Vocabulary, Economic terms, page 99
... but fell against the Japanese yen. The new currency will be pegged to the US dollar (= the value of the new currency will be linked to the value of the dollar). common/domestic/foreign/local/national currency a stable/strong/volatile/weak currency to buy/change/exchange/sell currency to devalue/depr ...
... but fell against the Japanese yen. The new currency will be pegged to the US dollar (= the value of the new currency will be linked to the value of the dollar). common/domestic/foreign/local/national currency a stable/strong/volatile/weak currency to buy/change/exchange/sell currency to devalue/depr ...
Chapter 29
... 4. What forces move exchange rates in the very short run? In the short run? 5. “A weak currency is a sign of a sick economy.” True or false? Explain. 6. What is purchasing power parity? Why might exchange rates deviate from purchasing power parity? 7. Suppose the purchasing power parity exchange rat ...
... 4. What forces move exchange rates in the very short run? In the short run? 5. “A weak currency is a sign of a sick economy.” True or false? Explain. 6. What is purchasing power parity? Why might exchange rates deviate from purchasing power parity? 7. Suppose the purchasing power parity exchange rat ...
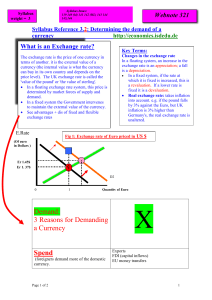
Demand for a currency - yELLOWSUBMARINER.COM
... Changes in the exchange rate In a floating system, an increase in the exchange rate is an appreciation; a fall is a depreciation. In a fixed system, if the rate at which it is fixed is increased, this is a revaluation. If a lower rate is fixed it is a devaluation. Real exchange rate: takes infla ...
... Changes in the exchange rate In a floating system, an increase in the exchange rate is an appreciation; a fall is a depreciation. In a fixed system, if the rate at which it is fixed is increased, this is a revaluation. If a lower rate is fixed it is a devaluation. Real exchange rate: takes infla ...
4.6 B More on Exchange Rates
... occurs, this imbalance adjusts the exchange rate automatically to counteract that change. But – regardless of how the CA is changing, International flows of money in the capital account may affect the exchange rate, and thus worsen the current account unintentionally. 2. No need to employ monetary ...
... occurs, this imbalance adjusts the exchange rate automatically to counteract that change. But – regardless of how the CA is changing, International flows of money in the capital account may affect the exchange rate, and thus worsen the current account unintentionally. 2. No need to employ monetary ...
A country`s current account • balance equals the change
... A country’s current account balance equals the change in its net foreign wealth What accounts for most of the activity in the foreign exchange market Inter-Bank trading A foreign exchange swap is a spot sale of a currency combined with a forward repurchase of the currency Covered interest pari ...
... A country’s current account balance equals the change in its net foreign wealth What accounts for most of the activity in the foreign exchange market Inter-Bank trading A foreign exchange swap is a spot sale of a currency combined with a forward repurchase of the currency Covered interest pari ...
Chapter 3 Review
... Completion 9. The primary effects on a country’s level of economic development are its literacy level, agricultural dependency, and _________________________. 10. Making, buying, and selling goods and services within a country is referred to as _______________________. 11. When a country can produce ...
... Completion 9. The primary effects on a country’s level of economic development are its literacy level, agricultural dependency, and _________________________. 10. Making, buying, and selling goods and services within a country is referred to as _______________________. 11. When a country can produce ...
Exchange Rates - Continental Economics
... Price relations are the inverse of the exchange relation 3 beer/1pack of cigarettes means that cigarettes cost three times more than one beer One can also say: 3 beer exchange for 1 pack of cigarettes in a barter Thus exchange rates are prices and are linked to the exchange ratios of goods ...
... Price relations are the inverse of the exchange relation 3 beer/1pack of cigarettes means that cigarettes cost three times more than one beer One can also say: 3 beer exchange for 1 pack of cigarettes in a barter Thus exchange rates are prices and are linked to the exchange ratios of goods ...
Monetary Intergration
... • in the first equilibrium local pricing; foreign price determined by the Law of One Price. Optimal policy rules then target the domestic output gap and floating exchange rates support the flex-price allocation. • in the second equilibrium local pricing; a monetary union is the optimal policy choice ...
... • in the first equilibrium local pricing; foreign price determined by the Law of One Price. Optimal policy rules then target the domestic output gap and floating exchange rates support the flex-price allocation. • in the second equilibrium local pricing; a monetary union is the optimal policy choice ...
