Mississippian Rocks in Illinois - Illinois State Geological Survey
... Various combinations of the rocks described above were deposited in Illinois during the 40 million years of the Mississippian Period. The oldest rocks were laid down first and are at the bottom of the sequence (fig. 1). Pre-Mississippian Before Mississippian times, late in the Devonian Period (fig. ...
... Various combinations of the rocks described above were deposited in Illinois during the 40 million years of the Mississippian Period. The oldest rocks were laid down first and are at the bottom of the sequence (fig. 1). Pre-Mississippian Before Mississippian times, late in the Devonian Period (fig. ...
Orta Anadolu`nun jeolojisi hakkında E. LAHN ÖZET: RAN 8).
... In the Beyşehir region; narrow scales of flysch strata, slates, limes*tone Mocks,, radiolaiites and' a mixture of basic rocks (serpentines, diorites, melaphyres etc«) appear between the limestones, from which they are always separated by faults or over-thrusts. The age of these rocks is considered p ...
... In the Beyşehir region; narrow scales of flysch strata, slates, limes*tone Mocks,, radiolaiites and' a mixture of basic rocks (serpentines, diorites, melaphyres etc«) appear between the limestones, from which they are always separated by faults or over-thrusts. The age of these rocks is considered p ...
The SEEK Project: Stimulating Exploration in the
... Compilation of historical geophysical data may prove to be one of the most challenging aspects of the SEEK Project. Ground geophysical gravity data has been demonstrated to be an excellent tool for the targeting of a variety of mineral deposit types. A project led by T. Sanders is focused on bringin ...
... Compilation of historical geophysical data may prove to be one of the most challenging aspects of the SEEK Project. Ground geophysical gravity data has been demonstrated to be an excellent tool for the targeting of a variety of mineral deposit types. A project led by T. Sanders is focused on bringin ...
Dynamic landscapes and human dispersal patterns: tectonics
... Processes of active tectonics are especially marked near plate boundaries, and have different surface effects depending on the nature of the plate motions and the spatial and temporal scale of observation. Where plates are diverging the dominant large-scale effect is crustal stretching, subsidence a ...
... Processes of active tectonics are especially marked near plate boundaries, and have different surface effects depending on the nature of the plate motions and the spatial and temporal scale of observation. Where plates are diverging the dominant large-scale effect is crustal stretching, subsidence a ...
Continental Margins
... Prominent features of the deep ocean basins include rugged oceanic ridges, flat abyssal plains, occasional deep trenches, and curving chains of volcanic islands. The processes of plate tectonics, erosion, and sediment deposition have shaped the continental margins and ocean basins. In the next chapt ...
... Prominent features of the deep ocean basins include rugged oceanic ridges, flat abyssal plains, occasional deep trenches, and curving chains of volcanic islands. The processes of plate tectonics, erosion, and sediment deposition have shaped the continental margins and ocean basins. In the next chapt ...
83. Tectonic Synthesis and Implications of Japan Sea ODP Drilling
... Legs 127 and 128 completed drilling of six sites in the Japan Sea. Sites 795 and 796 are in the Japan Basin, Sites 794 and 797 in the Yamato Basin, Site 799 on the Yamato Rise, and Site 798 on the Oki Ridge. Basement was penetrated at Sites 794, 795, and 797 where basaltic rocks were recovered. The ...
... Legs 127 and 128 completed drilling of six sites in the Japan Sea. Sites 795 and 796 are in the Japan Basin, Sites 794 and 797 in the Yamato Basin, Site 799 on the Yamato Rise, and Site 798 on the Oki Ridge. Basement was penetrated at Sites 794, 795, and 797 where basaltic rocks were recovered. The ...
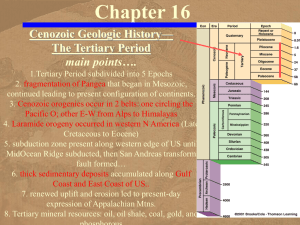
Chapter 16 - Cenozoic - Tertiary
... – It is probably a volcanic neck although – some geologists think it is an eroded laccolith – It was emplaced during the Eocene, 45-50 million years ago ...
