The New-Keynesian Theory of Aggregate Supply Chapter 8
... The Theory of Sticky Wages • The new-Keynesian theory of AS begins with the efficiency wage model and adds to it, assuming that the nominal wage is chosen less frequently than employment. ...
... The Theory of Sticky Wages • The new-Keynesian theory of AS begins with the efficiency wage model and adds to it, assuming that the nominal wage is chosen less frequently than employment. ...
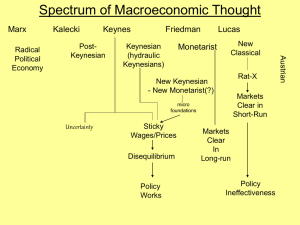
Macro Spectrum
... New Classicals in Their Own Words • Lucas critique: …modern macroeconomic models are of no value in guiding policy … For purposes of conditional forecasting (what will happen conditional on some action), one needs to know the structural parameters. (But) a change in policy necessarily alters some p ...
... New Classicals in Their Own Words • Lucas critique: …modern macroeconomic models are of no value in guiding policy … For purposes of conditional forecasting (what will happen conditional on some action), one needs to know the structural parameters. (But) a change in policy necessarily alters some p ...
Real GDP and price indexes Practice problems Problem: Suppose
... production was 8 units at a price of $10 each. The next year, production increased to 9 units and the price of the good increased to $12. a. b. c. ...
... production was 8 units at a price of $10 each. The next year, production increased to 9 units and the price of the good increased to $12. a. b. c. ...
Worksheet 15 6.1 Price inflation - Liceo Ginnasio Statale «Virgilio
... A measure of inflation that monitors the weighted average price of a basket of consumer goods and services regularly purchased by a ‘typical’ household ...
... A measure of inflation that monitors the weighted average price of a basket of consumer goods and services regularly purchased by a ‘typical’ household ...
Introduction to Business
... Opportunity cost • The benefit forgone when you choose one activity over another ...
... Opportunity cost • The benefit forgone when you choose one activity over another ...
Why Has This Recession Not Produced a Price Deflation?
... There was therefore an effective segmentation of the world economy where the “Southern” wages remained tied to some subsistence level because of the existence of huge labour reserves, while the “Northern” wages could move up with increases in labour productivity, notwithstanding the existence of som ...
... There was therefore an effective segmentation of the world economy where the “Southern” wages remained tied to some subsistence level because of the existence of huge labour reserves, while the “Northern” wages could move up with increases in labour productivity, notwithstanding the existence of som ...
Chapt13
... Some Evidence on Models of Aggregate Supply • Lucas International Comparison Paper -- Imperfect Information Model: Volatility of aggregate demand determines slope of shortrun aggregate supply curve. Steeper supply curve for countries with greater volatility in aggregate demand and hence in the pric ...
... Some Evidence on Models of Aggregate Supply • Lucas International Comparison Paper -- Imperfect Information Model: Volatility of aggregate demand determines slope of shortrun aggregate supply curve. Steeper supply curve for countries with greater volatility in aggregate demand and hence in the pric ...
Comparative Static Analysis of the Keynesian Model
... Simple IS-LM, Continued Applying Cramer’s rule for solution: ...
... Simple IS-LM, Continued Applying Cramer’s rule for solution: ...
9-1 - Intro to Macro
... Why study the whole economy? • The field of macroeconomics was born during the Great Depression. • Government didn’t understand how to fix a depressed economy with 25% unemployment. • Macro was created to: 1. Measure the health of the whole economy. 2. Guide government policies to fix problems. Copy ...
... Why study the whole economy? • The field of macroeconomics was born during the Great Depression. • Government didn’t understand how to fix a depressed economy with 25% unemployment. • Macro was created to: 1. Measure the health of the whole economy. 2. Guide government policies to fix problems. Copy ...
Mankiw 5/e Chapter 5: The Open Economy
... A price reduction by one firm causes the overall price level to fall (albeit slightly). This raises real money balances and increases aggregate demand, which benefits other firms. ...