PDF Download
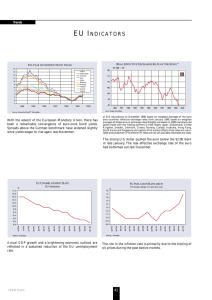
... area countries’ effective exchange rates; from January 1999, based on weighted averages of bilateral euro exchange rates. Weights are based on 1990 manufactured goods trade with the trading partners United States, Japan, Switzerland, United Kingdom, Sweden, Denmark, Greece, Norway, Canada, Australia ...
... area countries’ effective exchange rates; from January 1999, based on weighted averages of bilateral euro exchange rates. Weights are based on 1990 manufactured goods trade with the trading partners United States, Japan, Switzerland, United Kingdom, Sweden, Denmark, Greece, Norway, Canada, Australia ...
AP Macroeconomics Study Guide for Unit 7, The
... expected to calculate these balances or other balances, like the balance of payments on goods and services. Which transactions, those falling under the current account or those falling under the financial account, create liabilities that must be paid in the future? What is the basic rule of balance ...
... expected to calculate these balances or other balances, like the balance of payments on goods and services. Which transactions, those falling under the current account or those falling under the financial account, create liabilities that must be paid in the future? What is the basic rule of balance ...
The Euro: Past and Future
... Motivated the European Economic Community to create a monetary system not dependant on the US dollar. ...
... Motivated the European Economic Community to create a monetary system not dependant on the US dollar. ...
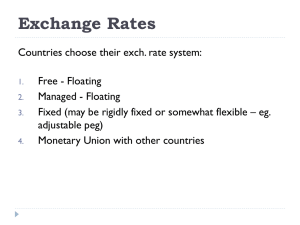
Exchange-Rates
... Fixed (may be rigidly fixed or somewhat flexible – eg. adjustable peg) Monetary Union with other countries ...
... Fixed (may be rigidly fixed or somewhat flexible – eg. adjustable peg) Monetary Union with other countries ...
FM.2 Currency Exchange - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... It also shows that the bank will pay customers C$0.9957 for each American dollar. (a) Calculate the value of C$500 in US currency. (b) Calculate the amount of Canadian currency you will receive if you immediately exchange the amount of US currency in (a) back to Canadian currency. ...
... It also shows that the bank will pay customers C$0.9957 for each American dollar. (a) Calculate the value of C$500 in US currency. (b) Calculate the amount of Canadian currency you will receive if you immediately exchange the amount of US currency in (a) back to Canadian currency. ...
ECB and EMU Exchange Rates
... multinational company in one country has spare cash and another branch in a different country is in need of cash, then they will transfer the spare cash to save interest charges on overdrafts. This will create a supply of one currency, bringing down its value, and a demand for the other, increasing ...
... multinational company in one country has spare cash and another branch in a different country is in need of cash, then they will transfer the spare cash to save interest charges on overdrafts. This will create a supply of one currency, bringing down its value, and a demand for the other, increasing ...
Exchange rate
.jpg?width=300)
In finance, an exchange rate (also known as a foreign-exchange rate, forex rate, FX rate or Agio) between two currencies is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another. It is also regarded as the value of one country’s currency in terms of another currency. For example, an interbank exchange rate of 119 Japanese yen (JPY, ¥) to the United States dollar (US$) means that ¥119 will be exchanged for each US$1 or that US$1 will be exchanged for each ¥119. In this case it is said that the price of a dollar in terms of yen is ¥119, or equivalently that the price of a yen in terms of dollars is $1/119.Exchange rates are determined in the foreign exchange market, which is open to a wide range of different types of buyers and sellers where currency trading is continuous: 24 hours a day except weekends, i.e. trading from 20:15 GMT on Sunday until 22:00 GMT Friday. The spot exchange rate refers to the current exchange rate. The forward exchange rate refers to an exchange rate that is quoted and traded today but for delivery and payment on a specific future date.In the retail currency exchange market, a different buying rate and selling rate will be quoted by money dealers. Most trades are to or from the local currency. The buying rate is the rate at which money dealers will buy foreign currency, and the selling rate is the rate at which they will sell the currency. The quoted rates will incorporate an allowance for a dealer's margin (or profit) in trading, or else the margin may be recovered in the form of a commission or in some other way. Different rates may also be quoted for cash (usually notes only), a documentary form (such as traveler's cheques) or electronically (such as a credit card purchase). The higher rate on documentary transactions has been justified to compensate for the additional time and cost of clearing the document, while the cash is available for resale immediately. Some dealers on the other hand prefer documentary transactions because of the security concerns with cash.