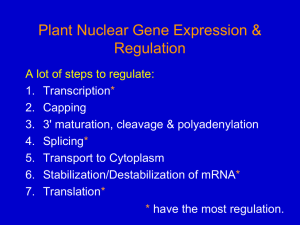
Nuclear gene expression 1
... • AAUAA is the key signal in higher plants, its found ~20 nt from the polyA-tail. – Other sequences 5' to the AAUAA also ...
... • AAUAA is the key signal in higher plants, its found ~20 nt from the polyA-tail. – Other sequences 5' to the AAUAA also ...
Bio 2 final n
... e. They do not recombine homologous chromosomes during meiosis. ____ 18. Which of the following sets of materials are required by both eukaryotes and prokaryotes for ...
... e. They do not recombine homologous chromosomes during meiosis. ____ 18. Which of the following sets of materials are required by both eukaryotes and prokaryotes for ...
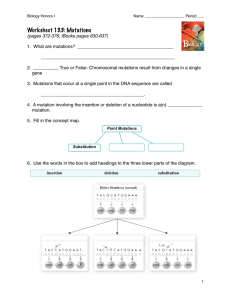
Worksheet 13.3
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
... 2. __________ True or False: Chromosomal mutations result from changes in a single gene 3. Mutations that occur at a single point in the DNA sequence are called ...
Molecular Biology Fourth Edition
... • In many cases, the 2′-hydroxyl group on ribose, a chemical feature that distinguishes RNA from DNA, seems to be directly or indirectly responsible for these unique structural properties. • The presence of the 2′ hydroxyl makes RNA vulnerable to hydrolysis, but it also allows for additional hydroge ...
... • In many cases, the 2′-hydroxyl group on ribose, a chemical feature that distinguishes RNA from DNA, seems to be directly or indirectly responsible for these unique structural properties. • The presence of the 2′ hydroxyl makes RNA vulnerable to hydrolysis, but it also allows for additional hydroge ...
Inquiry into Life Twelfth Edition
... • cDNAs don’t have the sticky ends of genomic DNA cleaved with restriction enzymes • Blunt ends will ligate, but is inefficient • Generate sticky ends using enzyme terminal ...
... • cDNAs don’t have the sticky ends of genomic DNA cleaved with restriction enzymes • Blunt ends will ligate, but is inefficient • Generate sticky ends using enzyme terminal ...
Lecture 2
... DNA exists in the nucleus as a condensed, compact structure. To prepare DNA for replication, a series of proteins aid in the unwinding and separation of the double-stranded DNA molecule. These proteins are required because DNA must be single-stranded before replication can proceed. 1. Тоpoisomerases ...
... DNA exists in the nucleus as a condensed, compact structure. To prepare DNA for replication, a series of proteins aid in the unwinding and separation of the double-stranded DNA molecule. These proteins are required because DNA must be single-stranded before replication can proceed. 1. Тоpoisomerases ...
Chapter 12
... • The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can be used to quickly clone a very large number of DNA copies for analysis – DNA sample mixed with DNA polymerase, nucleotide monomers, other ingredients – Mixture exposed to cycles of heating to separate the DNA strands – During each cycle, DNA replicates, dou ...
... • The polymerase chain reaction (PCR) can be used to quickly clone a very large number of DNA copies for analysis – DNA sample mixed with DNA polymerase, nucleotide monomers, other ingredients – Mixture exposed to cycles of heating to separate the DNA strands – During each cycle, DNA replicates, dou ...
GP3 Study Guide (Topic 3) 2017 Topic 3.1
... Genome refers to the whole or complete genetic information of an organism. When genes change in an organism, a mutation is said to have occurred. A mutation involves a base change in a gene, sequence of DNA. Base substitution is the simplest type of mutation in which one base in a gene is replaced b ...
... Genome refers to the whole or complete genetic information of an organism. When genes change in an organism, a mutation is said to have occurred. A mutation involves a base change in a gene, sequence of DNA. Base substitution is the simplest type of mutation in which one base in a gene is replaced b ...
DNA Transcription and Translation
... 1. Where in the cell does transcription occur? 2. What nucleic acids are involved in the process of transcription? 3. What is the importance of transcription? 4. In transcription, how come the whole DNA molecule is not copied into mRNA? 5. How does one gene differ structurally from another? 6. Becau ...
... 1. Where in the cell does transcription occur? 2. What nucleic acids are involved in the process of transcription? 3. What is the importance of transcription? 4. In transcription, how come the whole DNA molecule is not copied into mRNA? 5. How does one gene differ structurally from another? 6. Becau ...
