MACROECONOMICS 1. A supply curve slopes upward - FBLA-PBL
... b. the quantity supplied of most goods and services increases over time c. an increase in price gives producers an incentive to supply a larger quantity d. as more is produced, total cost of production falls 2. The aggregate demand curve, when plotted against price: a. slopes upwards because all gov ...
... b. the quantity supplied of most goods and services increases over time c. an increase in price gives producers an incentive to supply a larger quantity d. as more is produced, total cost of production falls 2. The aggregate demand curve, when plotted against price: a. slopes upwards because all gov ...
3.E Money in the European Union High School Lesson Plan
... manipulate and transform units appropriately when multiplying or dividing quantities. Materials needed: Euro Coins PowerPoint Currency Exchange Worksheet Why the euro? Via Europa Current exchange rate information, which can be found at websites including: http://money.cnn.com/data/currencies/ ...
... manipulate and transform units appropriately when multiplying or dividing quantities. Materials needed: Euro Coins PowerPoint Currency Exchange Worksheet Why the euro? Via Europa Current exchange rate information, which can be found at websites including: http://money.cnn.com/data/currencies/ ...
Home Economics - Green Economist
... stakes in two banks • Why £1bn. From taxpayers?—for highrisk securitised loans? ...
... stakes in two banks • Why £1bn. From taxpayers?—for highrisk securitised loans? ...
Chapter 3
... system, allowed for changes in exchange rates when economic circumstances required such changes. Therefore, the system can be considered as an “adjustable peg.” The system may also be thought as a “gold exchange standard” since the key currency, the dollar, was convertible into gold for official hol ...
... system, allowed for changes in exchange rates when economic circumstances required such changes. Therefore, the system can be considered as an “adjustable peg.” The system may also be thought as a “gold exchange standard” since the key currency, the dollar, was convertible into gold for official hol ...
Exchange Rate
... Kong SAR (4.1%). The share of the top five global FX trading centres moved up by 4 percentage points to 75% in ...
... Kong SAR (4.1%). The share of the top five global FX trading centres moved up by 4 percentage points to 75% in ...
Слайд 1 - English Studies
... PPP is an economic theory and a technique used to determine the relative value of currencies, estimating the amount of adjustment needed on the exchange rate between countries in order for the exchange to be equivalent to (or on par with) each currency's purchasing power. It asks how much money woul ...
... PPP is an economic theory and a technique used to determine the relative value of currencies, estimating the amount of adjustment needed on the exchange rate between countries in order for the exchange to be equivalent to (or on par with) each currency's purchasing power. It asks how much money woul ...
Exchange Rates - Uniservity CLC
... Trade flows and capital flows are the main factors affecting the exchange rate In the long run it is the macro economic performance of the economy (including trends in competitiveness) that drives the value of the currency No pre-determined official target for the exchange rate is set by the Governm ...
... Trade flows and capital flows are the main factors affecting the exchange rate In the long run it is the macro economic performance of the economy (including trends in competitiveness) that drives the value of the currency No pre-determined official target for the exchange rate is set by the Governm ...
New Keynesian Economics
... • The interest rate term might seem counter-intuitive; but, recall that the real rate is assumed to be constant so a rise in i means an increase in expected inflation, which, in turn, reduces the desirability of holding home’s currency • Also, for a country that is not inflating, rising rates of GDP ...
... • The interest rate term might seem counter-intuitive; but, recall that the real rate is assumed to be constant so a rise in i means an increase in expected inflation, which, in turn, reduces the desirability of holding home’s currency • Also, for a country that is not inflating, rising rates of GDP ...
Downlaod File
... (and experience a decline in inflation and interest rates as a result), how will their currency values (relative to the U.S. dollar) be affected? ANSWER: There will be a relative decline in Asian economic growth that will reduce Asian demand for U.S. products, which will place an upward pressure on ...
... (and experience a decline in inflation and interest rates as a result), how will their currency values (relative to the U.S. dollar) be affected? ANSWER: There will be a relative decline in Asian economic growth that will reduce Asian demand for U.S. products, which will place an upward pressure on ...
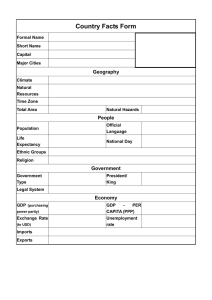
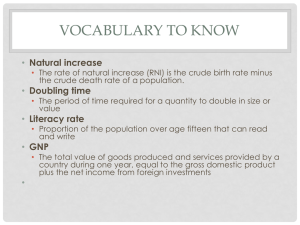
Demography Vocabulary
... country during one year, equal to the gross domestic product plus the net income from foreign investments ...
... country during one year, equal to the gross domestic product plus the net income from foreign investments ...
Document
... Ex. a preference for Japanese goods creates an increase in the supply of dollars in the currency exchange market which leads to depreciation of the Dollar and an appreciation of Yen ...
