silk and bamboo music - Indiana University Bloomington
... instrumentation and timbral coloring peculiar to its local origin, there is also a commonality. When playing a piece, two or more performers will simultaneously modify the same melody, sometimes quite elaborately. Thus, improvisation is highly valued among traditional sizhu performers as it is these ...
... instrumentation and timbral coloring peculiar to its local origin, there is also a commonality. When playing a piece, two or more performers will simultaneously modify the same melody, sometimes quite elaborately. Thus, improvisation is highly valued among traditional sizhu performers as it is these ...
Slide 1
... • Jews forced to leave (Northern Kingdom, Israel, destroyed by Assyrians in 722BCE, Southern Kingdom, Judah, destroyed by Babylonians in 586BCE). • Merchants travel abroad to make their fortunes in the Indian Ocean • Africans brought to the New World and to areas of the Middle East ...
... • Jews forced to leave (Northern Kingdom, Israel, destroyed by Assyrians in 722BCE, Southern Kingdom, Judah, destroyed by Babylonians in 586BCE). • Merchants travel abroad to make their fortunes in the Indian Ocean • Africans brought to the New World and to areas of the Middle East ...
3D Silk Road
... and others—formed part of a steppe culture that soon stretched all the way across Asia. The distinctive art of these steppe peoples, characterized by bronze weapons and ornamental goods decorated with depictions of stylized animals, is found everywhere from Europe near the Black Sea to northern Chin ...
... and others—formed part of a steppe culture that soon stretched all the way across Asia. The distinctive art of these steppe peoples, characterized by bronze weapons and ornamental goods decorated with depictions of stylized animals, is found everywhere from Europe near the Black Sea to northern Chin ...
Holy Roman Empire
... • In the post-classical era, Persians and Arabs dominated trade in the Indian Ocean • Connected ports in eastern Africa (Swahili Coast) with ports in Western India and the Persian Gulf • Boats used monsoon winds to travel • Safer travel in Indian Ocean compared to the Mediterranean (where warfare wa ...
... • In the post-classical era, Persians and Arabs dominated trade in the Indian Ocean • Connected ports in eastern Africa (Swahili Coast) with ports in Western India and the Persian Gulf • Boats used monsoon winds to travel • Safer travel in Indian Ocean compared to the Mediterranean (where warfare wa ...
Slide 1 - Cloudfront.net
... • In the post-classical era, Persians and Arabs dominated trade in the Indian Ocean • Connected ports in eastern Africa (Swahili Coast) with ports in Western India and the Persian Gulf • Boats used monsoon winds to travel • Safer travel in Indian Ocean compared to the Mediterranean (where warfare wa ...
... • In the post-classical era, Persians and Arabs dominated trade in the Indian Ocean • Connected ports in eastern Africa (Swahili Coast) with ports in Western India and the Persian Gulf • Boats used monsoon winds to travel • Safer travel in Indian Ocean compared to the Mediterranean (where warfare wa ...
AP WORLD HISTORY - Auburn High School
... – Foreigner emplolyed in bureaucracy, civil service not used – Marco Polo Ilkhanate of Persia (Hulegu: Kublai’s brother) – Persia-Baghdad: stopped in Syria by Egyptian forces Timur Lang (1370) – Aka Tamerlane – Ghengis Khan = role model – Capital Samarkand – Conquered parts of India ...
... – Foreigner emplolyed in bureaucracy, civil service not used – Marco Polo Ilkhanate of Persia (Hulegu: Kublai’s brother) – Persia-Baghdad: stopped in Syria by Egyptian forces Timur Lang (1370) – Aka Tamerlane – Ghengis Khan = role model – Capital Samarkand – Conquered parts of India ...
Ancient China: Inventions and Technology
... valuable export that the trade route running from Europe to China became known as the Silk Road. The Chinese learned how to make silk from the cocoons of silkworms. They managed to keep the process for making silk a secret for hundreds of years. Paper - Paper was invented by the Chinese as well as m ...
... valuable export that the trade route running from Europe to China became known as the Silk Road. The Chinese learned how to make silk from the cocoons of silkworms. They managed to keep the process for making silk a secret for hundreds of years. Paper - Paper was invented by the Chinese as well as m ...
Monks, Merchants & “Heretics”: Christianity en route to
... Monks, Merchants & “Heretics”: Christianity en route to China Introduction I. Trade & Travel from Constantinople to Chang’an A. The Silk Road B. Silk and Salvation Religions II. Nestorian Missions: From Persia to China A. Among the Huns B. The First Christian Mission in China 1. The Setting: T’ang ...
