goals - s3.amazonaws.com
... short repetitive sequence seen within an intron sequence. • This sequence is referred to as an Alu sequence after a restriction enzyme site that is located within this 300 base pair length of DNA. ...
... short repetitive sequence seen within an intron sequence. • This sequence is referred to as an Alu sequence after a restriction enzyme site that is located within this 300 base pair length of DNA. ...
Chapter 8
... 8.1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins 1. What is a gene? A gene must be able to make copies of itself; mutate; store information that determines the characteristics of a cell; use this information synthesize proteins. 2. What four functions are performed by nucleic acids? 1) store information that ...
... 8.1 DNA and the Importance of Proteins 1. What is a gene? A gene must be able to make copies of itself; mutate; store information that determines the characteristics of a cell; use this information synthesize proteins. 2. What four functions are performed by nucleic acids? 1) store information that ...
Growth hormone - Life Sciences Outreach at Harvard University
... “The border zone … is not a sharp line, for it is in truth the fighting line where the conflict between the maternal cells and the invading trophoderm takes place, and it is strewn with such of the dead on both sides as have not already been carried off the field or otherwise disposed of.” ...
... “The border zone … is not a sharp line, for it is in truth the fighting line where the conflict between the maternal cells and the invading trophoderm takes place, and it is strewn with such of the dead on both sides as have not already been carried off the field or otherwise disposed of.” ...
Audesirk, Audesirk, Byers BIOLOGY: Life on Earth Eighth Edition
... nucleotides different from their normal meaning. ...
... nucleotides different from their normal meaning. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Ch. 10 Molecular Biology of the Gene
... specify amino acids. They’re called… • Codons • 3 base codons in DNA are transcribed into complementary RNA codon, then translated into amino acids that form a polypeptide chain. ...
... specify amino acids. They’re called… • Codons • 3 base codons in DNA are transcribed into complementary RNA codon, then translated into amino acids that form a polypeptide chain. ...
Prenatal Testing for Genetic Disorders
... chromosome abnormalities (e.g. Down syndrome) In most cases, testing is done only when there is a family history or some other indication, like advanced maternal age, points to risk for the fetus having a genetic disorder ...
... chromosome abnormalities (e.g. Down syndrome) In most cases, testing is done only when there is a family history or some other indication, like advanced maternal age, points to risk for the fetus having a genetic disorder ...
Nucleic Acids - Informational Polymers
... • Describe the characteristics that distinguish nucleic acids from the other classes of macromolecules • Summarize the functions of nucleic acids • List the major components of a nucleotide and describe how these monomers are linked together to form a nucleic acid • Distinguish between a pyrimidine ...
... • Describe the characteristics that distinguish nucleic acids from the other classes of macromolecules • Summarize the functions of nucleic acids • List the major components of a nucleotide and describe how these monomers are linked together to form a nucleic acid • Distinguish between a pyrimidine ...
File - Siegel Science
... • The goal is to create a plant that can produce a protein that will kill insects that try to eat it. • The bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis contain a gene that carries the instructions for making this protein. • You created a genetically modified plant that contained the Bt gene so that the plant wi ...
... • The goal is to create a plant that can produce a protein that will kill insects that try to eat it. • The bacteria Bacillus thuringiensis contain a gene that carries the instructions for making this protein. • You created a genetically modified plant that contained the Bt gene so that the plant wi ...
Structural Analysis of DNA-binding Domain of YycF
... contained only the carboxyl terminal half (see “Results and discussion”). Refinements and manual model building were performed with CNS [5s] and XtalView [6s], respectively. The details of X-ray crystallography are provided in Supplementary TABLE 1. The atomic coordinates and structure factors for ...
... contained only the carboxyl terminal half (see “Results and discussion”). Refinements and manual model building were performed with CNS [5s] and XtalView [6s], respectively. The details of X-ray crystallography are provided in Supplementary TABLE 1. The atomic coordinates and structure factors for ...
Bio 111
... Which of the following consists of a single strand of nucleotides? a. carbohydrates b. lipids c. proteins d. DNA e. RNA ...
... Which of the following consists of a single strand of nucleotides? a. carbohydrates b. lipids c. proteins d. DNA e. RNA ...
Genes
... by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the affected person has an extra 47th chromosome in all body cells. Risk = 1 in 75 at the age of 40 ...
... by abnormal genes, one from each parent. Down Syndrome: Caused by a chromosomal abnormality known as Trisony-21,( the presence of three copies of the 21st chromosome). As a result, the affected person has an extra 47th chromosome in all body cells. Risk = 1 in 75 at the age of 40 ...
