
You Light Up My Life
... Theory Vs. Scientific Law Theory is a hypothesis that has been supported by many lines of evidence A law is a theory that has been supported for a significant amount of time Can a theory ever be proven 100% correct? ...
... Theory Vs. Scientific Law Theory is a hypothesis that has been supported by many lines of evidence A law is a theory that has been supported for a significant amount of time Can a theory ever be proven 100% correct? ...
What are the characteristics of living things?
... needed to perform life processes. oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2) & nitrogen (N). 4. PROPER TEMPERATURE - needed to maintain “homeostasis” or “dynamic equilibrium” which means to have a constant, stable internal environment. ...
... needed to perform life processes. oxygen (O2), carbon dioxide (CO2) & nitrogen (N). 4. PROPER TEMPERATURE - needed to maintain “homeostasis” or “dynamic equilibrium” which means to have a constant, stable internal environment. ...
organisms - Lyndhurst Schools
... • BIOLOGY is the study of life. • Living things are called ORGANISMS. o Include animals, plants, fungi, protist, and bacteria. ...
... • BIOLOGY is the study of life. • Living things are called ORGANISMS. o Include animals, plants, fungi, protist, and bacteria. ...
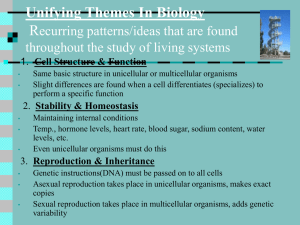
Unifying Themes in Biology Represent recurring patterns
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
... Temp., hormone levels, heart rate, blood sugar, sodium content, water levels, etc. Even unicellular organisms must do this ...
Biology II – Chapter 1 Study Guide
... 6. __________________________________________ is the process of generating a hypothesis of how an experiment or observation will turn out – usually an “if…then” statement. 7. The portion of the experiment that makes sure all other possible variables are constant is the __________________. 8. The sma ...
... 6. __________________________________________ is the process of generating a hypothesis of how an experiment or observation will turn out – usually an “if…then” statement. 7. The portion of the experiment that makes sure all other possible variables are constant is the __________________. 8. The sma ...
1-2 Notes
... • All living things are mainly water, but with other chemicals too, such as DNA • All living things need energy, some make their own, others must eat things • All organisms grow and develop, some more complex than others • All living things reproduce, some sexually, some asexually ...
... • All living things are mainly water, but with other chemicals too, such as DNA • All living things need energy, some make their own, others must eat things • All organisms grow and develop, some more complex than others • All living things reproduce, some sexually, some asexually ...
Chapter 1/2 PPT - Mr. Martino`s Blog
... community population (species) organism organ systems organs tissues cells molecules atoms The full spectrum of these interactions encompasses the scope of biology (study of life) Organisms are highly interdependent - energy flow begins with producers: plants and other organisms that make their ...
... community population (species) organism organ systems organs tissues cells molecules atoms The full spectrum of these interactions encompasses the scope of biology (study of life) Organisms are highly interdependent - energy flow begins with producers: plants and other organisms that make their ...
Biology and the Living World
... possible explanations of these observations that can be used in forming predictions that can be tested experimentally. Some hypotheses are rejected based on experimentation, while others are tentatively accepted. Scientific investigations use a series of six stages, called the scientific process, to ...
... possible explanations of these observations that can be used in forming predictions that can be tested experimentally. Some hypotheses are rejected based on experimentation, while others are tentatively accepted. Scientific investigations use a series of six stages, called the scientific process, to ...
Introduction to Biology
... Human body has 11 organ systems - circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory (urinary), immune (lymphatic), integumentary, muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory & skeletal ...
... Human body has 11 organ systems - circulatory, digestive, endocrine, excretory (urinary), immune (lymphatic), integumentary, muscular, nervous, reproductive, respiratory & skeletal ...
Biology Chapter 1
... • Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems, and organ systems make an organism • All living things are made of cells ...
... • Cells make tissues, tissues make organs, organs make organ systems, and organ systems make an organism • All living things are made of cells ...
Characteristics Of Life
... Recognize the use of “Big Ideas” in the study of Biology. Identify the general and specific properties of life. Recognize that the study of life does not make sense without evolution. Appreciate that science is a process. Recognize and use the steps of the scientific method. Differentiate between a ...
... Recognize the use of “Big Ideas” in the study of Biology. Identify the general and specific properties of life. Recognize that the study of life does not make sense without evolution. Appreciate that science is a process. Recognize and use the steps of the scientific method. Differentiate between a ...
A Course Outline Template [blank]
... An integrated introduction to scientific method and science content relevant to understanding both how science works and how science is relevant to many of the major world issues we face today. Questions to be investigated include the origin of life, energy and energy conservation and environmental ...
... An integrated introduction to scientific method and science content relevant to understanding both how science works and how science is relevant to many of the major world issues we face today. Questions to be investigated include the origin of life, energy and energy conservation and environmental ...
Vitalism

Vitalism is an obsolete scientific doctrine that ""living organisms are fundamentally different from non-living entities because they contain some non-physical element or are governed by different principles than are inanimate things"". Where vitalism explicitly invokes a vital principle, that element is often referred to as the ""vital spark"", ""energy"" or ""élan vital"", which some equate with the soul.Although rejected by modern science, vitalism has a long history in medical philosophies: most traditional healing practices posited that disease results from some imbalance in vital forces. In the Western tradition founded by Hippocrates, these vital forces were associated with the four temperaments and humours; Eastern traditions posited an imbalance or blocking of qi or prana.









![A Course Outline Template [blank]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/022920314_1-6a3ed0923450f16edce59c910af2e929-300x300.png)