Leica DNA digital levels Equipment List
... stations provide the right solution for every application. They unite reliable results with easy operation and user-friendly applications. Our total stations are designed to meet your specific requirements. Modern technology enables you to work fast and productively, thanks to the straightforward an ...
... stations provide the right solution for every application. They unite reliable results with easy operation and user-friendly applications. Our total stations are designed to meet your specific requirements. Modern technology enables you to work fast and productively, thanks to the straightforward an ...
Questions - National Biology Competition
... Since your score on the exam is based on the number of questions you answered correctly minus one-third of the number you answered incorrectly, it is improbable that guessing will improve your score (it is more likely to lower your score). (No points are deducted or awarded for unanswered questions. ...
... Since your score on the exam is based on the number of questions you answered correctly minus one-third of the number you answered incorrectly, it is improbable that guessing will improve your score (it is more likely to lower your score). (No points are deducted or awarded for unanswered questions. ...
4.1
... two-stranded molecule with a shape like a ladder that has been twisted into a spiral. DNA stores instructions for how to form cells, for the chemicals and structures that cells must make, and for everything that the cell does. DNA also stores genetic material—information that is passed on from one g ...
... two-stranded molecule with a shape like a ladder that has been twisted into a spiral. DNA stores instructions for how to form cells, for the chemicals and structures that cells must make, and for everything that the cell does. DNA also stores genetic material—information that is passed on from one g ...
Biotechnology toolkit part 2
... Exons are the coding parts of a gene and introns are the non-coding parts of a gene which are removed before translation (splicing). About 90% of the human genome has no known function and mainly consists on intron. Exons that code for the amino acid sequence in essential proteins vary little, sinc ...
... Exons are the coding parts of a gene and introns are the non-coding parts of a gene which are removed before translation (splicing). About 90% of the human genome has no known function and mainly consists on intron. Exons that code for the amino acid sequence in essential proteins vary little, sinc ...
Model of unequal chromosomal crossing over in DNA sequences1
... parental chromosome changes in length, one becomes longer, while the other becomes shorter. We base our model on this mechanism of unequal chromosomal crossing over, which is de ned as follows: Model. Consider a segment with a DTR of length ‘ (see Fig. 2). We de ne unequal crossing over to be when a ...
... parental chromosome changes in length, one becomes longer, while the other becomes shorter. We base our model on this mechanism of unequal chromosomal crossing over, which is de ned as follows: Model. Consider a segment with a DTR of length ‘ (see Fig. 2). We de ne unequal crossing over to be when a ...
What do we need DNA for?
... Amplification of RNA (monitor gene expression): reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) Step 1: generate a 1st strand cDNA using reverse transcriptase (catalyzes synthesis of DNA from an RNA template) ...
... Amplification of RNA (monitor gene expression): reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR) Step 1: generate a 1st strand cDNA using reverse transcriptase (catalyzes synthesis of DNA from an RNA template) ...
Molecular taxonomy,use of modern methods in the identification of a
... compare two different species, one employes same types of restriction enzymes to cleave the DNA of both species and the comparison of the two may reveal the similarity or dissimilarity between them. In PCR identification, a single segment of DNA is amplified. Such DNA segment can be a particular pro ...
... compare two different species, one employes same types of restriction enzymes to cleave the DNA of both species and the comparison of the two may reveal the similarity or dissimilarity between them. In PCR identification, a single segment of DNA is amplified. Such DNA segment can be a particular pro ...
Nucleic Acids and Proteins
... DNA consist of two long polymers of simple units called nucleotides, with backbones made of sugars and phosphate groups. These strands are anti-parallel. It is the sequence of the four bases attached to each sugar that encodes information which is read by copying stretches of DNA into mRNA in transc ...
... DNA consist of two long polymers of simple units called nucleotides, with backbones made of sugars and phosphate groups. These strands are anti-parallel. It is the sequence of the four bases attached to each sugar that encodes information which is read by copying stretches of DNA into mRNA in transc ...
DNA supercoil

DNA supercoiling refers to the over- or under-winding of a DNA strand, and is an expression of the strain on that strand. Supercoiling is important in a number of biological processes, such as compacting DNA. Additionally, certain enzymes such as topoisomerases are able to change DNA topology to facilitate functions such as DNA replication or transcription. Mathematical expressions are used to describe supercoiling by comparing different coiled states to relaxed B-form DNA.As a general rule, the DNA of most organisms is negatively supercoiled.