Shavuot: - InterfaithFamily
... First Fruit) as it marks the beginning of the fruit harvest when the first ripe fruits were brought to the Temple as an offering of thanksgiving. ...
... First Fruit) as it marks the beginning of the fruit harvest when the first ripe fruits were brought to the Temple as an offering of thanksgiving. ...
a new kind of judaism
... two reasons why that has ever been questioned. One is that the Rabbis were not literalists. But that only means that in their view the Bible doesn't always mean what at first sight it appears to mean. What it does mean has to be understood in the light of the Oral Tradition. But what it does mean, so ...
... two reasons why that has ever been questioned. One is that the Rabbis were not literalists. But that only means that in their view the Bible doesn't always mean what at first sight it appears to mean. What it does mean has to be understood in the light of the Oral Tradition. But what it does mean, so ...
Principles of Judaism - Congregation Beth El–Keser Israel
... Our Rabbis taught: A man should always be gentle like Hillel, and not impatient like Shammai. It once happened that two men made a wager with each other, saying, He who goes and makes Hillel angry shall receive four hundred zuz. Said one, 'I will go and incense him.' That day was the Sabbath eve, an ...
... Our Rabbis taught: A man should always be gentle like Hillel, and not impatient like Shammai. It once happened that two men made a wager with each other, saying, He who goes and makes Hillel angry shall receive four hundred zuz. Said one, 'I will go and incense him.' That day was the Sabbath eve, an ...
What is the Tanakh? The Tanakh is composed of the Torah, Nevi`im
... division reflected in the acronym “Tanakh” is well attested to in documents from the Second Beit HaMikdash period. During that period, however, “Tanakh” was not used as a word or term. Instead, the proper title was Miqra, because the biblical texts were read publicly. Miqra continues to be used in H ...
... division reflected in the acronym “Tanakh” is well attested to in documents from the Second Beit HaMikdash period. During that period, however, “Tanakh” was not used as a word or term. Instead, the proper title was Miqra, because the biblical texts were read publicly. Miqra continues to be used in H ...
Understanding the Shabbat Service
... Because a day on the Jewish calendar starts at sunset, we mark the beginning of Shabbat on Friday evenings by lighting candles, accompanied by a prayer. While many families do this at home, it is our tradition to also light candles in the synagogue. The Friday evening service is called Kabbalat Shab ...
... Because a day on the Jewish calendar starts at sunset, we mark the beginning of Shabbat on Friday evenings by lighting candles, accompanied by a prayer. While many families do this at home, it is our tradition to also light candles in the synagogue. The Friday evening service is called Kabbalat Shab ...
ecum-chapter-2-power-point
... Faith and obedience of Abraham to leave Ur, Mesopotamia with Sarah Settled in Fertile Crescent & 3 promises fulfilled (land = Canaan, people = Isaac to habiru to Hebrews, blessing = later with Law and Covenants) Nomadic and foreign controlled to agricultural to Egyptian slaves to covenantal pe ...
... Faith and obedience of Abraham to leave Ur, Mesopotamia with Sarah Settled in Fertile Crescent & 3 promises fulfilled (land = Canaan, people = Isaac to habiru to Hebrews, blessing = later with Law and Covenants) Nomadic and foreign controlled to agricultural to Egyptian slaves to covenantal pe ...
ECUM Chapter 2: Judaism Power Point
... Faith and obedience of Abraham to leave Ur, Mesopotamia with Sarah Settled in Fertile Crescent & 3 promises fulfilled (land = Canaan, people = Isaac to habiru to Hebrews, blessing = later with Law and Covenants) Nomadic and foreign controlled to agricultural to Egyptian slaves to covenantal pe ...
... Faith and obedience of Abraham to leave Ur, Mesopotamia with Sarah Settled in Fertile Crescent & 3 promises fulfilled (land = Canaan, people = Isaac to habiru to Hebrews, blessing = later with Law and Covenants) Nomadic and foreign controlled to agricultural to Egyptian slaves to covenantal pe ...
Chapter 2, Section 4
... Temple built by Solomon in Jerusalem; became a political & religious center Oral tradition began to be written down as Torah = law or instructions Power and comfort led to secularism so God sent prophets like Samuel & Nathan to call back to covenant & monotheism away from idolatry Kingdom divided; c ...
