Digestion 2
... The molecules pass from the lumen of the small intestine and are carried to blood vessels or the lacteal The capillary carries blood too (oxygenated) and from (deoxygenated with nutrients) and maintains the concentration gradient The lacteal will transport the fats (lipoproteins to the circulatory s ...
... The molecules pass from the lumen of the small intestine and are carried to blood vessels or the lacteal The capillary carries blood too (oxygenated) and from (deoxygenated with nutrients) and maintains the concentration gradient The lacteal will transport the fats (lipoproteins to the circulatory s ...
Enterohepatic circulation of bile acids
... stimulated by insulin. LPL activated by apo CII on circulating lipoprotein particles to yield fatty acids and glycerol. The fatty acids are stored (by the adipose tissue) or used for energy (by the muscle). If they are not immediately taken up by a cell, the long-chain fatty acids are transported by ...
... stimulated by insulin. LPL activated by apo CII on circulating lipoprotein particles to yield fatty acids and glycerol. The fatty acids are stored (by the adipose tissue) or used for energy (by the muscle). If they are not immediately taken up by a cell, the long-chain fatty acids are transported by ...
Florida Gulf Coast University
... 8. ____Digestion of carbohydrates is initiated by amylase released into the duodenum from the pancreas. 9. ____ No digestion of dietary fats occurs until they reach the small intestine. 10. ____The primary site of nutrient and water absorption is in the small intestine. by osmosis. 11. ____Unlike fa ...
... 8. ____Digestion of carbohydrates is initiated by amylase released into the duodenum from the pancreas. 9. ____ No digestion of dietary fats occurs until they reach the small intestine. 10. ____The primary site of nutrient and water absorption is in the small intestine. by osmosis. 11. ____Unlike fa ...
No Slide Title
... Mechanical digestion in the mouth results in a ball of food that can be swallowed. What is this ball of food called? ...
... Mechanical digestion in the mouth results in a ball of food that can be swallowed. What is this ball of food called? ...
Bacteria Isolated From Patients With Cholelithiasis and Their
... the bile or gallbladder wall (2). Microscopic examinations indicated that 20-50% of the patients with chronic cholecystitis have positive bile culture (3). Different reasons for biliary tract infection have been presented, e.g. ascending infection due to reflux of duodenal contents, blood-borne infe ...
... the bile or gallbladder wall (2). Microscopic examinations indicated that 20-50% of the patients with chronic cholecystitis have positive bile culture (3). Different reasons for biliary tract infection have been presented, e.g. ascending infection due to reflux of duodenal contents, blood-borne infe ...
The_Digestive_System notes
... who have hepatitis C develop a chronic infection. This may lead to a scarring of the liver, called cirrhosis. ...
... who have hepatitis C develop a chronic infection. This may lead to a scarring of the liver, called cirrhosis. ...
Digestive Web Quest 1. a. What are the 3 parts of the small intestine
... c. What is found in the wall of the stomach that is not found in the rest of the alimentary canal ...
... c. What is found in the wall of the stomach that is not found in the rest of the alimentary canal ...
Digestive System
... esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine (colon) Accessory Organs: Teeth, tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder ...
... esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine (colon) Accessory Organs: Teeth, tongue, salivary glands, pancreas, liver, and gallbladder ...
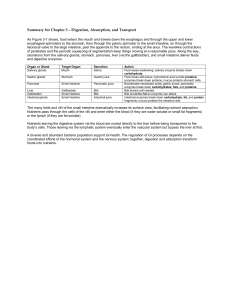
Summary for Chapter 3 – Digestion, Absorption, and
... As Figure 3-1 shows, food enters the mouth and travels down the esophagus and through the upper and lower esophageal sphincters to the stomach, then through the pyloric sphincter to the small intestine, on through the ileocecal valve to the large intestine, past the appendix to the rectum, ending at ...
... As Figure 3-1 shows, food enters the mouth and travels down the esophagus and through the upper and lower esophageal sphincters to the stomach, then through the pyloric sphincter to the small intestine, on through the ileocecal valve to the large intestine, past the appendix to the rectum, ending at ...
Digestive System Process Grid student version
... food stays here from 4-8 seconds; 1-2 seconds for soft food ...
... food stays here from 4-8 seconds; 1-2 seconds for soft food ...
frog dissection - Westminster College
... 12. Gallbladder: stores bile and makes it more concentrated. 13. Liver: Cleans the blood and manufactures essential chemicals. 14. Stomach: a flexible bag that secretes acids and other digestive juices. 15. Bile Duct: transports bile from the gallbladder to the duodenum. 16. Pancreas: makes digestiv ...
... 12. Gallbladder: stores bile and makes it more concentrated. 13. Liver: Cleans the blood and manufactures essential chemicals. 14. Stomach: a flexible bag that secretes acids and other digestive juices. 15. Bile Duct: transports bile from the gallbladder to the duodenum. 16. Pancreas: makes digestiv ...
