Untitled
... -The Impact of InflationInflation has three main effects: decreasing the value of money, increasing interest rates, and decreasing real return on savings. With inflation, money buys less and less over time. This is a big problem for people who have a fixed income. However, people who borrow money at ...
... -The Impact of InflationInflation has three main effects: decreasing the value of money, increasing interest rates, and decreasing real return on savings. With inflation, money buys less and less over time. This is a big problem for people who have a fixed income. However, people who borrow money at ...
loanable funds market
... Occurs when government wants to increase spending (G) and needs to borrow money to do so…deficit spending ...
... Occurs when government wants to increase spending (G) and needs to borrow money to do so…deficit spending ...
Press release: The Riksbank`s Business Survey: Strong domestic
... interest rate for companies’ investment decisions. It shows that internal interest rates used in investment calculations are relatively unaffected by the general interest rate level. Accordingly, the direct connection between the interest rate level and its effect on investment decisions is weak for ...
... interest rate for companies’ investment decisions. It shows that internal interest rates used in investment calculations are relatively unaffected by the general interest rate level. Accordingly, the direct connection between the interest rate level and its effect on investment decisions is weak for ...
The Austrian School
... funds charged by the banks • When the market rate is below the natural rate companies borrow to invest and the economy expands • In opposite case investment is reduced and the ...
... funds charged by the banks • When the market rate is below the natural rate companies borrow to invest and the economy expands • In opposite case investment is reduced and the ...
Monetary policy and the Mpc: Recognising the facts
... The sooner the members of the MPC fully recognise these facts of SA economic life, the less likely they are to damage the growth prospects of the economy. The exchange value of the rand and so the inflation rate and the expectation of inflation (that take their cue from the exchange rate, for good ...
... The sooner the members of the MPC fully recognise these facts of SA economic life, the less likely they are to damage the growth prospects of the economy. The exchange value of the rand and so the inflation rate and the expectation of inflation (that take their cue from the exchange rate, for good ...
ECO 202-03
... Explain and graph actual real GDP (the business cycle), and potential real GDP (longterm economic growth) and explain why there may be a change in the underlying rate of growth of potential real GDP. ...
... Explain and graph actual real GDP (the business cycle), and potential real GDP (longterm economic growth) and explain why there may be a change in the underlying rate of growth of potential real GDP. ...
The Federal Reserve
... 3. The bond in #2 was given to you by your kindly aunt. She told you it matures in 2024, but her eyesight isn’t so good. You take a close look at the bond and see that it matures in 2020. Market i=7.25%. a) What is the price of this bond? Why is it different than what you calculated in #2a? ...
... 3. The bond in #2 was given to you by your kindly aunt. She told you it matures in 2024, but her eyesight isn’t so good. You take a close look at the bond and see that it matures in 2020. Market i=7.25%. a) What is the price of this bond? Why is it different than what you calculated in #2a? ...
Chapter 12 The Money Market and the Interest Rate
... make the purchase. c. Since people often borrow money to purchase consumer durables, an increase in the interest rate raises the monthly payments on these items. Consequently, consumers purchase fewer durables when interest rates rise. ...
... make the purchase. c. Since people often borrow money to purchase consumer durables, an increase in the interest rate raises the monthly payments on these items. Consequently, consumers purchase fewer durables when interest rates rise. ...
Contribution of Monetarism in Macroeconomic Policy
... Households and firms save part of their income. They also borrow from their banks if their savings are not enough to meet their expenses. If deposits are not enough these banks borrow from the central bank. Central bank lends them by creating reserves at a prespecified interest rate. By doing so it ...
... Households and firms save part of their income. They also borrow from their banks if their savings are not enough to meet their expenses. If deposits are not enough these banks borrow from the central bank. Central bank lends them by creating reserves at a prespecified interest rate. By doing so it ...
14.02 Solutions Quiz II Spring 03
... i.e. prices are expected to be higher in the future, so that the dividend of $1 buys less. This makes stock prices fall today. The explanation was worth 2 points. d) Assume that the real interest rate is fixed, and that the dividend in period 2 and 3 are fixed in real terms. What is the impact on th ...
... i.e. prices are expected to be higher in the future, so that the dividend of $1 buys less. This makes stock prices fall today. The explanation was worth 2 points. d) Assume that the real interest rate is fixed, and that the dividend in period 2 and 3 are fixed in real terms. What is the impact on th ...
growth rate - Left Foot Forward
... • Complement behavioural changes induced by increase in oil price with policies to steer large-scale structural change to low-carbon economy • Boost to tradeables from depreciation – use complementary not conflicting policies such as immigration controls that damage higher education & other high VA ...
... • Complement behavioural changes induced by increase in oil price with policies to steer large-scale structural change to low-carbon economy • Boost to tradeables from depreciation – use complementary not conflicting policies such as immigration controls that damage higher education & other high VA ...
