NBER WORKING PAPER SERIES TECHNOLOGY SHOCKS IN THE NEW KEYNESIAN MODEL
... intertemporal marginal rate of substitution. The household’s first-order conditions also include the budget constraint (1) with equality and an optimality condition for money holdings, which plays the role of the model’s money demand relationship. Under an interest rate rule for monetary policy like ...
... intertemporal marginal rate of substitution. The household’s first-order conditions also include the budget constraint (1) with equality and an optimality condition for money holdings, which plays the role of the model’s money demand relationship. Under an interest rate rule for monetary policy like ...
SEDP-2014-11-Chen-Kirsanova-Leith
... ln At = ln γ + ln At−1 + ln zt ln zt = ρz ln zt−1 + εz,t Households decide the composition of the consumption basket to minimize expenditures, and the demand for individual good i is ...
... ln At = ln γ + ln At−1 + ln zt ln zt = ρz ln zt−1 + εz,t Households decide the composition of the consumption basket to minimize expenditures, and the demand for individual good i is ...
Chapter 4 - Dr. George Fahmy
... Gross domestic product (GDP) measures total output in the domestic economy. Nominal GDP, real GDP, and potential GDP are three different measures of aggregate output. Nominal GDP is the market value of all-final goods and services produced in the domestic economy in a one-year period at current pric ...
... Gross domestic product (GDP) measures total output in the domestic economy. Nominal GDP, real GDP, and potential GDP are three different measures of aggregate output. Nominal GDP is the market value of all-final goods and services produced in the domestic economy in a one-year period at current pric ...
Macro-economics of balance-sheet problems and the
... The main advantage of micro-founded macro-models is that they are internally consistent and able to handle expectations. This makes them resilient – if they describe economic behaviour correctly – to the Lucas critique (Lucas, 1976); all economic actors correctly internalise all policy changes. A di ...
... The main advantage of micro-founded macro-models is that they are internally consistent and able to handle expectations. This makes them resilient – if they describe economic behaviour correctly – to the Lucas critique (Lucas, 1976); all economic actors correctly internalise all policy changes. A di ...
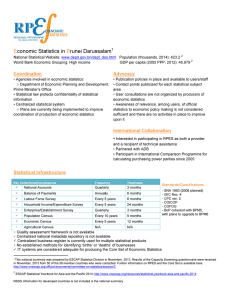
E B conomic Statistics in runei Darussalam
... This national summary was prepared by ESCAP Statistics Division in November, 2013. Results of the Capacity Screening questionnaire were received in November, 2013 from 50 of the 58 member countries who were contacted. Further information on RPES and the Core Set is available here: http://www.unescap ...
... This national summary was prepared by ESCAP Statistics Division in November, 2013. Results of the Capacity Screening questionnaire were received in November, 2013 from 50 of the 58 member countries who were contacted. Further information on RPES and the Core Set is available here: http://www.unescap ...
Forecasting Real GDP
... General Approach to Forecasting GDP General procedure • Start with analyzing the past: what were key developments and how are they going to affect the present and future? We looked at recent economic developments during the first session • What do we know about the present (nowcast)? We will lo ...
... General Approach to Forecasting GDP General procedure • Start with analyzing the past: what were key developments and how are they going to affect the present and future? We looked at recent economic developments during the first session • What do we know about the present (nowcast)? We will lo ...
Chapter 1 - IDEAS/RePEc
... component of GDP and include items that last longer than the current period such as automobiles and furniture. Nondurables are goods that are consumed or “used up” within the period such as food. Services are non-tangible items such as haircuts and massages. Investment consists of fixed investment, ...
... component of GDP and include items that last longer than the current period such as automobiles and furniture. Nondurables are goods that are consumed or “used up” within the period such as food. Services are non-tangible items such as haircuts and massages. Investment consists of fixed investment, ...
Inflation
... set of consumer goods and services that is used to compare changing price levels over time. What six items were in our classroom’s market basket? ...
... set of consumer goods and services that is used to compare changing price levels over time. What six items were in our classroom’s market basket? ...
Practical Guide To Contemporary Economics
... something is measured by what you are willing to give up getting one more unit of it People make rational choices and use our scarce resources in the way that makes them as well off as possible when they take those actions for which marginal benefits exceed or equals marginal costs. In making their ...
... something is measured by what you are willing to give up getting one more unit of it People make rational choices and use our scarce resources in the way that makes them as well off as possible when they take those actions for which marginal benefits exceed or equals marginal costs. In making their ...
Sample Chapter 2 (PDF, 28 Pages
... produced in Canada, regardless of who produced them. GDP is closely related to employment, industrial production, and other economic variables that do not take the nationality of the firm into account. You may think of GDP as a measure of economic activity in Canada. To understand the concept of mea ...
... produced in Canada, regardless of who produced them. GDP is closely related to employment, industrial production, and other economic variables that do not take the nationality of the firm into account. You may think of GDP as a measure of economic activity in Canada. To understand the concept of mea ...
Mankiw 6e PowerPoints
... Real variables: Measured in physical units – quantities and relative prices, for example: quantity of output produced real wage: output earned per hour of work real interest rate: output earned in the future by lending one unit of output today Nominal variables: Measured in money units, e.g., ...
... Real variables: Measured in physical units – quantities and relative prices, for example: quantity of output produced real wage: output earned per hour of work real interest rate: output earned in the future by lending one unit of output today Nominal variables: Measured in money units, e.g., ...