... Monks, Merchants & “Heretics”: Christianity en route to China Introduction I. Trade & Travel from Constantinople to Chang’an A. The Silk Road B. Silk and Salvation Religions II. Nestorian Missions: From Persia to China A. Among the Huns B. The First Christian Mission in China 1. The Setting: T’ang ...
unit2test
... e) Fear of the spread of the plague to China 18. Which of the following languages came into existence after 1000 as the direct result of expanding global trade patterns? a) Arabic b) Chinese c) Latin d) Sanskrit e) Swahili 19. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the Mongol Empire? ...
... e) Fear of the spread of the plague to China 18. Which of the following languages came into existence after 1000 as the direct result of expanding global trade patterns? a) Arabic b) Chinese c) Latin d) Sanskrit e) Swahili 19. Which of the following is an accurate statement about the Mongol Empire? ...
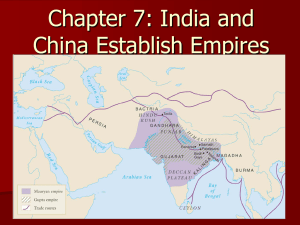
Chapter 7: India and China Establish Empires
... – Indians began to use a calendar based on sun rather than on cycles of the moon – 7 day week- broke each day into hours – Discovered earth was round, based on shadow on the moon from a lunar eclipse – zero, decimal system invented in India – had medical guides that classified 1,000 diseases and 500 ...
... – Indians began to use a calendar based on sun rather than on cycles of the moon – 7 day week- broke each day into hours – Discovered earth was round, based on shadow on the moon from a lunar eclipse – zero, decimal system invented in India – had medical guides that classified 1,000 diseases and 500 ...
Han Dynasty Packet
... to trade their new items. Little by little, goods from the East and the West made their way to the other end of the trade routes. In that way, the West eventually learned of such Chinese inventions as paper. Heavy Traffic on Cultural Highways Once China was reunited under the Tang dynasty in 618 CE, ...
... to trade their new items. Little by little, goods from the East and the West made their way to the other end of the trade routes. In that way, the West eventually learned of such Chinese inventions as paper. Heavy Traffic on Cultural Highways Once China was reunited under the Tang dynasty in 618 CE, ...
Ancient China Inventions and Technology
... Silk - Silk was a soft and light material much desired by the wealthy throughout the world. It became such a valuable export that the trade route running from Europe to China became known as the Silk Road. The Chinese learned how to make silk from the cocoons of silkworms. They managed to keep the p ...
... Silk - Silk was a soft and light material much desired by the wealthy throughout the world. It became such a valuable export that the trade route running from Europe to China became known as the Silk Road. The Chinese learned how to make silk from the cocoons of silkworms. They managed to keep the p ...
Part 3: Age of Accelerating Connections 600-1450
... – Foreigner emplolyed in bureaucracy, civil service not used – Marco Polo Ilkhanate of Persia (Hulegu: Kublai’s brother) – Persia-Baghdad: stopped in Syria by Egyptian forces Timur Lang (1370) – Aka Tamerlane – Ghengis Khan = role model – Capital Samarkand – Conquered parts of India ...
... – Foreigner emplolyed in bureaucracy, civil service not used – Marco Polo Ilkhanate of Persia (Hulegu: Kublai’s brother) – Persia-Baghdad: stopped in Syria by Egyptian forces Timur Lang (1370) – Aka Tamerlane – Ghengis Khan = role model – Capital Samarkand – Conquered parts of India ...
Lesson
... on pages 278–279.) Because these trails stretched across two continents, Europe and Asia, they were called trans-Eurasian. China was part of a huge global trade network. By 100 B.C., the Silk Roads were well established. Goods leaving China included silk, paper, and pottery. Exchange goods coming fr ...
... on pages 278–279.) Because these trails stretched across two continents, Europe and Asia, they were called trans-Eurasian. China was part of a huge global trade network. By 100 B.C., the Silk Roads were well established. Goods leaving China included silk, paper, and pottery. Exchange goods coming fr ...
Classical Review Guide
... d. Long distance trade expanded greatly during the classical period, allowing for the movement of goods and ideas. e. There’re were a few factors: The Han Empire secured the trade routes through Central Asia, the Mauryan Empire had declined in India, but regional states were able to provide the nece ...
... d. Long distance trade expanded greatly during the classical period, allowing for the movement of goods and ideas. e. There’re were a few factors: The Han Empire secured the trade routes through Central Asia, the Mauryan Empire had declined in India, but regional states were able to provide the nece ...
Page 15 Essence of China - Epoch Times | Print Archive
... Zhang Qian on his second mission to the west with the aim of forming an alliance with another nomadic tribe, the Wusun ( ૻ੪), against the Xiongnu. The Wusun lived in an area north of the Tarim Basin in what is today’s Xinjiang region in northwest China. Although the goal to form a military alliance ...
... Zhang Qian on his second mission to the west with the aim of forming an alliance with another nomadic tribe, the Wusun ( ૻ੪), against the Xiongnu. The Wusun lived in an area north of the Tarim Basin in what is today’s Xinjiang region in northwest China. Although the goal to form a military alliance ...