... – It is probably a volcanic neck although – some geologists think it is an eroded laccolith – It was emplaced during the Eocene, 45-50 million years ago ...
Structure and evolution of the continental margin off Norway and the
... Pre-breakup basin evolution The pre-opening, structural margin framework is dominated by the NE Atlantic-Arctic Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous rift episode responsible for the development of major Cretaceous basins such as the Møre and Vøring basins off mid-Norway, and the deep basins in the SW Bare ...
... Pre-breakup basin evolution The pre-opening, structural margin framework is dominated by the NE Atlantic-Arctic Late Jurassic–Early Cretaceous rift episode responsible for the development of major Cretaceous basins such as the Møre and Vøring basins off mid-Norway, and the deep basins in the SW Bare ...
e@ntlr rnrrul ll ng €dJuJeortttt ornr
... or combinations of these influencels in Lonics, flexure of lithosphere, include geometric configKey facets of basin evolution space or time. ...
... or combinations of these influencels in Lonics, flexure of lithosphere, include geometric configKey facets of basin evolution space or time. ...
Field Trip to the Fall Zone, Cape Fear River, Raven Rock State Park
... be directly addressed by EarthScope and related research. These questions include, but are not limited to the assembly, structure, and evolution of the lithosphere of the eastern U.S., the dynamic flow of the underlying asthenosphere, Appalachian orogenesis, post-Appalachian rift initiation and evol ...
... be directly addressed by EarthScope and related research. These questions include, but are not limited to the assembly, structure, and evolution of the lithosphere of the eastern U.S., the dynamic flow of the underlying asthenosphere, Appalachian orogenesis, post-Appalachian rift initiation and evol ...
Regional Geology of the Bight Basin
... Gnarlyknots 1/1A, all wells have been drilled in relatively shallow water near the basin margin and the deeper part of the sub-basin remains largely untested. There have been no hydrocarbon discoveries in the Bight Basin and the area remains an exploration frontier. Recently, exploration activity in ...
... Gnarlyknots 1/1A, all wells have been drilled in relatively shallow water near the basin margin and the deeper part of the sub-basin remains largely untested. There have been no hydrocarbon discoveries in the Bight Basin and the area remains an exploration frontier. Recently, exploration activity in ...
1 Chapter 4 Continental Margins and Ocean Basins
... deepest places in Earth’ Earth’s crust, 3 to 6 kilometers (1.9 to 3.7 miles) deeper than the adjacent basin floor. The ocean’ ocean’s greatest depth is the Mariana Trench where the depth reaches 11,022 meters (36,163 miles) below sea level. ...
... deepest places in Earth’ Earth’s crust, 3 to 6 kilometers (1.9 to 3.7 miles) deeper than the adjacent basin floor. The ocean’ ocean’s greatest depth is the Mariana Trench where the depth reaches 11,022 meters (36,163 miles) below sea level. ...
DOC, 365KB - Offshore Petroleum Exploration Acreage Release
... The Roebuck Basin covers approximately 93,000 km2 on the North West Shelf. It forms the central part of the Westralian Superbasin, which is a northeast-trending passive margin of late Paleozoic and Mesozoic age. The inboard part of the Roebuck Basin overlies a major northwest-trending intracratonic ...
... The Roebuck Basin covers approximately 93,000 km2 on the North West Shelf. It forms the central part of the Westralian Superbasin, which is a northeast-trending passive margin of late Paleozoic and Mesozoic age. The inboard part of the Roebuck Basin overlies a major northwest-trending intracratonic ...
Supersequences, superbasins, supercontinents ± evidence from the
... continental crust that varies from c. 40±50 km in thickness. Whilst the crust was in part formed during the Archaean and early Palaeoproterozoic, its final assembly occurred at approximately 1.1 Ga as the Neoproterozoic supercontinent, Rodinia, came into being. The assembly process left an indelible ...
... continental crust that varies from c. 40±50 km in thickness. Whilst the crust was in part formed during the Archaean and early Palaeoproterozoic, its final assembly occurred at approximately 1.1 Ga as the Neoproterozoic supercontinent, Rodinia, came into being. The assembly process left an indelible ...
