestinal wall and enter the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space (2). After maturation into adults and copulation, the male worms die and the females (length: 70-120 cm) migrate in the subcutaneous tissues toward the skin surface (3). Approximately 1 year after infection, the fem ...
Newcastle Disease
... The neurotropic velogenic form of ND has been reported mainly in the United States. In chickens, it is marked by sudden onset of severe respiratory disease followed a day or two later by neurologic signs. Egg production falls dramatically, but diarrhea is usually absent. Morbidity may reach 100%. Mo ...
... The neurotropic velogenic form of ND has been reported mainly in the United States. In chickens, it is marked by sudden onset of severe respiratory disease followed a day or two later by neurologic signs. Egg production falls dramatically, but diarrhea is usually absent. Morbidity may reach 100%. Mo ...
CYTOMEGALOVIRUS FACT SHEET
... SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: Clinical manifestations of this infection vary with the age and immunocompetence of the infected person. Asymptomatic infections are most common, especially in children. A syndrome similar to infectious mononucleosis may occur in adults. Congenital infection of an infant born to ...
... SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS: Clinical manifestations of this infection vary with the age and immunocompetence of the infected person. Asymptomatic infections are most common, especially in children. A syndrome similar to infectious mononucleosis may occur in adults. Congenital infection of an infant born to ...
T.R.
... infection is spreading throughout their body and if their lungs are infected they can spread the disease to others. ...
... infection is spreading throughout their body and if their lungs are infected they can spread the disease to others. ...
How does the immune system protect the body against disease?
... Schistosoma mansoni (fluke) is a major parasitic pathogen that causes schistosomiasis. You can become infected when your skin comes in contact with contaminated freshwater. Schistosomiasis account for greater than a quarter of a million deaths per annum. Worms not found in the U.S. ...
... Schistosoma mansoni (fluke) is a major parasitic pathogen that causes schistosomiasis. You can become infected when your skin comes in contact with contaminated freshwater. Schistosomiasis account for greater than a quarter of a million deaths per annum. Worms not found in the U.S. ...
Unit 8: Communicable/Infectious Diseases
... Disease caused by pathogens that can be spread from one living thing to another ...
... Disease caused by pathogens that can be spread from one living thing to another ...
Chapter 15: Epidemiology and Infectious Diseases
... •Carriers usually do not know they are carriers and are often difficult to identify ...
... •Carriers usually do not know they are carriers and are often difficult to identify ...
osce_feverinareturnedtraveller - OSCE-Aid
... OSCE scenario: This 36 year old lady has presented to A+E with a fever. She has returned from West Africa 5 days ago. Please take an appropriate history. History of presenting complaint Symptoms – clarify exactly what symptoms the patient has had o Fever: Any patterns to the fever, e.g. cyclical ...
... OSCE scenario: This 36 year old lady has presented to A+E with a fever. She has returned from West Africa 5 days ago. Please take an appropriate history. History of presenting complaint Symptoms – clarify exactly what symptoms the patient has had o Fever: Any patterns to the fever, e.g. cyclical ...
Feline Infectious Anemia (Hemobart)
... itself to the surface of the cat’s red blood cell and destroys the cell, resulting in anemia. The anemia may be mild, at least early in the infection, and not cause any obvious signs. Many cases of hemobart can go undetected for some period of time. Some of these subclinical cats remain long-term ca ...
... itself to the surface of the cat’s red blood cell and destroys the cell, resulting in anemia. The anemia may be mild, at least early in the infection, and not cause any obvious signs. Many cases of hemobart can go undetected for some period of time. Some of these subclinical cats remain long-term ca ...
Disease Process - De Anza College
... • Extraction of tooth • Perianal skin flora enters urinary tract ...
... • Extraction of tooth • Perianal skin flora enters urinary tract ...
Coxiella burnetii
... Under circumstances of a bioterrorism threat, the need for and potential effectiveness of specific donorscreening questions would need to be addressed. ...
... Under circumstances of a bioterrorism threat, the need for and potential effectiveness of specific donorscreening questions would need to be addressed. ...
Disease Match up Activity
... attacks of chills and fever. It kills 1 million people worldwide each year. It is common in tropical and subtropical countries. Preventative measures, like mosquito bed nets, bug sprays, and protective clothing are best as the malaria parasites are immune to all available drugs to treat the disease. ...
... attacks of chills and fever. It kills 1 million people worldwide each year. It is common in tropical and subtropical countries. Preventative measures, like mosquito bed nets, bug sprays, and protective clothing are best as the malaria parasites are immune to all available drugs to treat the disease. ...
African Sleeping Sickness: Drugs for Disease or Beauty? Beth
... countries whose access to healthcare and education is limited, and where unsanitary conditions like no clean water allow the spread of deadly diseases such as Trypanosomiasis, or African Sleeping Sickness. An estimated 300,000- 500,000 people suffer from the disease with over 66,000 deaths a year, a ...
... countries whose access to healthcare and education is limited, and where unsanitary conditions like no clean water allow the spread of deadly diseases such as Trypanosomiasis, or African Sleeping Sickness. An estimated 300,000- 500,000 people suffer from the disease with over 66,000 deaths a year, a ...
Hemobartonellosis in Cats
... is transferred via blood-sucking insects or by entry into the body through the mouth, in bite wounds, or through blood transfusions. The parasites are active in the blood 2-17 days after infection and can remain active for 3-8 weeks. The cat’s immune system attempts to clear infected RBCs by destroy ...
... is transferred via blood-sucking insects or by entry into the body through the mouth, in bite wounds, or through blood transfusions. The parasites are active in the blood 2-17 days after infection and can remain active for 3-8 weeks. The cat’s immune system attempts to clear infected RBCs by destroy ...
Schistosomiasis

Schistosomiasis, also known as bilharzia, snail fever, and Katayama fever, is a disease caused by parasitic worms of the Schistosoma type. It may infect the urinary tract or the intestines. Signs and symptoms may include abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloody stool, or blood in the urine. In those who have been infected for a long time, liver damage, kidney failure, infertility, or bladder cancer may occur. In children it may cause poor growth and learning difficulty.The disease is spread by contact with water contaminated with the parasites. These parasites are released from infected freshwater snails. The disease is especially common among children in developing countries as they are more likely to play in contaminated water. Other high risk groups include farmers, fishermen, and people using unclean water for their daily chores. It belongs to the group of helminth infections. Diagnosis is by finding the eggs of the parasite in a person's urine or stool. It can also be confirmed by finding antibodies against the disease in the blood.Methods to prevent the disease include improving access to clean water and reducing the number of snails. In areas where the disease is common entire groups may be treated all at once and yearly with the medication praziquantel. This is done to decrease the number of people infected and therefore decrease the spread of the disease. Praziquantel is also the treatment recommended by the World Health Organization for those who are known to be infected.Schistosomiasis affects almost 210 million people worldwide, and an estimated 12,000 to 200,000 people die from it a year. The disease is most commonly found in Africa, as well as Asia and South America. Around 700 million people, in more than 70 countries, live in areas where the disease is common. Schistosomiasis is second only to malaria, as a parasitic disease with the greatest economic impact. It is classified as a neglected tropical disease.