Chapter 7 Cellular control
... in the ribosome, so that just six of its bases are exposed. This is two codons. A tRNA with an anticodon that is complementary to the first mRNA codon then binds with it (Figure 7.6). Complementary base pairing makes sure that only the ‘correct’ tRNA can bind. For example, if the mRNA codon is AUG, ...
... in the ribosome, so that just six of its bases are exposed. This is two codons. A tRNA with an anticodon that is complementary to the first mRNA codon then binds with it (Figure 7.6). Complementary base pairing makes sure that only the ‘correct’ tRNA can bind. For example, if the mRNA codon is AUG, ...
Comparison between the efficiency of liposome and
... animals such as mice and rats. Moreover, sperms that collected from only one male have the ability to fertilize several females. Add to that, collection of rabbit sperms can be done twice a week without effecting on its efficiency, easier superovulation of rabbits with continuous reproducibility all ...
... animals such as mice and rats. Moreover, sperms that collected from only one male have the ability to fertilize several females. Add to that, collection of rabbit sperms can be done twice a week without effecting on its efficiency, easier superovulation of rabbits with continuous reproducibility all ...
Crash course on Computational Biology for Computer Scientists
... efficiency (some random reads not mapped) if it increases the speed of overall mapping This is in particular true in cases where we want to count reads rather than identify the variants One such case is mRNA expression profiling, when we are interested in relative abundances of fragments of the refe ...
... efficiency (some random reads not mapped) if it increases the speed of overall mapping This is in particular true in cases where we want to count reads rather than identify the variants One such case is mRNA expression profiling, when we are interested in relative abundances of fragments of the refe ...
Document
... is green and dunking it in the media. Twice should be enough. Grow overnight. Usually 10 ml of broth in a 50 ml centrifuge is adequate but 50 ml in a 250 ml flask may be necessary for large scale extractions. 2. There are two ways to collect the tissue. The preferred way is to pour the media over a ...
... is green and dunking it in the media. Twice should be enough. Grow overnight. Usually 10 ml of broth in a 50 ml centrifuge is adequate but 50 ml in a 250 ml flask may be necessary for large scale extractions. 2. There are two ways to collect the tissue. The preferred way is to pour the media over a ...
DNA Transcription All#read
... number of essential cofactors (collectively called general transcription factors), and one of these, TFIID, recognizes the TATA box and ensures that the correct start site is used. Another cofactor, TFIIB, recognizes a different common consensus sequence, G/C G/C G/C G C C C, approximately 38 to 32 ...
... number of essential cofactors (collectively called general transcription factors), and one of these, TFIID, recognizes the TATA box and ensures that the correct start site is used. Another cofactor, TFIIB, recognizes a different common consensus sequence, G/C G/C G/C G C C C, approximately 38 to 32 ...
why care
... Chromosome Anatomy A few key points The chromosome shown on the right is seen for a fleeting period during the cell division cycle. The rest of the time the DNA is much less tightly packed ...
... Chromosome Anatomy A few key points The chromosome shown on the right is seen for a fleeting period during the cell division cycle. The rest of the time the DNA is much less tightly packed ...
From DNA to Protein
... C What happened in the gene region? RNA polymerase catalyzed the covalent bonding of many nucleotides to one another to form an RNA strand. The base sequence of the new RNA strand is complementary to the base sequence of its DNA template—a copy of the gene. Fig. 14-5b, p. 219 ...
... C What happened in the gene region? RNA polymerase catalyzed the covalent bonding of many nucleotides to one another to form an RNA strand. The base sequence of the new RNA strand is complementary to the base sequence of its DNA template—a copy of the gene. Fig. 14-5b, p. 219 ...
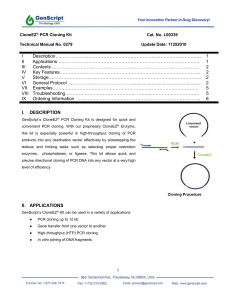
CloneEZ PCR Cloning Kit
... restriction site in the middle, and the insert-specific sequence at the 3’-end. How to choose the 15-base sequence add-on is illustrated in the graph below. ...
... restriction site in the middle, and the insert-specific sequence at the 3’-end. How to choose the 15-base sequence add-on is illustrated in the graph below. ...
Document
... C What happened in the gene region? RNA polymerase catalyzed the covalent bonding of many nucleotides to one another to form an RNA strand. The base sequence of the new RNA strand is complementary to the base sequence of its DNA template—a copy of the gene. Fig. 14-5b, p. 219 ...
... C What happened in the gene region? RNA polymerase catalyzed the covalent bonding of many nucleotides to one another to form an RNA strand. The base sequence of the new RNA strand is complementary to the base sequence of its DNA template—a copy of the gene. Fig. 14-5b, p. 219 ...
DNA and Cell Division
... 1. mRNA travels to the ribosome from the nucleus. 2. The base code in the mRNA determines the order of the amino acids in the protein. The genetic code in mRNA is read in “words” of three letters (triplets), called codons. There are 20 amino acids and different codons code for different ones. For ex ...
... 1. mRNA travels to the ribosome from the nucleus. 2. The base code in the mRNA determines the order of the amino acids in the protein. The genetic code in mRNA is read in “words” of three letters (triplets), called codons. There are 20 amino acids and different codons code for different ones. For ex ...
Messenger RNA
... material, and the sequence of the nucleotide bases in its strands must carry some sort of code. For the code to work, the cell has to be able to understand it…so…what exactly do the bases code for and where is the cell’s decoding system? ...