... Ex. a preference for Japanese goods creates an increase in the supply of dollars in the currency exchange market which leads to depreciation of the Dollar and an appreciation of Yen ...
SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY Department of Economics Econ 345 Prof. Kasa
... 2. Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market predicts that interest rates and exchange rates (defined as the price of foreign currency) are negatively correlated. 3. According to the Balassa-Samuelson theory of real exchange rates, rapid productivity growth in the tradeable goods sector produces an ...
... 2. Equilibrium in the foreign exchange market predicts that interest rates and exchange rates (defined as the price of foreign currency) are negatively correlated. 3. According to the Balassa-Samuelson theory of real exchange rates, rapid productivity growth in the tradeable goods sector produces an ...
Macro_5.2-_Foreign_Exchange_FOREX
... What happens if you need less dollar to buy one euro (the price for a euro decreases)? Ex: From $3= €2 to $1= €2 •The U.S. Dollar APPRECIATES relative to the euro. Appreciation- The increase of value of a country's currency with respect to a foreign currency •Less units of dollars are needed to buy ...
... What happens if you need less dollar to buy one euro (the price for a euro decreases)? Ex: From $3= €2 to $1= €2 •The U.S. Dollar APPRECIATES relative to the euro. Appreciation- The increase of value of a country's currency with respect to a foreign currency •Less units of dollars are needed to buy ...
The most visible roots of the crisis were the excess capital inflows
... Servicing this debt soon became an increasing problem, as it was dollar denominated and required dollar denominated debt service. The Russian current account (while a healthy surplus of $15 - $20 billion per year) was not finding its way into internal investment and external debt service. Capi ...
... Servicing this debt soon became an increasing problem, as it was dollar denominated and required dollar denominated debt service. The Russian current account (while a healthy surplus of $15 - $20 billion per year) was not finding its way into internal investment and external debt service. Capi ...
chapter 29
... 4. In the very short run, exchange rates move mainly due to changes in interest rates and expectations of future exchanges rates since these forces drive hot money. In the short run, business cycles account for most of the change in exchange rates. Countries with higher relative GDPs demand more for ...
... 4. In the very short run, exchange rates move mainly due to changes in interest rates and expectations of future exchanges rates since these forces drive hot money. In the short run, business cycles account for most of the change in exchange rates. Countries with higher relative GDPs demand more for ...
Chapter 33: International Finance
... of the yuan, and thereby reducing the pressure on the yuan to rise. 28. a. This is an enormous change. In order to bring it about, the Never-Never government would have to run an enormously expansionary monetary policy, reducing the real interest rate possibly to negative amounts and probably genera ...
... of the yuan, and thereby reducing the pressure on the yuan to rise. 28. a. This is an enormous change. In order to bring it about, the Never-Never government would have to run an enormously expansionary monetary policy, reducing the real interest rate possibly to negative amounts and probably genera ...
Chapter 33: International Finance
... of the yuan, and thereby reducing the pressure on the yuan to rise. 28. a. This is an enormous change. In order to bring it about, the Never-Never government would have to run an enormously expansionary monetary policy, reducing the real interest rate possibly to negative amounts and probably genera ...
... of the yuan, and thereby reducing the pressure on the yuan to rise. 28. a. This is an enormous change. In order to bring it about, the Never-Never government would have to run an enormously expansionary monetary policy, reducing the real interest rate possibly to negative amounts and probably genera ...
Exchange rate
.jpg?width=300)
In finance, an exchange rate (also known as a foreign-exchange rate, forex rate, FX rate or Agio) between two currencies is the rate at which one currency will be exchanged for another. It is also regarded as the value of one country’s currency in terms of another currency. For example, an interbank exchange rate of 119 Japanese yen (JPY, ¥) to the United States dollar (US$) means that ¥119 will be exchanged for each US$1 or that US$1 will be exchanged for each ¥119. In this case it is said that the price of a dollar in terms of yen is ¥119, or equivalently that the price of a yen in terms of dollars is $1/119.Exchange rates are determined in the foreign exchange market, which is open to a wide range of different types of buyers and sellers where currency trading is continuous: 24 hours a day except weekends, i.e. trading from 20:15 GMT on Sunday until 22:00 GMT Friday. The spot exchange rate refers to the current exchange rate. The forward exchange rate refers to an exchange rate that is quoted and traded today but for delivery and payment on a specific future date.In the retail currency exchange market, a different buying rate and selling rate will be quoted by money dealers. Most trades are to or from the local currency. The buying rate is the rate at which money dealers will buy foreign currency, and the selling rate is the rate at which they will sell the currency. The quoted rates will incorporate an allowance for a dealer's margin (or profit) in trading, or else the margin may be recovered in the form of a commission or in some other way. Different rates may also be quoted for cash (usually notes only), a documentary form (such as traveler's cheques) or electronically (such as a credit card purchase). The higher rate on documentary transactions has been justified to compensate for the additional time and cost of clearing the document, while the cash is available for resale immediately. Some dealers on the other hand prefer documentary transactions because of the security concerns with cash.