... A price reduction by one firm causes the overall price level to fall (albeit slightly). This raises real money balances and increases aggregate demand, which benefits other firms. ...
Price Stickiness - Personal.psu.edu
... ship into port. If fact, the Keynesians go one step farther and argue that it is the obligation or duty of policymakers to pursue full employment and stable prices, many times referred to as a dual mandate. Click Here for more. So why are prices sticky? The first observation is that we need to note ...
... ship into port. If fact, the Keynesians go one step farther and argue that it is the obligation or duty of policymakers to pursue full employment and stable prices, many times referred to as a dual mandate. Click Here for more. So why are prices sticky? The first observation is that we need to note ...
Section L
... Suppose you wanted to buy a quantity of oil in 6 months time. Spot Price = $60 per barrel. Two possibilities: - Could wait 6 months and purchase at new spot price. - Could purchase forward today of $65 per barrel and lock in a fixed price today. Eliminates risk if price is higher than $65 ...
... Suppose you wanted to buy a quantity of oil in 6 months time. Spot Price = $60 per barrel. Two possibilities: - Could wait 6 months and purchase at new spot price. - Could purchase forward today of $65 per barrel and lock in a fixed price today. Eliminates risk if price is higher than $65 ...
Trend of the price of spot-LNG (Preliminary Figures for January 2016
... link) is excluded from these statistics. Objects of these statistics are spot-LNGs the prices of which are determined at the time of contract (so-called “fixed price”). ・Delivery conditions of prices (prior to averaging) are all converted into equivalent DES basis. ・Prices in the table are the simpl ...
... link) is excluded from these statistics. Objects of these statistics are spot-LNGs the prices of which are determined at the time of contract (so-called “fixed price”). ・Delivery conditions of prices (prior to averaging) are all converted into equivalent DES basis. ・Prices in the table are the simpl ...
Lecture 2: New Keynesian Model in Continuous Time
... RBC model: cannot even think about these issues! Real variables are completely separate from nominal variables (“monetary neutrality”, “classical dichotomy”). Corollary: monetary policy has no effect on any real variables. Sticky prices break “monetary neutrality” Workhorse model at central banks (s ...
... RBC model: cannot even think about these issues! Real variables are completely separate from nominal variables (“monetary neutrality”, “classical dichotomy”). Corollary: monetary policy has no effect on any real variables. Sticky prices break “monetary neutrality” Workhorse model at central banks (s ...
Last day to sign up for AP Exam
... 1. A decrease in AD will lead to a persistent recession because prices of resources (wages) are NOT flexible. 2. Increase in AD during a recession puts no pressure on prices ...
... 1. A decrease in AD will lead to a persistent recession because prices of resources (wages) are NOT flexible. 2. Increase in AD during a recession puts no pressure on prices ...
Chapter 13 vocabulary - Econ
... area where companies can locate free of certain local, state and ...
... area where companies can locate free of certain local, state and ...
Macroeconomics
... If AD decreases, recession and cyclical unemployment may result Wage contracts are not flexible, business can’t afford to reduce prices Employers are reluctant to cut wages b/c impact on EE effort Minimum Wage Laws keep wages up Menu Costs are difficult to change Fear of price wars keeps prices from ...
... If AD decreases, recession and cyclical unemployment may result Wage contracts are not flexible, business can’t afford to reduce prices Employers are reluctant to cut wages b/c impact on EE effort Minimum Wage Laws keep wages up Menu Costs are difficult to change Fear of price wars keeps prices from ...
Collection of Prices
... products to represent price trend of discontinued product without direct comparison between price of old and new product. Difference in price of imputed price (old product) and new product is the implicit quality adjustment • Substitution bias: Use formulae that allow for substitution effects e. g t ...
... products to represent price trend of discontinued product without direct comparison between price of old and new product. Difference in price of imputed price (old product) and new product is the implicit quality adjustment • Substitution bias: Use formulae that allow for substitution effects e. g t ...