The Marine Environment
... century, Earth’s average surface temperature has increased by approximately 0.5°C. As Earth’s surface temperature rises, seawater warms up and as it warms, it also expands, which adds to the total volume of the seas. In addition, higher temperatures on Earth’s surface cause glaciers to melt, and the ...
... century, Earth’s average surface temperature has increased by approximately 0.5°C. As Earth’s surface temperature rises, seawater warms up and as it warms, it also expands, which adds to the total volume of the seas. In addition, higher temperatures on Earth’s surface cause glaciers to melt, and the ...
documenting the sangre de cristo uplift
... (Gregory and Chase, 1994). Three finegrained volcanic ash layers were discovered within this section, ranging in thickness from .04 m to 1.5 m. Samples of each were collected from the lowest portions of the beds, where the ash had not been reworked after initial deposition. William McIntosh at ...
... (Gregory and Chase, 1994). Three finegrained volcanic ash layers were discovered within this section, ranging in thickness from .04 m to 1.5 m. Samples of each were collected from the lowest portions of the beds, where the ash had not been reworked after initial deposition. William McIntosh at ...
Tertiary stratigraphy and tectonic evolution of southern Sumatra
... The exposed base of the Barisan Zone comprises calc . . alkaline andesitic volcanics which are interpreted to have been formed by subduction close to an active continental margin. The intercalated nature of the contact between this volcanic formation and the lowest sedimentary rocks of the Bengkulu ...
... The exposed base of the Barisan Zone comprises calc . . alkaline andesitic volcanics which are interpreted to have been formed by subduction close to an active continental margin. The intercalated nature of the contact between this volcanic formation and the lowest sedimentary rocks of the Bengkulu ...
Geographic Location of the basin Mumbai Offshore basin
... paleo-highs like Mumbai High, Heera etc. Its thickness varies from almost nil to hundreds of meters in deep sinks. Shelf Margin block, though under deep marine realm seem to have received lesser quantities of sediments which were either derived from the Diu Arch (?) or from localized provenances. Th ...
... paleo-highs like Mumbai High, Heera etc. Its thickness varies from almost nil to hundreds of meters in deep sinks. Shelf Margin block, though under deep marine realm seem to have received lesser quantities of sediments which were either derived from the Diu Arch (?) or from localized provenances. Th ...
Chapter 4 Continental Margins and Ocean Basins
... •Current sea level rise which began approximately 18-19,000 years ago (during latest Pleistocene time and continuing progressively during Holocene time to the present). •This rise in sea level is directly related to the melting of continental polar and mountain piedmont glaciers. •During the "climax ...
... •Current sea level rise which began approximately 18-19,000 years ago (during latest Pleistocene time and continuing progressively during Holocene time to the present). •This rise in sea level is directly related to the melting of continental polar and mountain piedmont glaciers. •During the "climax ...
Copyright © 2006, The Geological Society of America, Inc
... of the Apenninic-Maghrebian chain and the Afro-Adriatic continental crusts. From Quaternary times, the more pronounced slab retreat beneath the Calabrian arc with respect to the southern Apennines and Sicily produced a tearing of the crust through two transfer fault systems: the Vulcano line to the ...
... of the Apenninic-Maghrebian chain and the Afro-Adriatic continental crusts. From Quaternary times, the more pronounced slab retreat beneath the Calabrian arc with respect to the southern Apennines and Sicily produced a tearing of the crust through two transfer fault systems: the Vulcano line to the ...
44. Mesozoic-Cenozoic Geology of the Eastern Margin of the Grand
... is zone of "intermediate" crust defined by Parson et al. (1985). Numbered dots are selected well locations: 1 = Gabriel, 2 = Hibernia, 3 = Bonnition, 4 = Skua, 5 = Osprey, 6 = Jaeger. Lettered lines mark locations of seismic lines and cross sections in Figures 9 through 13. X's trace continent/ocean ...
... is zone of "intermediate" crust defined by Parson et al. (1985). Numbered dots are selected well locations: 1 = Gabriel, 2 = Hibernia, 3 = Bonnition, 4 = Skua, 5 = Osprey, 6 = Jaeger. Lettered lines mark locations of seismic lines and cross sections in Figures 9 through 13. X's trace continent/ocean ...