Transcription Worksheet
... 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of mRNA called?___________________________________________ 4. ...
... 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of mRNA called?___________________________________________ 4. ...
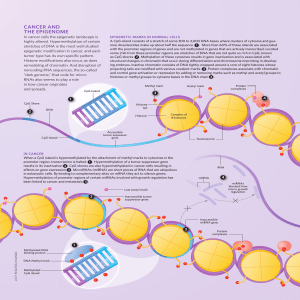
CaNCer aND THe ePIGeNOMe
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
... epigenetic modification in cancer, and each tumor type has its own specific pattern. Histone modifications also occur, as does remodeling of chromatin. And disruption of noncoding RNA sequences, the so-called “dark genome,” that code for microRNAs also seems to play a role in how cancer originates a ...
Transcription Worksheet
... 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of mRNA called?___________________________________________ 4. ...
... 1. What is the enzyme that is important for the process of transcription?______________________________ 2. In DNA, what is the sugar called?___________________________________________________________ 3. What is a three nucleotide sequence of mRNA called?___________________________________________ 4. ...
NIPT
... False-positive rate of 3.8% would potentially limit the clinical utility as a stand-alone screening test Of 55 false-positive samples, 35 were caused by deletions/duplications present in maternal DNA ...
... False-positive rate of 3.8% would potentially limit the clinical utility as a stand-alone screening test Of 55 false-positive samples, 35 were caused by deletions/duplications present in maternal DNA ...
dna_notes - KScience
... Point mutations are changes to single bases in genes. There are 3 types of point mutations. Insertions – a base is added to the sequence between two existing bases. Deletions – a base is lost from the sequence. Substitutions – a base is replaced with a different base. Mutations are sometimes b ...
... Point mutations are changes to single bases in genes. There are 3 types of point mutations. Insertions – a base is added to the sequence between two existing bases. Deletions – a base is lost from the sequence. Substitutions – a base is replaced with a different base. Mutations are sometimes b ...
BIO 132: Genes and People
... Week 3: Illustrating the percentage of traits in a population via mono and di hybrid crosses In class group assignment Topic 8. Pedigrees Week 9: Analyze pedigrees to understand patterns (dominant, recessive, sex-linked diseases) of disease occurrence in populations In class group assignment ...
... Week 3: Illustrating the percentage of traits in a population via mono and di hybrid crosses In class group assignment Topic 8. Pedigrees Week 9: Analyze pedigrees to understand patterns (dominant, recessive, sex-linked diseases) of disease occurrence in populations In class group assignment ...
The Secret Code of Life: - Richmond School District
... in Latin) • When just one base is changed in the DNA, it is considered a mutation. It would also create a new allele for the gene. Not all mutations are harmful. ...
... in Latin) • When just one base is changed in the DNA, it is considered a mutation. It would also create a new allele for the gene. Not all mutations are harmful. ...
90718-exm-04
... Discuss the benefits and problems associated with making recombinant human growth hormone compared to previous methods of extracting this protein. ...
... Discuss the benefits and problems associated with making recombinant human growth hormone compared to previous methods of extracting this protein. ...
AP Biology Review Chapters 13-14 Review Questions Chapter 12
... a) Describe the role of THREE of the following in the regulation of protein synthesis: RNA splicing Repressor proteins Methylation siRNA b) Information flow can be altered by mutation. Describe THREE different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis. c) Identify TWO environm ...
... a) Describe the role of THREE of the following in the regulation of protein synthesis: RNA splicing Repressor proteins Methylation siRNA b) Information flow can be altered by mutation. Describe THREE different types of mutations and their effect on protein synthesis. c) Identify TWO environm ...
DNA TECHNOLOGY - Mount Mansfield Union High School
... Klimanskaya I, Chung Y, Becker S, Lu SJ, Lanza R. (2006). "Human embryonic stem cell lines derived from single blastomeres.". Nature ...
... Klimanskaya I, Chung Y, Becker S, Lu SJ, Lanza R. (2006). "Human embryonic stem cell lines derived from single blastomeres.". Nature ...
BioSc 231 Exam 3 2005
... Meselson and Stahl used a heavy form of nitrogen to demonstrate semi-conservative DNA replication. Bacterial cells were grown in the presence of heavy nitrogen until all the DNA contained the heavy form. The bacteria were then transferred to a medium that only contained the light form of nitrogen. ...
... Meselson and Stahl used a heavy form of nitrogen to demonstrate semi-conservative DNA replication. Bacterial cells were grown in the presence of heavy nitrogen until all the DNA contained the heavy form. The bacteria were then transferred to a medium that only contained the light form of nitrogen. ...