The Binomial distribution
... The number of “successes” in the binomial experiment. Let Y = # of success in the above model. Then Y is a binomial random variable with parameters n (sample size) and p (success probability). It is often denoted Y ∼ B(n, p). ...
... The number of “successes” in the binomial experiment. Let Y = # of success in the above model. Then Y is a binomial random variable with parameters n (sample size) and p (success probability). It is often denoted Y ∼ B(n, p). ...
Section 9.5 The Binomial Theorem
... 3) The sum of the powers in each term is n. 4) The coefficients increase and then decrease in a symmetric pattern. The Binomial Theorem states that in the expansion of (x + y)n = xn + nxn – 1y + . . . + nCrxn – ryr + . . . + nxyn – 1 + yn, the coefficient ...
... 3) The sum of the powers in each term is n. 4) The coefficients increase and then decrease in a symmetric pattern. The Binomial Theorem states that in the expansion of (x + y)n = xn + nxn – 1y + . . . + nCrxn – ryr + . . . + nxyn – 1 + yn, the coefficient ...
Document
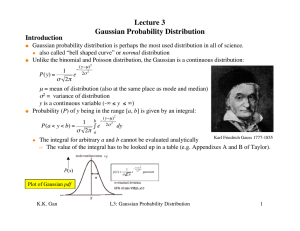
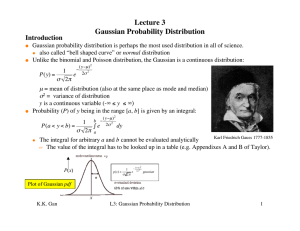
... The probability distribution for a random variable describes how probabilities are distributed over the values of the random variable. The probability distribution is defined by a probability function, denoted by f(x), which provides the probability for each value of the random variable. The require ...
... The probability distribution for a random variable describes how probabilities are distributed over the values of the random variable. The probability distribution is defined by a probability function, denoted by f(x), which provides the probability for each value of the random variable. The require ...
Document
... Queueing systems Inventory and supply-chain systems Reliability and maintainability ...
... Queueing systems Inventory and supply-chain systems Reliability and maintainability ...
Math Lesson-2.notebook
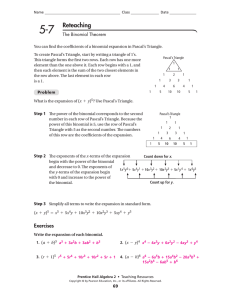
... The values of nCr in a triangular pattern in which each row corresponds with to a value of n. ...
... The values of nCr in a triangular pattern in which each row corresponds with to a value of n. ...
notebook05
... The plot shows the probability histograms of S1 = X, S2 , S3 , . . ., S10 . Note that the distribution of S10 is approximately bell-shaped. The convergence for other types of distributions may take much longer. For example, if the distribution of X is very skewed, then the convergence will be slow. ...
... The plot shows the probability histograms of S1 = X, S2 , S3 , . . ., S10 . Note that the distribution of S10 is approximately bell-shaped. The convergence for other types of distributions may take much longer. For example, if the distribution of X is very skewed, then the convergence will be slow. ...
2.1 One-dimensional random variable and distribution
... for black. Remember X as the numbers of taking white balls, remember Y as the numbers of taking balls ,Get the probability distribution for X, Y and the probability for taking at least three times. Solution (1) The possible value for X is 0,1,2,3, P(X=0)=5/8, P(X=1)=(3×5)/(8×7)=15/56 P(X=2)=(3×2×5)/ ...
... for black. Remember X as the numbers of taking white balls, remember Y as the numbers of taking balls ,Get the probability distribution for X, Y and the probability for taking at least three times. Solution (1) The possible value for X is 0,1,2,3, P(X=0)=5/8, P(X=1)=(3×5)/(8×7)=15/56 P(X=2)=(3×2×5)/ ...
3.6 Binomial probabilities
... = number of ways of selecting k different items in order from n objects = number of permutations of n things taken k at a time An important special case is where k = n. A vector (i1, ..., in) which uses all of x1, ..., xn exactly once is just a rearrangement of x1, ..., xn and is often called a perm ...
... = number of ways of selecting k different items in order from n objects = number of permutations of n things taken k at a time An important special case is where k = n. A vector (i1, ..., in) which uses all of x1, ..., xn exactly once is just a rearrangement of x1, ..., xn and is often called a perm ...
AP 7.5B Notes
... Shape: The probability distribution of X is skewed to the right. It is more likely to have 0, 1, or 2 children with type O blood than a larger value. Center: The median number of children with type O blood is 1. Based on our formula for the mean (find the expected value): ...
... Shape: The probability distribution of X is skewed to the right. It is more likely to have 0, 1, or 2 children with type O blood than a larger value. Center: The median number of children with type O blood is 1. Based on our formula for the mean (find the expected value): ...
Ch4 How to Do it: Calculate Relative Frequency Probabilities from
... Determining Cumulative Probabilities for Normal Distribution: - Click on Calc > Probability Distributions > Normal - Chose Cumulative probability - Type in Mean and the Standard Deviation - Check Input Constant, enter in the number ...
... Determining Cumulative Probabilities for Normal Distribution: - Click on Calc > Probability Distributions > Normal - Chose Cumulative probability - Type in Mean and the Standard Deviation - Check Input Constant, enter in the number ...
5-7 Reteaching answers
... To create Pascal’s Triangle, start by writing a triangle of 1’s. This triangle forms the first two rows. Each row has one more element than the one above it. Each row begins with a 1, and then each element is the sum of the two closest elements in the row above. The last element in each row is a 1. ...
... To create Pascal’s Triangle, start by writing a triangle of 1’s. This triangle forms the first two rows. Each row has one more element than the one above it. Each row begins with a 1, and then each element is the sum of the two closest elements in the row above. The last element in each row is a 1. ...