nowthat`swhatIcallKa..
... the motor cortex.in the muscles” Seeing each other do this activates the Occipital lobe. ...
... the motor cortex.in the muscles” Seeing each other do this activates the Occipital lobe. ...
Chap 5: The Cognitive Approach II
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
Learning Skill
... memory of what we should look like while we do it and we make conscious adjustments to mimic the conscious memory of the skill. Integration of conscious and subconscious adjustments based on conscious and subconscious memories of the performance result in the actual performance. ...
... memory of what we should look like while we do it and we make conscious adjustments to mimic the conscious memory of the skill. Integration of conscious and subconscious adjustments based on conscious and subconscious memories of the performance result in the actual performance. ...
SESSION TWO: - WOW! Locations
... – brain cell generation and migration is complete in human embryos at about 16 weeks (4 months) of age – yet the brain may not be fully mature until about 10 years, or even 18 years, of age – even so, human brains are plastic; they change with experience (though this ability may decrease with age) – ...
... – brain cell generation and migration is complete in human embryos at about 16 weeks (4 months) of age – yet the brain may not be fully mature until about 10 years, or even 18 years, of age – even so, human brains are plastic; they change with experience (though this ability may decrease with age) – ...
05powerpoint
... Consists of several distinct subtypes. Implicit or procedural memory holds knowledge for skills such as riding a bicycle. It is demonstrated by doing and occurs without conscious recall. Explicit or declarative memory holds memory for facts and events. It is demonstrated by saying and occurs with co ...
... Consists of several distinct subtypes. Implicit or procedural memory holds knowledge for skills such as riding a bicycle. It is demonstrated by doing and occurs without conscious recall. Explicit or declarative memory holds memory for facts and events. It is demonstrated by saying and occurs with co ...
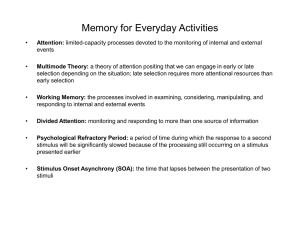
Memory for Everyday Activities
... Multimode Theory: a theory of attention positing that we can engage in early or late selection depending on the situation; late selection requires more attentional resources than early selection ...
... Multimode Theory: a theory of attention positing that we can engage in early or late selection depending on the situation; late selection requires more attentional resources than early selection ...
When neurons form memories
... that produce our conscious experience of an event cannot at the same time directly store this event for later recall. Rather, an intermediate trace is initially stored in the medial temporal lobe (MTL), an area that includes the archicortical hippocampus and the adjacent cortical areas (the entorhin ...
... that produce our conscious experience of an event cannot at the same time directly store this event for later recall. Rather, an intermediate trace is initially stored in the medial temporal lobe (MTL), an area that includes the archicortical hippocampus and the adjacent cortical areas (the entorhin ...
Learning skills - Personal web pages for people of Metropolia
... method that is called memory condition, which includes presenting the material which students have to memorize and represent. In the analytical condition, students are asked to compare and contrast theories. In the creative condition, they are asked to formulate their own theory based on the facts. ...
... method that is called memory condition, which includes presenting the material which students have to memorize and represent. In the analytical condition, students are asked to compare and contrast theories. In the creative condition, they are asked to formulate their own theory based on the facts. ...
Learning & Memory
... and Long-term Memory Machinery Patient E.E. has damage to the left angular gyrus causing a deficit in shortterm, but not long term memory Patient H.M. had damage to the medial temporal lobe causing a deficit in longterm, but not short-term memory ...
... and Long-term Memory Machinery Patient E.E. has damage to the left angular gyrus causing a deficit in shortterm, but not long term memory Patient H.M. had damage to the medial temporal lobe causing a deficit in longterm, but not short-term memory ...
1 - U-System
... channels become leaky resulting in higher than normal resting levels of calcium within neurons calcium that enters during a train of stimuli (tetanus) produces less effect than in younger individuals 5. Important structures for learning and memory abilities - limbic system plays a role in deciding ...
