Person Perceptions & Attributions
... another person based on a first impression. – If 1st impression positive we’ll be more likely to get to know them. – We’ll interpret a person’s future behaviors more positively if their first impressions was a good one. ...
... another person based on a first impression. – If 1st impression positive we’ll be more likely to get to know them. – We’ll interpret a person’s future behaviors more positively if their first impressions was a good one. ...
Study Guide 1
... anchoring heuristic. Explain the halo effect, the positivity effect, and the negativity effect. Explain the actor-observer effect. ...
... anchoring heuristic. Explain the halo effect, the positivity effect, and the negativity effect. Explain the actor-observer effect. ...
chpt. 16 ppt.
... and views about themselves – Unified self-schemas – regard their attributes as stable across every situation and role – Differentiated self-schemas – regard their attributes as changing in different roles or situations ...
... and views about themselves – Unified self-schemas – regard their attributes as stable across every situation and role – Differentiated self-schemas – regard their attributes as changing in different roles or situations ...
File
... • She used the research method of naturalistic observation • Collect information like most people do in everyday life-only more carefully and more systematically ...
... • She used the research method of naturalistic observation • Collect information like most people do in everyday life-only more carefully and more systematically ...
CHAPTER 2
... Discuss how Asch's research on central and peripheral traits support his view that forming impressions involves more than simply adding together individual traits. ...
... Discuss how Asch's research on central and peripheral traits support his view that forming impressions involves more than simply adding together individual traits. ...
Module 16.1 Perceiving Others Lecture Outline
... A. Subfield dealing with the influence of our social interactions on thoughts, feelings, and behaviors II. Social Perception (Concept Chart 16.1) A. Process of forming impressions, judgments, and attitudes about people and events in our social world III. Impression Formation: Why First Impressions C ...
... A. Subfield dealing with the influence of our social interactions on thoughts, feelings, and behaviors II. Social Perception (Concept Chart 16.1) A. Process of forming impressions, judgments, and attitudes about people and events in our social world III. Impression Formation: Why First Impressions C ...
chapter 17 - Cengage Learning
... and behaviors are inconsistent (or “dissonant”), people feel uneasy and are motivated to make them consistent. One way to do so is to change the inconsistent attitude. 3. Self-Perception Theory. The self-perception theory suggests that when situations occur in which people are unsure about their att ...
... and behaviors are inconsistent (or “dissonant”), people feel uneasy and are motivated to make them consistent. One way to do so is to change the inconsistent attitude. 3. Self-Perception Theory. The self-perception theory suggests that when situations occur in which people are unsure about their att ...
part I - Educational Psychology Interactive
... teachers (two confederates and one naive participant) • One confederate was instructed to refuse to continue after 150 volts, and the other confederate after 210 volts • In this situation, 36 out of 40 naive participants defied the experimenter before the maximum shock could be given • The presence ...
... teachers (two confederates and one naive participant) • One confederate was instructed to refuse to continue after 150 volts, and the other confederate after 210 volts • In this situation, 36 out of 40 naive participants defied the experimenter before the maximum shock could be given • The presence ...
Social Psychology
... The result of social categorization is stereotyping, prejudice, and discrimination. Stereotyping (Cognitive) – we assign common characteristics to all members of a social categorized group. Prejudice (Emotional) – we develop negative attitudes toward members of the outgroup Discrimination (Behaviora ...
... The result of social categorization is stereotyping, prejudice, and discrimination. Stereotyping (Cognitive) – we assign common characteristics to all members of a social categorized group. Prejudice (Emotional) – we develop negative attitudes toward members of the outgroup Discrimination (Behaviora ...
Chapter 4
... Knowledge of predictor bias Refers to the positive expectation and subsequent differential treatment by managers or co-workers that is based on knowledge of valid performance indicators For example, a new employee is known to be an excellent performer from their previous employment. Stereotyping The ...
... Knowledge of predictor bias Refers to the positive expectation and subsequent differential treatment by managers or co-workers that is based on knowledge of valid performance indicators For example, a new employee is known to be an excellent performer from their previous employment. Stereotyping The ...
Lecture 11. Social psychology
... themselves, they turn to social comparison, using others as criteria against which to judge themselves. Ê Categories of people that are habitually used for social comparison are known as reference groups. ...
... themselves, they turn to social comparison, using others as criteria against which to judge themselves. Ê Categories of people that are habitually used for social comparison are known as reference groups. ...
Psychological origins of attraction
... problem to other cultures) It is also possible that we conform our behavior in order to be liked. (social identity theory) It is possible that we are attracted to people with complementary traits (e.g someone dominant needs someone submissive) However, little research supports this idea. Research is ...