... Temple built by Solomon in Jerusalem; became a political & religious center Oral tradition began to be written down as Torah = law or instructions Power and comfort led to secularism so God sent prophets like Samuel & Nathan to call back to covenant & monotheism away from idolatry Kingdom divided; c ...
Matthew and the Torah in Jewish society
... nations. The synagogue activities played an important role in this self-affirmation (Knight 2004:11). It was at this point that the distinction between Judaism in its diversity and Israelite religion became evident.6 Specific interpretation of the Torah was used to assure Jewish exclusivity and crea ...
... nations. The synagogue activities played an important role in this self-affirmation (Knight 2004:11). It was at this point that the distinction between Judaism in its diversity and Israelite religion became evident.6 Specific interpretation of the Torah was used to assure Jewish exclusivity and crea ...
Session 2 – Modern Day Judaism
... to traditional Jewish monotheism, but would emphasized ethical behavior almost to the exclusion of ritual. For the most part the Talmud was rejected, Reformed rabbis prefer the ethical teachings of the Prophets (good for them). ...
... to traditional Jewish monotheism, but would emphasized ethical behavior almost to the exclusion of ritual. For the most part the Talmud was rejected, Reformed rabbis prefer the ethical teachings of the Prophets (good for them). ...
RLST 124I: Varieties of Ancient Judaism
... “Tannaitic midrashim” (Mekhilta of R. Ishmael [Exodus], Sifra [Leviticus], Sifre to Numbers, Sifre to Deuteronomy): commentaries of the Torah executed around (or soon after) the compilation of the Mishnah, primarily concerned with legal interpretations Midrash Rabbah: rabbinic commentaries on Genesi ...
... “Tannaitic midrashim” (Mekhilta of R. Ishmael [Exodus], Sifra [Leviticus], Sifre to Numbers, Sifre to Deuteronomy): commentaries of the Torah executed around (or soon after) the compilation of the Mishnah, primarily concerned with legal interpretations Midrash Rabbah: rabbinic commentaries on Genesi ...
Methods to maintain Judaism`s most sacred texts
... scribe or a conservative scribe, you follow the exact same set of laws and the same set of traditions." Jews trace this tradition back to Moses, who is believed to have been the first scribe. ...
... scribe or a conservative scribe, you follow the exact same set of laws and the same set of traditions." Jews trace this tradition back to Moses, who is believed to have been the first scribe. ...
Judaism
... memorialized for all Jews, at least until the twentieth century. Of course, Judaism continued to operate in history, but historical events became less important as symbols for Judaism as a religion. Textual and religious practices began to replace more straightforward political developments. After ...
... memorialized for all Jews, at least until the twentieth century. Of course, Judaism continued to operate in history, but historical events became less important as symbols for Judaism as a religion. Textual and religious practices began to replace more straightforward political developments. After ...
Archived Articles
... such practices. Jesus was the first "Christian," who had come to announce the end of the Torah and Judaism. Draining Jesus of his Jewishness reached its unfortunate peak with the rise of Nazism when Jesus was even cast by some as an Aryan! However, ever since the end of World War II, the Jewishness ...
... such practices. Jesus was the first "Christian," who had come to announce the end of the Torah and Judaism. Draining Jesus of his Jewishness reached its unfortunate peak with the rise of Nazism when Jesus was even cast by some as an Aryan! However, ever since the end of World War II, the Jewishness ...
Judaism and the New Testament Faith
... practice largely remained in the fashion of the established churches, but in recent years a sharpening of that ideology has been occurring. The UMJC in particular has defined Messianic Judaism in solidarity with the church and with Judaism. The UMJC has embraced Torah faithfulness as an obligation ...
... practice largely remained in the fashion of the established churches, but in recent years a sharpening of that ideology has been occurring. The UMJC in particular has defined Messianic Judaism in solidarity with the church and with Judaism. The UMJC has embraced Torah faithfulness as an obligation ...
Shavuot Study Guide - Edythe Mencher
... reading and studying a variety of sacred texts. Traditionally, readings from the Torah and Talmud are included. Many synagogues hold a Tikkun Leil Shavuot. Some host programs that go on all night, culminating in morning services at sunrise. Other congregations gather for a few hours of study. Whethe ...