4. Digestive System WEB
... • Large surface area due to the presence of villi • Villi – one cell thick; ↑ surface area for diffusion • Next to each villus are blood vessels which carry nutrients to other cells of the body ...
... • Large surface area due to the presence of villi • Villi – one cell thick; ↑ surface area for diffusion • Next to each villus are blood vessels which carry nutrients to other cells of the body ...
The Digestive System - science
... • Most digestion occurs here • Molecules pass out through villi into blood • About 690 cm long ...
... • Most digestion occurs here • Molecules pass out through villi into blood • About 690 cm long ...
The Digestive System
... The Digestive System Food passes through the digestive system. Match the descriptions to each part. Note the first one has been done for you! Digestion begins here. Food is mechanically broken down by teeth. Saliva aids digestion. Mouth ...
... The Digestive System Food passes through the digestive system. Match the descriptions to each part. Note the first one has been done for you! Digestion begins here. Food is mechanically broken down by teeth. Saliva aids digestion. Mouth ...
Human Digestive System - HHS-Biology-3C
... – Peristalsis finishes mechanical digestion – Pancreatic juice contains enzymes to finish chemical digestion of fats, proteins and carbohydrates – Bile from liver breaks fat into small droplets (much like a detergent breaks down grease) ...
... – Peristalsis finishes mechanical digestion – Pancreatic juice contains enzymes to finish chemical digestion of fats, proteins and carbohydrates – Bile from liver breaks fat into small droplets (much like a detergent breaks down grease) ...
Obstructive Jaundice - The Cabrini Code
... •Unlike ERCP, both are non-invasive but not therapeutic ...
... •Unlike ERCP, both are non-invasive but not therapeutic ...
A. Hepatic portal vein
... Q. Name a process by which soluble foods are absorbed into the blood from the small intestine. A. Diffusion or Passive transport ...
... Q. Name a process by which soluble foods are absorbed into the blood from the small intestine. A. Diffusion or Passive transport ...
Digestive System
... This trap door belongs to both the respiratory and the digestive systems. Prevents food and fluids from draining into the lungs. ...
... This trap door belongs to both the respiratory and the digestive systems. Prevents food and fluids from draining into the lungs. ...
Mouth Digestive System Mind Map
... break food into usable nutrient molecules molecules are absorbed into the blood eliminates waste ...
... break food into usable nutrient molecules molecules are absorbed into the blood eliminates waste ...
Accessory Organs in Digestion
... 4) Breaks down hemoglobin in Red Blood Cells -forms bilirubin -pigment in bile 5) Makes Urea -from broken down amino acids 6) Makes blood proteins -from amino acids ...
... 4) Breaks down hemoglobin in Red Blood Cells -forms bilirubin -pigment in bile 5) Makes Urea -from broken down amino acids 6) Makes blood proteins -from amino acids ...
Lecture Two
... Feed adult 50 g lactose and measure rise in blood glucose. An increase in BG < 20 mg/dL indicative of intolerance. Hydrogen Breath Test Feed 1.75 g lactose/kg BW; If present, undigested CHO will be fermented by colonic bacteria and produce large increase in Breath Hydrogen= Malabsorption ...
... Feed adult 50 g lactose and measure rise in blood glucose. An increase in BG < 20 mg/dL indicative of intolerance. Hydrogen Breath Test Feed 1.75 g lactose/kg BW; If present, undigested CHO will be fermented by colonic bacteria and produce large increase in Breath Hydrogen= Malabsorption ...
Cholangitis/ Cholangiohepatitis Syndrome
... (known as “hepatomegaly”); thickened intestines with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); variable yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (jaundice or icterus); rare fluid buildup in the abdomen (known as “abdominal effusion” or “ascites”) • Decreased number of bile ducts (kn ...
... (known as “hepatomegaly”); thickened intestines with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD); variable yellowish discoloration to the gums and other tissues of the body (jaundice or icterus); rare fluid buildup in the abdomen (known as “abdominal effusion” or “ascites”) • Decreased number of bile ducts (kn ...
Ascending cholangitis

Ascending cholangitis or acute cholangitis (or sometimes cholangitis without a modifier - from Greek chol-, bile + ang-, vessel + itis-, inflammation) is an infection of the bile duct (cholangitis), usually caused by bacteria ascending from its junction with the duodenum (first part of the small intestine). It tends to occur if the bile duct is already partially obstructed by gallstones.Cholangitis can be life-threatening, and is regarded as a medical emergency. Characteristic symptoms include yellow discoloration of the skin or whites of the eyes, fever, abdominal pain, and in severe cases, low blood pressure and confusion. Initial treatment is with intravenous fluids and antibiotics, but there is often an underlying problem (such as gallstones or narrowing in the bile duct) for which further tests and treatments may be necessary, usually in the form of endoscopy to relieve obstruction of the bile duct.