... material, and the sequence of the nucleotide bases in its strands must carry some sort of code. For the code to work, the cell has to be able to understand it…so…what exactly do the bases code for and where is the cell’s decoding system? ...
File - Molecular Biology 2
... double-stranded circular molecules of DNA present in bacteria. Plasmids range from about 1 kb (1 kilobase = 1,000 base pairs) to over 200 kb in size, and many replicate autonomously. Many plasmids also carry antibiotic-resistance genes, which are ideal selectable markers. A limiting factor in using ...
... double-stranded circular molecules of DNA present in bacteria. Plasmids range from about 1 kb (1 kilobase = 1,000 base pairs) to over 200 kb in size, and many replicate autonomously. Many plasmids also carry antibiotic-resistance genes, which are ideal selectable markers. A limiting factor in using ...
The Mysteries of Life
... needed; so the population can never die out because of lack of reproduction. This process is much faster, and easier than a sexual reproduction- since there are less steps. It also doesn’t allow any variation-there can only be replications of the original organism. This can be a good trait, because ...
... needed; so the population can never die out because of lack of reproduction. This process is much faster, and easier than a sexual reproduction- since there are less steps. It also doesn’t allow any variation-there can only be replications of the original organism. This can be a good trait, because ...
Mutations - GK-12 Program at the University of Houston
... by their effect on the structure of DNA or a chromosome. For this categorization, mutations can be separated into two main groups, each with multiple specific types. The two general categories are large-scale and small-scale mutations. Small-Scale Mutations Small-scale mutations are those which effe ...
... by their effect on the structure of DNA or a chromosome. For this categorization, mutations can be separated into two main groups, each with multiple specific types. The two general categories are large-scale and small-scale mutations. Small-Scale Mutations Small-scale mutations are those which effe ...
Fishel, R., Lescoe, M. K., Rao, M. R., Copeland, N. G., Jenkins, N. A.
... result from the pairing of two different parental DNA sequences (Holliday, 1964). Mismatched nucleotides produced by each of these mechanisms are known to be repaired by specific enzyme systems (Friedberg, 1990; Modrich, 1991). The best-defined mismatch repair pathway is the Escherichia coli MutHLS ...
... result from the pairing of two different parental DNA sequences (Holliday, 1964). Mismatched nucleotides produced by each of these mechanisms are known to be repaired by specific enzyme systems (Friedberg, 1990; Modrich, 1991). The best-defined mismatch repair pathway is the Escherichia coli MutHLS ...
ch_07_clicker_questions
... Which statement regarding prokaryotic chromosomes is incorrect? a) There are two copies of the chromosome so that cells are diploid. b) There is a single copy of the chromosome so that cells are haploid. c) Prokaryotic chromosomes are located in the nucleoid. d) Prokaryotic chromosomes are now know ...
... Which statement regarding prokaryotic chromosomes is incorrect? a) There are two copies of the chromosome so that cells are diploid. b) There is a single copy of the chromosome so that cells are haploid. c) Prokaryotic chromosomes are located in the nucleoid. d) Prokaryotic chromosomes are now know ...
Recombinant DNA Technology
... Recombinant technology begins with the isolation of a gene of interest (target gene). The target gene is then inserted into the plasmid or phage (vector) to form replicon. The replicon is then introduced into host cells to cloned and either express the protein or not. The cloned replicon is refe ...
... Recombinant technology begins with the isolation of a gene of interest (target gene). The target gene is then inserted into the plasmid or phage (vector) to form replicon. The replicon is then introduced into host cells to cloned and either express the protein or not. The cloned replicon is refe ...
Structure and Physiological significance of lipid
... Recombinant DNA molecules are created in nature more often than in the laboratory; • for example, every time a bacteria phage or eukaryotic virus infects its host cell and integrates its DNA into the host genome, a recombinant is created. • Occasionally, these viruses pick up a fragment of host DN ...
... Recombinant DNA molecules are created in nature more often than in the laboratory; • for example, every time a bacteria phage or eukaryotic virus infects its host cell and integrates its DNA into the host genome, a recombinant is created. • Occasionally, these viruses pick up a fragment of host DN ...
From DNA to Protein: Genotype to Phenotype Reading Assignments
... acids, the genetic code is redundant; that is, there is more than one codon for certain amino acids. However, a single codon does not specify more than one amino acid. • The genetic code is degenerate but not ...
... acids, the genetic code is redundant; that is, there is more than one codon for certain amino acids. However, a single codon does not specify more than one amino acid. • The genetic code is degenerate but not ...
Chapter 21: Genomics I: Analysis of DNA and Transposable Elements
... elements (TEs), also called transposons, have sometimes been referred to as “jumping genes” because they are inherently mobile. They were discovered by Barbara McClintock in the 1950s through her classic studies with corn. Since then, geneticists have discovered many different types of TEs in organi ...
... elements (TEs), also called transposons, have sometimes been referred to as “jumping genes” because they are inherently mobile. They were discovered by Barbara McClintock in the 1950s through her classic studies with corn. Since then, geneticists have discovered many different types of TEs in organi ...
What makes me tick…tock? June 2012 Lesson 3: How can genetics
... However, in essence, a protein is a strand of amino acids (like beads on a string) and the threedimensional structure is determined by the interactions of the amino acids with one another. There is inherent variability in protein shape and even when scientists know the amino acid sequence (primary s ...
... However, in essence, a protein is a strand of amino acids (like beads on a string) and the threedimensional structure is determined by the interactions of the amino acids with one another. There is inherent variability in protein shape and even when scientists know the amino acid sequence (primary s ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.