... reading and studying a variety of sacred texts. Traditionally, readings from the Torah and Talmud are included. Many synagogues hold a Tikkun Leil Shavuot. Some host programs that go on all night, culminating in morning services at sunrise. Other congregations gather for a few hours of study. Whethe ...
Chapter 2 Judaism
... the 40 years it took to return to Canaan from Egypt? • The Hebrews became a convenantal community, owing their allegiance to God. ...
... the 40 years it took to return to Canaan from Egypt? • The Hebrews became a convenantal community, owing their allegiance to God. ...
New Testament History - Rocky Mountain Christian
... Temple, Herod's .......................................................................................................................................28 Herodians ........................................................................................................................................ ...
... Temple, Herod's .......................................................................................................................................28 Herodians ........................................................................................................................................ ...
Augustus - Rocky Mountain Christian Institute
... Temple, Herod's ....................................................................................................................................... 28 Herodians ....................................................................................................................................... ...
... Temple, Herod's ....................................................................................................................................... 28 Herodians ....................................................................................................................................... ...
What is the Talmud? - Becoming Jewish.Org
... at Mount Sinai at the time that the Written Torah was transmitted. The Mishnah was kept in the oral tradition until it was written down in the time of Rabbi Judah the Holy (aka Rabbi Judah the Prince) ca. 130-220CE. It was written down to help ensure that in the time of duress and danger that it wou ...
... at Mount Sinai at the time that the Written Torah was transmitted. The Mishnah was kept in the oral tradition until it was written down in the time of Rabbi Judah the Holy (aka Rabbi Judah the Prince) ca. 130-220CE. It was written down to help ensure that in the time of duress and danger that it wou ...
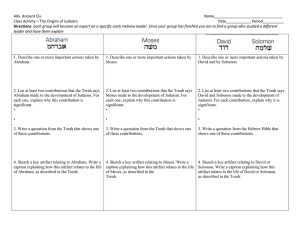
Adv. Ancient Civ. Name_________________________________
... the religion of the Jewish people and is one of the world’s most influential religious traditions. The origins of Judaism and its basic teachings and laws are recorded in its most sacred text, the Torah. The word Torah means “teaching.” The Torah consists of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible. ...
... the religion of the Jewish people and is one of the world’s most influential religious traditions. The origins of Judaism and its basic teachings and laws are recorded in its most sacred text, the Torah. The word Torah means “teaching.” The Torah consists of the first five books of the Hebrew Bible. ...
Chapter 2 Judaism
... Faith and obedience of Abraham to leave Ur, Mesopotamia with Sarah Settled in Fertile Crescent & 3 promises fulfilled (land = Canaan, people = Isaac to habiru to Hebrews, blessing = later with Law and Covenants) Nomadic and foreign controlled to agricultural to Egyptian slaves to covenantal pe ...
... Faith and obedience of Abraham to leave Ur, Mesopotamia with Sarah Settled in Fertile Crescent & 3 promises fulfilled (land = Canaan, people = Isaac to habiru to Hebrews, blessing = later with Law and Covenants) Nomadic and foreign controlled to agricultural to Egyptian slaves to covenantal pe ...
Introduction – Rabbinic Judaism
... Men of the Great Assembly…” Mishnah Avot 1:1 Judaism is often believed to be a religion based primarily in the Hebrew Bible, or even more specifically, the first five books of the Bible, known in Jewish tradition as the Torah. These five books, in the form of a Torah scroll, are found in nearly ever ...
... Men of the Great Assembly…” Mishnah Avot 1:1 Judaism is often believed to be a religion based primarily in the Hebrew Bible, or even more specifically, the first five books of the Bible, known in Jewish tradition as the Torah. These five books, in the form of a Torah scroll, are found in nearly ever ...
Simchat Torah - faithtutorials.co.uk
... the story of the Jewish people and G-d who looks after them. The laws that Jews aim to live by can be found in the Torah; most notably the 10 Commandments which Moses revealed to the people on Mount Sinai. These laws are not just seen as ways to live a good life but as revelation of G-d’s will for h ...
... the story of the Jewish people and G-d who looks after them. The laws that Jews aim to live by can be found in the Torah; most notably the 10 Commandments which Moses revealed to the people on Mount Sinai. These laws are not just seen as ways to live a good life but as revelation of G-d’s will for h ...