... problem to other cultures) It is also possible that we conform our behavior in order to be liked. (social identity theory) It is possible that we are attracted to people with complementary traits (e.g someone dominant needs someone submissive) However, little research supports this idea. Research is ...
Social Cognition
... • Modeling (Bandura, Skinner)– children learn from their parents what one should believe and feel about certain objects • Classical Conditioning (Pavlov)– people are more likely to form a positive attitude toward an object when it is paired with stimuli that elicit good feelings • Mere-exposure effe ...
... • Modeling (Bandura, Skinner)– children learn from their parents what one should believe and feel about certain objects • Classical Conditioning (Pavlov)– people are more likely to form a positive attitude toward an object when it is paired with stimuli that elicit good feelings • Mere-exposure effe ...
Sociology in Pleasantville
... Sociology of Pleasantville Social Contract - “an agreement, entered into by individuals implicitly, that results in the formation of the state or of organized society, the prime motive being the desire for protection, which entails the surrender of some personal liberties” Everything will be “Pleasa ...
... Sociology of Pleasantville Social Contract - “an agreement, entered into by individuals implicitly, that results in the formation of the state or of organized society, the prime motive being the desire for protection, which entails the surrender of some personal liberties” Everything will be “Pleasa ...
What is social psychology?
... What is social psychology? The scientific study of the ways in which the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of an individual are influenced by the real or imagined behavior of others. ...
... What is social psychology? The scientific study of the ways in which the thoughts, feelings, and behaviors of an individual are influenced by the real or imagined behavior of others. ...
NURS 1120 LILO Chp 3 (Cristina)
... d. Position 4: The issue isn’t as important as it seems: helps you realize that the controversy isn’t as critical as you thought e. Conclusion: There is truth in all four perspectives : recognizing that each of them has some merit ...
... d. Position 4: The issue isn’t as important as it seems: helps you realize that the controversy isn’t as critical as you thought e. Conclusion: There is truth in all four perspectives : recognizing that each of them has some merit ...
Social Psychology
... information about others and to formulate inferences from that information First Impressions: First Information ones learns about another ...
... information about others and to formulate inferences from that information First Impressions: First Information ones learns about another ...
ch_3 - Home - KSU Faculty Member websites
... 3- stereotypes beliefs that all members of specific group share similar traits and are prone to behave the same way. ...
... 3- stereotypes beliefs that all members of specific group share similar traits and are prone to behave the same way. ...
Social Cognition
... • Modeling (Bandura, Skinner)– children learn from their parents what one should believe and feel about certain objects • Classical Conditioning (Pavlov)– people are more likely to form a positive attitude toward an object when it is paired with stimuli that elicit good feelings • Mere-exposure effe ...
... • Modeling (Bandura, Skinner)– children learn from their parents what one should believe and feel about certain objects • Classical Conditioning (Pavlov)– people are more likely to form a positive attitude toward an object when it is paired with stimuli that elicit good feelings • Mere-exposure effe ...
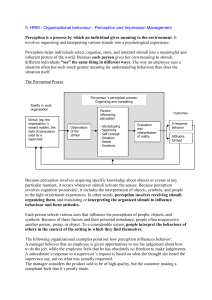
Perception and impression management
... Each person selects various cues that influence his perceptions of people, objects, and symbols. Because of these factors and their potential imbalance, people often misperceive another person, group, or object. To a considerable extent, people interpret the behaviour of others in the context of the ...
... Each person selects various cues that influence his perceptions of people, objects, and symbols. Because of these factors and their potential imbalance, people often misperceive another person, group, or object. To a considerable extent, people interpret the behaviour of others in the context of the ...
View Presentation
... People in all cultures seem to share the correspondence bias (tendency to infer behaviors as due to dispositions) But people in non-Western cultures are more likely to take situational and contextual information into account ...
... People in all cultures seem to share the correspondence bias (tendency to infer behaviors as due to dispositions) But people in non-Western cultures are more likely to take situational and contextual information into account ...
Social Development (Chapter 13)
... good team”, losing because they were “lucky” or you “did not get the bounces” • Self-handicapping is the opposite, e.g., pass a test because “it was easy”, fail “because I am stupid” ...
... good team”, losing because they were “lucky” or you “did not get the bounces” • Self-handicapping is the opposite, e.g., pass a test because “it was easy”, fail “because I am stupid” ...
Document
... PASSIVE STRATEGIES: we take the role of unobtrusive observers and do not participate in the situation. ACTIVE STRATEGIES: we actively seek information by asking questions about the individual. INTERACTIVE STRATEGIES: we communicate directly with the person by asking questions etc. ...
... PASSIVE STRATEGIES: we take the role of unobtrusive observers and do not participate in the situation. ACTIVE STRATEGIES: we actively seek information by asking questions about the individual. INTERACTIVE STRATEGIES: we communicate directly with the person by asking questions etc. ...