Fungus & Prions
... Cause disease by interfering with normal organ structure and function or by inflammation or allergy ...
... Cause disease by interfering with normal organ structure and function or by inflammation or allergy ...
Lecture 15-CNS Infections
... Dexamethasone (0.15mg/kg IV Q6h) for 2-4 days : 1st dose 15-20 min prior to or concomitant with 1st dose Abx to block TNF ...
... Dexamethasone (0.15mg/kg IV Q6h) for 2-4 days : 1st dose 15-20 min prior to or concomitant with 1st dose Abx to block TNF ...
What is diphtheria?
... diphtheria has been achieved by active immunisation with diphtheria vaccine. What is tetanus? Tetanus is an acute disease caused by spores of bacteria which can enter wounds on contaminated soil etc. Toxins produced in the body can act on the central nervous system and cause painful spasms and muscl ...
... diphtheria has been achieved by active immunisation with diphtheria vaccine. What is tetanus? Tetanus is an acute disease caused by spores of bacteria which can enter wounds on contaminated soil etc. Toxins produced in the body can act on the central nervous system and cause painful spasms and muscl ...
File
... - Last about a week - Spreads quickly and can become a local epidemic - Infects about 20% of Americans each year - 3 subtypes effect humans - Can jump from one species to another (Bird flu effecting humans) - Very similar to the flu ...
... - Last about a week - Spreads quickly and can become a local epidemic - Infects about 20% of Americans each year - 3 subtypes effect humans - Can jump from one species to another (Bird flu effecting humans) - Very similar to the flu ...
Chapter 27 Nervous System Infections
... Neisseria meningitidis. The meningococcus . A gramnegative diplococcus. There are 13 antigenic groups of N.meningitidis. Most serious infections are due to A,B,C,Y, and W135. incubation period: 1 to 7 days ...
... Neisseria meningitidis. The meningococcus . A gramnegative diplococcus. There are 13 antigenic groups of N.meningitidis. Most serious infections are due to A,B,C,Y, and W135. incubation period: 1 to 7 days ...
Fungi
... • fungal infection of the respiratory system caused by Histoplasma capsulatum • AKA reticuloendothelial cytomycosis, cave disease, spelunker’s disease, Darling’s disease • highest incidence: Ohio, Missouri and Missippi Delta • found in bird droppings and bats • airborne spores enter ventilation syst ...
... • fungal infection of the respiratory system caused by Histoplasma capsulatum • AKA reticuloendothelial cytomycosis, cave disease, spelunker’s disease, Darling’s disease • highest incidence: Ohio, Missouri and Missippi Delta • found in bird droppings and bats • airborne spores enter ventilation syst ...
Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis (Whooping Cough), Hepatitis B, Polio
... Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis (Whooping Cough), Hepatitis B, Polio, and Haemophilus Influenzae type b vaccine 1. What are Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Hepatitis B, Polio and Haemophilus Influenzae type b Diphtheria is caused by bacteria that infect the nose and throat. These bacteria release a p ...
... Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis (Whooping Cough), Hepatitis B, Polio, and Haemophilus Influenzae type b vaccine 1. What are Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis, Hepatitis B, Polio and Haemophilus Influenzae type b Diphtheria is caused by bacteria that infect the nose and throat. These bacteria release a p ...
NM Vaccination Poster
... comes from a wound and causes many complications, including paralysis and death. ...
... comes from a wound and causes many complications, including paralysis and death. ...
cns-infection
... Depending on their virulence/pathogenicity bacteria can induce: 1. Purulent lesions 2. Cellular inflammatory reactions with giant cells 3. Inflammatory oedema caused by toxins and other inflammatory substances released by bacterial secretions or lysis, in the absence of bacterial replication ...
... Depending on their virulence/pathogenicity bacteria can induce: 1. Purulent lesions 2. Cellular inflammatory reactions with giant cells 3. Inflammatory oedema caused by toxins and other inflammatory substances released by bacterial secretions or lysis, in the absence of bacterial replication ...
Article for Boyden
... They were called antibodies and were formed by lymphocytes, a cell type which is a major cellular component in lymph vessels feeding into lymph nodes. Antibody prevents infection by binding to the relevant antigen on the surface of the infecting agent and so prevents it from entering cells Some anti ...
... They were called antibodies and were formed by lymphocytes, a cell type which is a major cellular component in lymph vessels feeding into lymph nodes. Antibody prevents infection by binding to the relevant antigen on the surface of the infecting agent and so prevents it from entering cells Some anti ...