Settle-Carlisle booklet
... These desert conditions lasted some 30 – 40 million years, before giving way to a hot, arid plain of seasonal rivers, salt flats and lagoons, similar to the Persian Gulf today, in which the Eden Shales were deposited. The Boreal Ocean lay just to the north and occasionally flooded the region deposit ...
... These desert conditions lasted some 30 – 40 million years, before giving way to a hot, arid plain of seasonal rivers, salt flats and lagoons, similar to the Persian Gulf today, in which the Eden Shales were deposited. The Boreal Ocean lay just to the north and occasionally flooded the region deposit ...
Synclinal-horst basins: examples from the southern Rio Grande rift
... one another. Containing a maximum of 200 m of sediment, the Uvas Valley basin has a nearly symmetrical distribution of sediment thickness and appears to have been hydrologically closed throughout its history.The Miocene Gila Wilderness synclinal-horst basin is bordered on three sides by gently tilte ...
... one another. Containing a maximum of 200 m of sediment, the Uvas Valley basin has a nearly symmetrical distribution of sediment thickness and appears to have been hydrologically closed throughout its history.The Miocene Gila Wilderness synclinal-horst basin is bordered on three sides by gently tilte ...
gsa today - College of Science
... and Lawver et al. [1995]), because the more we learn about its structure and morphology, the more difficult it is to postulate a simple model to explain its tectonic evolution. Subduction has occurred along the southern South America–Antarctic Peninsula margin for most of the past 200 m.y. (Tanner e ...
... and Lawver et al. [1995]), because the more we learn about its structure and morphology, the more difficult it is to postulate a simple model to explain its tectonic evolution. Subduction has occurred along the southern South America–Antarctic Peninsula margin for most of the past 200 m.y. (Tanner e ...
The tectonic evolution of Sabah provides... development. The summary below was compiled... 2.1 TECTONIC EVOLUTION AND BASIN DEVELOPMENT IN SABAH
... General geology will discuss briefly on lithology distribution in Dent Peninsula, relative to the Dent Group sediments. The geological map (Figure 2.10) shows the Dent Group occurs in the eastern part of the Dent Peninsula, whereas the older Segama Group occurs in the western part. Generally, the se ...
... General geology will discuss briefly on lithology distribution in Dent Peninsula, relative to the Dent Group sediments. The geological map (Figure 2.10) shows the Dent Group occurs in the eastern part of the Dent Peninsula, whereas the older Segama Group occurs in the western part. Generally, the se ...
Messinian salinity crisis

The Messinian Salinity Crisis (MSC), also referred to as the Messinian Event, and in its latest stage as the Lago Mare event, was a geological event during which the Mediterranean Sea went into a cycle of partly or nearly complete desiccation throughout the latter part of the Messinian age of the Miocene epoch, from 5.96 to 5.33 Ma (million years ago). It ended with the Zanclean flood, when the Atlantic reclaimed the basin.Sediment samples from below the deep seafloor of the Mediterranean Sea, which include evaporite minerals, soils, and fossil plants, show that, about 5.96 million years ago in the late Miocene period, the precursor of the Strait of Gibraltar closed tight and the Mediterranean Sea, for the first time and then repeatedly, partially desiccated. The strait closed 5.6 Ma for the last time and, because of the generally dry climate conditions, within a millennium the Mediterranean basin nearly completely dried out, evaporating into a deep dry basin bottoming at some places 3 to 5 km (1.9 to 3.1 mi) below the world ocean level, with a few hypersaline Dead Sea-like pockets. Around 5.5 Ma, less dry climatic conditions allowed the basin to resume receiving more fresh water from rivers, with pockets of Caspian-like brackish waters getting progressively less hyper-saline, until the Strait of Gibraltar finally reopened 5.33 Ma with the Zanclean flood.Even now the Mediterranean is saltier than the North Atlantic because of its near isolation by the Strait of Gibraltar and its high rate of evaporation. If the Strait of Gibraltar closes again, which is likely to happen in the near geological future (though extremely distantly on a human time scale), the Mediterranean would mostly evaporate in about a thousand years. After that, continued northward movement of Africa may obliterate the Mediterranean: see Mediterranean Ridge.