Essential Understandings Economic Philosophies Basic concepts of
... Discuss the impact of interest rates on the demand for money (Theory of liquidity preference) Impact of interest rates on Money Supply? ...
... Discuss the impact of interest rates on the demand for money (Theory of liquidity preference) Impact of interest rates on Money Supply? ...
Notes on the Taylor Rule
... A question arises: what sort of macroeconomic developments might change the natural rate of interest? It’s perhaps easiest to answer this by first tackling the inverse question: taking the rate of interest as given, what sort of macroeconomic developments will tend to raise (or lower) Aggregate Dema ...
... A question arises: what sort of macroeconomic developments might change the natural rate of interest? It’s perhaps easiest to answer this by first tackling the inverse question: taking the rate of interest as given, what sort of macroeconomic developments will tend to raise (or lower) Aggregate Dema ...
Document
... A. The substitution effect of a decrease in the price of good X always leads a consumer to increase his consumption on good X. B. An increase in the interest rate induces the household to save more if income effect dominates the substitution. C. An increase in the wage rate induces the household to ...
... A. The substitution effect of a decrease in the price of good X always leads a consumer to increase his consumption on good X. B. An increase in the interest rate induces the household to save more if income effect dominates the substitution. C. An increase in the wage rate induces the household to ...
Argentina_en.pdf
... quarter-on-quarter growth), the GDP growth rate in 2014 is expected to be about -0.2%. The growth projection for 2015, when the country’s treasury has large currency repayments falling due (over US$ 10 billion in total), depends heavily on whether access to international credit markets is restored, ...
... quarter-on-quarter growth), the GDP growth rate in 2014 is expected to be about -0.2%. The growth projection for 2015, when the country’s treasury has large currency repayments falling due (over US$ 10 billion in total), depends heavily on whether access to international credit markets is restored, ...
Bank of England Inflation Report August 2012
... (a) On mortgages with a loan to value ratio of 75%. Data are to June 2012. (b) The estimated marginal funding cost of extending variable-rate sterling-denominated loans. This is calculated as the sum of three-month Libor plus a weighted average of the five-year CDS premia of the major UK lenders use ...
... (a) On mortgages with a loan to value ratio of 75%. Data are to June 2012. (b) The estimated marginal funding cost of extending variable-rate sterling-denominated loans. This is calculated as the sum of three-month Libor plus a weighted average of the five-year CDS premia of the major UK lenders use ...
ECON 409 October 31, 2012 International Monetary Order until the 1980s
... The World Bank (WB) The WB was in charge of providing loans to European countries for reconstruction and development after the second world war, a task that could not be left to private markets. World Bank can borrow from the private markets to fund its lending. Keynes had other ideas He ...
... The World Bank (WB) The WB was in charge of providing loans to European countries for reconstruction and development after the second world war, a task that could not be left to private markets. World Bank can borrow from the private markets to fund its lending. Keynes had other ideas He ...
PDF Download
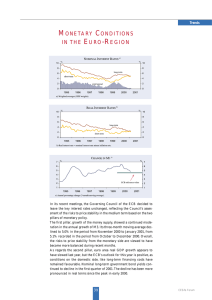
... The first pillar, growth of the money supply, showed a continued moderation in the annual growth of M3. Its three-month moving average declined to 5.0% in the period from November 2000 to January 2001, from 5.1% recorded in the period from October to December 2000. Overall, the risks to price stabil ...
... The first pillar, growth of the money supply, showed a continued moderation in the annual growth of M3. Its three-month moving average declined to 5.0% in the period from November 2000 to January 2001, from 5.1% recorded in the period from October to December 2000. Overall, the risks to price stabil ...
Interest rate
An interest rate is the rate at which interest is paid by borrowers (debtors) for the use of money that they borrow from lenders (creditors). Specifically, the interest rate is a percentage of principal paid a certain number of times per period for all periods during the total term of the loan or credit. Interest rates are normally expressed as a percentage of the principal for a period of one year, sometimes they are expressed for different periods such as a month or a day. Different interest rates exist parallelly for the same or comparable time periods, depending on the default probability of the borrower, the residual term, the payback currency, and many more determinants of a loan or credit. For example, a company borrows capital from a bank to buy new assets for its business, and in return the lender receives rights on the new assets as collateral and interest at a predetermined interest rate for deferring the use of funds and instead lending it to the borrower.Interest-rate targets are a vital tool of monetary policy and are taken into account when dealing with variables like investment, inflation, and unemployment. The central banks of countries generally tend to reduce interest rates when they wish to increase investment and consumption in the country's economy. However, a low interest rate as a macro-economic policy can be risky and may lead to the creation of an economic bubble, in which large amounts of investments are poured into the real-estate market and stock market. In developed economies, interest-rate adjustments are thus made to keep inflation within a target range for the health of economic activities or cap the interest rate concurrently with economic growth to safeguard economic momentum.