... channels become leaky resulting in higher than normal resting levels of calcium within neurons calcium that enters during a train of stimuli (tetanus) produces less effect than in younger individuals 5. Important structures for learning and memory abilities - limbic system plays a role in deciding ...
Answers to Test Your Knowledge questions for
... distinction is becoming more grey all the time. To constitute a case of learning, the change has to reflect environmental experience of the animal in question. Any learning experience is associated with a memory as its base. (Additional note: It used to be argued that learning can be characterized b ...
... distinction is becoming more grey all the time. To constitute a case of learning, the change has to reflect environmental experience of the animal in question. Any learning experience is associated with a memory as its base. (Additional note: It used to be argued that learning can be characterized b ...
Constructions in the Brain - Washington and Lee University
... Language Isn’t (Just) Association: Jackendoff’s Four Challenges for Cognitive Neuroscience ...
... Language Isn’t (Just) Association: Jackendoff’s Four Challenges for Cognitive Neuroscience ...
Module 24 Powerpoint
... rats who had learned a maze retained parts of that memory, even when various small parts of their brain were removed. ...
... rats who had learned a maze retained parts of that memory, even when various small parts of their brain were removed. ...
Economic Attention Networks: Associative Memory and Resource
... Adams State College (ASC), Singularity Institute for AI (SIAI), Novamente LLC, ...
... Adams State College (ASC), Singularity Institute for AI (SIAI), Novamente LLC, ...
PROCESSING APPROACHES
... These processes are modular (can be studied independently) Autonomous and active learners Processes take time The mind is a limited-capacity processor Learn a second language is to learn a skill Learning is a cognitive process ...
... These processes are modular (can be studied independently) Autonomous and active learners Processes take time The mind is a limited-capacity processor Learn a second language is to learn a skill Learning is a cognitive process ...
Cognitive Information Processing
... an ability old to miner select hid one a message box from of another gold. We Although do several this hundred by people focusing have our looked attention for on it, certain they cues have such not as found type it style. ...
... an ability old to miner select hid one a message box from of another gold. We Although do several this hundred by people focusing have our looked attention for on it, certain they cues have such not as found type it style. ...
Information Processing and Memory
... when (and if) you learned to type. At first, you watched your hands carefully and deliberated about which finger to press on which key. The process you used to develop typing skills was controlled, or conscious. Over time, this procedural knowledge became automatized; you no longer had conscious awa ...
... when (and if) you learned to type. At first, you watched your hands carefully and deliberated about which finger to press on which key. The process you used to develop typing skills was controlled, or conscious. Over time, this procedural knowledge became automatized; you no longer had conscious awa ...
Consolidation theory
... • In order for information to be transferred from Short-Term Memory to Long-Term Memory a period of time for consolidation is required to ensure it is permanently stored. • Consolidation refers to the physical changes are made to the neurons in the brain when something new is being learned and immed ...
... • In order for information to be transferred from Short-Term Memory to Long-Term Memory a period of time for consolidation is required to ensure it is permanently stored. • Consolidation refers to the physical changes are made to the neurons in the brain when something new is being learned and immed ...
Knowledge Representation
... what is it ? what do we represent ? how is it represented ? Kn Repn strategies inferencing example tasks ...
... what is it ? what do we represent ? how is it represented ? Kn Repn strategies inferencing example tasks ...
INTRODUCTION TO FUNCTIONAL NEUROBIOLOGY Tamás
... Brief summary: This series of lectures exemplifies different memory types by demonstrating human cases, animal experiments and behavioural tests. It describes the neuronal circuitries involved, the employed learning mechanisms and the evolutionary pressure leading to the two basic memory types, the ...
... Brief summary: This series of lectures exemplifies different memory types by demonstrating human cases, animal experiments and behavioural tests. It describes the neuronal circuitries involved, the employed learning mechanisms and the evolutionary pressure leading to the two basic memory types, the ...
“Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to
... “Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to learning based on current literature.” The difference between learning and memory is rather subtle; learning is the process by which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that i ...
... “Describe the neuroanatomy of and neural processes related to learning based on current literature.” The difference between learning and memory is rather subtle; learning is the process by which new information and abilities are incorporated into one’s mind, whereas memory is the way in which that i ...