Bacterial Meningitis - Boston Public Health Commission
... Many of the viruses that cause meningitis are spread through saliva or feces. The bacteria that can cause meningitis are usually spread through contact with infected saliva. Most people may already have immunity (natural protection) against many of these germs. Most of the germs that cause meningiti ...
... Many of the viruses that cause meningitis are spread through saliva or feces. The bacteria that can cause meningitis are usually spread through contact with infected saliva. Most people may already have immunity (natural protection) against many of these germs. Most of the germs that cause meningiti ...
Respiratory diseases - Academic Resources at Missouri Western
... cough Caused by- attachment to cilia of upper resp tract, produce 5 toxins which increase mucus secretions, inhibit phagocytosis, paralyze cilia Transmission: respiratory droplets, human only known reservoir Treatment and prevention: macrolides (reduce duration, do not eliminate symptoms), ...
... cough Caused by- attachment to cilia of upper resp tract, produce 5 toxins which increase mucus secretions, inhibit phagocytosis, paralyze cilia Transmission: respiratory droplets, human only known reservoir Treatment and prevention: macrolides (reduce duration, do not eliminate symptoms), ...
Common Infectious Disease Review
... 2. What is a virus? And how do they differ from other pathogens? A virus is the smallest pathogen that can only multiply after entering a living cell. ...
... 2. What is a virus? And how do they differ from other pathogens? A virus is the smallest pathogen that can only multiply after entering a living cell. ...
The Management of Meningitis Policy Infection Prevention and Control
... It is the intention of this policy to provide guidance to ensure that staff are aware of the appropriate steps they need to undertake to ensure the safety of all patients within LPT, whether receiving healthcare in LPT inpatient facilities, within their own home environment or as outpatients visitin ...
... It is the intention of this policy to provide guidance to ensure that staff are aware of the appropriate steps they need to undertake to ensure the safety of all patients within LPT, whether receiving healthcare in LPT inpatient facilities, within their own home environment or as outpatients visitin ...
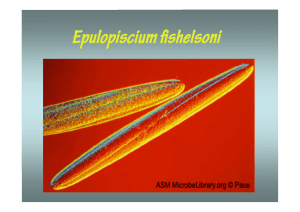
Epulopiscium fishelsoni - Academic lab pages
... Characteristics • Very large : ~600um in length, Normal E. coli is ~1um • 2000-million-folder larger in volume. Its cell wall contains many folds in order to increase surface area • Can contain 200,000 copies of the genome ...
... Characteristics • Very large : ~600um in length, Normal E. coli is ~1um • 2000-million-folder larger in volume. Its cell wall contains many folds in order to increase surface area • Can contain 200,000 copies of the genome ...
Family: Picornaviridae
... Clinically, the disease takes four forms. 1-- Asymptomatic infection: About 95% of infected ...
... Clinically, the disease takes four forms. 1-- Asymptomatic infection: About 95% of infected ...
Scientific Committee on Vaccine Preventable Diseases and
... - Young adolescents at 11-12 year old and those before high school entry that were not vaccinated before (tetravalent meningococcal A,C, Y, W-135 conjugate vaccine) - Groups at increased risk (11-55 year old): military recruits & college freshmen living in dormitories (tetravalent meningococcal A ,C ...
... - Young adolescents at 11-12 year old and those before high school entry that were not vaccinated before (tetravalent meningococcal A,C, Y, W-135 conjugate vaccine) - Groups at increased risk (11-55 year old): military recruits & college freshmen living in dormitories (tetravalent meningococcal A ,C ...
Neisseria meningitidis
.png?width=300)
Neisseria meningitidis, often referred to as meningococcus, is a gram negative bacterium that can cause meningitis and other forms of meningococcal disease such as meningococcemia, a life-threatening sepsis. The bacterium is referred to as a coccus because it is round, and more specifically, diplococcus because of its tendency to form pairs. About 10% of adults are carrier of the bacteria in their nasopharynx. As an exclusively human pathogen it is the main cause of bacterial meningitis in children and young adults, causing developmental impairment and death in about 10% of cases. It causes the only form of bacterial meningitis known to occur epidemically, mainly in Africa and Asia.N. meningitidis is spread through saliva and respiratory secretions during coughing, sneezing, kissing, and chewing on toys. It infects the cell by sticking to it with long thin extensions called pili and the surface-exposed proteins Opa and Opc and has several virulence factors.