The Silk Road
... Magao Caves or Grottoes • Located in an Oasis within the Gobi Desert along the Silk Road • System of caves and temples dug out of limestone rock between 366 – 1002 CE • Includes 492 Buddhist temples with elaborate sculptures and artwork • A sealed cave containing thousands of manuscripts discovered ...
... Magao Caves or Grottoes • Located in an Oasis within the Gobi Desert along the Silk Road • System of caves and temples dug out of limestone rock between 366 – 1002 CE • Includes 492 Buddhist temples with elaborate sculptures and artwork • A sealed cave containing thousands of manuscripts discovered ...
Holy Roman Empire
... • In the post-classical era, Persians and Arabs dominated trade in the Indian Ocean • Connected ports in eastern Africa (Swahili Coast) with ports in Western India and the Persian Gulf • Boats used monsoon winds to travel • Safer travel in Indian Ocean compared to the Mediterranean (where warfare wa ...
... • In the post-classical era, Persians and Arabs dominated trade in the Indian Ocean • Connected ports in eastern Africa (Swahili Coast) with ports in Western India and the Persian Gulf • Boats used monsoon winds to travel • Safer travel in Indian Ocean compared to the Mediterranean (where warfare wa ...
Shirley Huang 5.17.2013 Outline # 1 Period 3 ESSAY PROMPT 1
... 10. Analyze how EAST ASIA'S relationship to global trade patterns changed from 1750 to the present. From 1750 to the present East Asian countries flourished and currently play a major role in global trade by providing other countries with many different items Japan during 1750 was still in isola ...
... 10. Analyze how EAST ASIA'S relationship to global trade patterns changed from 1750 to the present. From 1750 to the present East Asian countries flourished and currently play a major role in global trade by providing other countries with many different items Japan during 1750 was still in isola ...
The Silk Roads
... • Result a two-way fertilization: China’s neighbors were ‘Sinotized’, but Chinese culture ‘barbarized’ (Sima Qian, Ban Gu) • Similar experience at the western end of the routes: Roman elites concerned about the ‘pollution’ of pure Greco-Roman culture (Horace, Ovid) ...
... • Result a two-way fertilization: China’s neighbors were ‘Sinotized’, but Chinese culture ‘barbarized’ (Sima Qian, Ban Gu) • Similar experience at the western end of the routes: Roman elites concerned about the ‘pollution’ of pure Greco-Roman culture (Horace, Ovid) ...
Ancient History Review Early Humans Early humans were . They
... Under the Han dynasty, the civil service exam created a government run by scholars. (If you wanted a job you had to pass a test and couldn’t just be given a job based on who you know). ...
... Under the Han dynasty, the civil service exam created a government run by scholars. (If you wanted a job you had to pass a test and couldn’t just be given a job based on who you know). ...
Life Along the Silk Road - UCLA Confucius Institute
... China and met with Kublai Khan, an emperor of the Yuan Dynasty. In 1269, they returned to Venice with a letter Kublai Khan had written to Pope Clement IV. In fact, Clement IV had died the ye ...
... China and met with Kublai Khan, an emperor of the Yuan Dynasty. In 1269, they returned to Venice with a letter Kublai Khan had written to Pope Clement IV. In fact, Clement IV had died the ye ...
Silk Road

The Silk Road or Silk Route is an ancient network of trade and cultural transmission routes that were central to cultural interaction through regions of the Asian continent connecting the West and East by merchants, pilgrims, monks, soldiers, nomads, and urban dwellers from China and India to the Mediterranean Sea during various periods of time.Extending 6,000 kilometres (4,000 miles), the Silk Road derives its name from the lucrative trade in Chinese silk carried out along its length, beginning during the Han dynasty (206 BCE – 220 CE). The Central Asian sections of the trade routes were expanded around 114 BCE by the Han dynasty, largely through the missions and explorations of Chinese imperial envoy, Zhang Qian. The Chinese took great interest in the safety of their trade products and extended the Great Wall of China to ensure the protection of the trade route.Trade on the Silk Road was a significant factor in the development of the civilizations of China, the Indian subcontinent, Persia, Europe, the Horn of Africa and Arabia, opening long-distance, political and economic relations between the civilizations. Though silk was certainly the major trade item from China, many other goods were traded, and religions, syncretic philosophies, and various technologies, as well as diseases, also travelled along the Silk Routes. In addition to economic trade, the Silk Road served as a means of carrying out cultural trade among the civilizations along its network.The main traders during antiquity were the Chinese, Persians, Somalis, Greeks, Syrians, Romans, Armenians, Indians, and Bactrians, and from the 5th to the 8th century the Sogdians. Following the emergence of Islam, Arab traders became prominent.In June 2014 UNESCO designated the Chang'an-Tianshan corridor of the Silk Road as a World Heritage Site.