Money and Inflation
... political perceptions impose tight limits on the degree to which government expenditures can increase. ...
... political perceptions impose tight limits on the degree to which government expenditures can increase. ...
Module 19 Equilibrium in the Aggregate Demand
... Figure 19.4 combines the aggregate demand curve with both the short-run and longrun aggregate supply curves. The aggregate demand curve, AD, crosses the short-run aggregate supply curve, SRAS, at ELR. Here we assume that enough time has elapsed that the economy is also on the long-run aggregate supp ...
... Figure 19.4 combines the aggregate demand curve with both the short-run and longrun aggregate supply curves. The aggregate demand curve, AD, crosses the short-run aggregate supply curve, SRAS, at ELR. Here we assume that enough time has elapsed that the economy is also on the long-run aggregate supp ...
The Consequences of Information Revealed in Auctions
... telecommunications markets.1 In these situations, a number of authors have pointed out that information contained in bids can be used in subsequent competition, should those bids be announced. For instance, Rothkopf et al. (1990) and Engelbrecht-Wiggans and Kahn (1991) argue that third parties may b ...
... telecommunications markets.1 In these situations, a number of authors have pointed out that information contained in bids can be used in subsequent competition, should those bids be announced. For instance, Rothkopf et al. (1990) and Engelbrecht-Wiggans and Kahn (1991) argue that third parties may b ...
PDF Full Text
... GBP/USD), stock index (S&P/ASX200, FSTE 100), GDP growth rate, unemployment rate, inflation rate, consumer price index (CPI), Official Cash Rate (OCR), national current account, imports, exports, government debt, business confidence, consumer confidence, and 10-year government bonds for both countri ...
... GBP/USD), stock index (S&P/ASX200, FSTE 100), GDP growth rate, unemployment rate, inflation rate, consumer price index (CPI), Official Cash Rate (OCR), national current account, imports, exports, government debt, business confidence, consumer confidence, and 10-year government bonds for both countri ...
The US economy from 1992 to 1998: historical and decom-
... where Zj is the activity level (overall level of output) in industry j; and BijBi is the input of i per unit of activity in industry j with Bij and Bi being technological variables which can be used in simulating the effects of changes in the input of i per unit of activity in j and the input of i p ...
... where Zj is the activity level (overall level of output) in industry j; and BijBi is the input of i per unit of activity in industry j with Bij and Bi being technological variables which can be used in simulating the effects of changes in the input of i per unit of activity in j and the input of i p ...
2014-15 Budget medium-term economic projections
... Government’s budget balance than had been provided prior to that date. This change was a manifestation of the extraordinary circumstances of the time; the Australian economy was emerging from recession, activity levels were well below potential and the budget deficit had reached four per cent of GDP ...
... Government’s budget balance than had been provided prior to that date. This change was a manifestation of the extraordinary circumstances of the time; the Australian economy was emerging from recession, activity levels were well below potential and the budget deficit had reached four per cent of GDP ...
Public Debt and Redistribution with Borrowing Constraints
... assumption that government spending is fixed implies that exogenous variations in taxes will readily constitute a test of whether Ricardian equivalence holds in our model. In an equilibrium of this economy, all agents take as given prices (with the exception of monopolists who reset their good’s pri ...
... assumption that government spending is fixed implies that exogenous variations in taxes will readily constitute a test of whether Ricardian equivalence holds in our model. In an equilibrium of this economy, all agents take as given prices (with the exception of monopolists who reset their good’s pri ...
View/Open
... reality, however, key factors such as the position of the feedstock supply curve and the level of world oil prices are likely to be variable. McPhail and Babcock (2008) use a stochastic partial equilibrium model to examine the effect of U.S. ethanol expansion and mandates on price risk for corn. Usi ...
... reality, however, key factors such as the position of the feedstock supply curve and the level of world oil prices are likely to be variable. McPhail and Babcock (2008) use a stochastic partial equilibrium model to examine the effect of U.S. ethanol expansion and mandates on price risk for corn. Usi ...
IS-LM and Monetarism
... money is solely a positive function of income. In a more general Keynesian model, money demand depends on both income (the transaction demand) and the interest rate (the speculative demand). Money supply is assumed to be fixed by the central bank. From the equality of money demand and supply, the LM ...
... money is solely a positive function of income. In a more general Keynesian model, money demand depends on both income (the transaction demand) and the interest rate (the speculative demand). Money supply is assumed to be fixed by the central bank. From the equality of money demand and supply, the LM ...
This PDF is a selection from a published volume from
... drive the U.S. macroeconomy. These shocks explain the fundamental business-cycle behavior of all key variables and, in particular, of the federal funds rate, inflation, and output. Second, the two orthogonal shocks can be robustly identified as generating, respectively, medium- and long-run output d ...
... drive the U.S. macroeconomy. These shocks explain the fundamental business-cycle behavior of all key variables and, in particular, of the federal funds rate, inflation, and output. Second, the two orthogonal shocks can be robustly identified as generating, respectively, medium- and long-run output d ...
PL 1 - Alvinisd.net
... • In the years following Phillips' 1958 paper, many economists in the advanced industrial countries believed that his results showed that there was a permanently stable relationship between inflation and unemployment. • One implication of this for government policy was that governments could control ...
... • In the years following Phillips' 1958 paper, many economists in the advanced industrial countries believed that his results showed that there was a permanently stable relationship between inflation and unemployment. • One implication of this for government policy was that governments could control ...