* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Introduction to Business
Participatory economics wikipedia , lookup
Fiscal multiplier wikipedia , lookup
Non-monetary economy wikipedia , lookup
Criticisms of socialism wikipedia , lookup
Economics of fascism wikipedia , lookup
Nominal rigidity wikipedia , lookup
Economic democracy wikipedia , lookup
Production for use wikipedia , lookup
Business cycle wikipedia , lookup
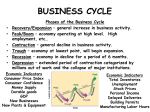
Introduction to Business Concepts Review Factors of Production Resources nations need to create wealth Land Labor Capital Entrepreneurship Knowledge Economic Terms Opportunity cost • The benefit forgone when you choose one activity over another Economic decision rule • If benefits exceed costs, do it. If costs exceed benefits, don’t do it. More Economic Terms Output • A result of an activity Input • What you put in to achieve that output Productive efficiency • Getting as much output for as few inputs as possible Economic Systems Capitalism (free-market economy) • All or most factors of production and distribution privately owned and operated for profit Foundations of Capitalism Freedom to own private property Freedom to own business and keep profits Freedom of competition Freedom of choice Socialism Based on premise that government should own most basic business Business profits should be evenly distributed among the people Communism Government makes almost all economic decisions Government owns almost all factors of production • • • • • Land Labor Capital Knowledge Entrepreneurship (not encouraged) Key Economic Indicators Gross Domestic Product (GDP) • Total value of final goods and services produced in a given period Consumption+investment+net exports+government spending = GDP • China 2010 4Q GDP = 9.8% • U.S. 2010 4Q GDP = 3.2% Key Economic Indicators Consumer Price Index (CPI) • Monthly statistic measures pace of inflation or deflation Producer Price Index (PPI) • A/k/a Manufacturers’ Index • Monthly statistic measures prices at wholesale level Unemployment rate • Number of civilians at least 16 years old who are unemployed and tried to find a job within the prior four weeks Key Economic Indicators Inflation rate • A general rise in prices of goods and services over time Deflation • A situation in which price increases are slowing; inflation rate is declining Disinflation • A situation in which prices are declining Stagflation • A combination of high inflation and high unemployment Key Financial Indicators Money supply • Monthly statistic measures amount of money in circulation Fiscal policy • Federal government efforts to stabilize economy with taxes and spending Monetary policy • Management of money supply and interest rates • Controlled by Federal Reserve (the Fed) National debt • The sum of government deficits over time Business Cycles Periodic rises and falls that occur in economies over time • Boom—recession—depression—recovery • Recession Two or more consecutive quarters of decline in GDP • Depression A severe recession, usually accompanied by deflation Rule of 72 Useful for understanding inflation A quick computation of how long it takes prices to double at various rates of growth Example: If houses increase in price at 9% a year, how long for the price to double? Answer: Divide 72 by 9% and you get the approximate number of years it takes to double the price, 8 years