10/16
... Areas of DNA from very small samples can be amplified by PCR, and then cut with restriction enzymes for RFLP analysis. ...
... Areas of DNA from very small samples can be amplified by PCR, and then cut with restriction enzymes for RFLP analysis. ...
Dia 1 - BeSHG
... different genes but specific neuropathological characteristics: same pathogenesis ? new paradigm for genetic disease - anticipation repeats in non-coding regions of disease genes 3’ UTR in myotonic dystrophy, 5’ in fragile X mental retardation intronic in Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) putative antisense ...
... different genes but specific neuropathological characteristics: same pathogenesis ? new paradigm for genetic disease - anticipation repeats in non-coding regions of disease genes 3’ UTR in myotonic dystrophy, 5’ in fragile X mental retardation intronic in Friedreich ataxia (FRDA) putative antisense ...
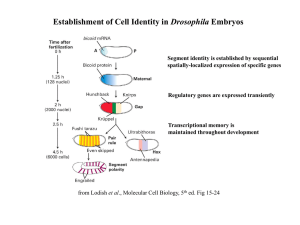
Establishment of Cell Identity in Drosophila Embryos
... PcG genes maintain the regional identity of segments by repressing Hox genes in specific regions ...
... PcG genes maintain the regional identity of segments by repressing Hox genes in specific regions ...
D.N.A. activity
... If considering length/volume compaction (a better analysis): 20 meters thread into a capsule volume of .02 x .01 x .01 meter or (2 x 10-6 m3). Cell manages to fit 2 meters of DNA into approximately (1 x 10-6m)3 or 1 x 10-18 m3. The difference in compaction ratios is on the order of 1013, or thirteen ...
... If considering length/volume compaction (a better analysis): 20 meters thread into a capsule volume of .02 x .01 x .01 meter or (2 x 10-6 m3). Cell manages to fit 2 meters of DNA into approximately (1 x 10-6m)3 or 1 x 10-18 m3. The difference in compaction ratios is on the order of 1013, or thirteen ...
RHD - Labex
... RhD immunoglobulin is becoming increasingly expensive Many women today receive unnecessary injections of human blood products Human material is a precious source ...
... RhD immunoglobulin is becoming increasingly expensive Many women today receive unnecessary injections of human blood products Human material is a precious source ...
Horizontal Gene transfer
... In order to study “viral specific genes”, need to examine phenotypes these genes impart One phenotype: plaque formation Lytic phages lyse bacteria in regions within the lawn of organims, producing zones of ...
... In order to study “viral specific genes”, need to examine phenotypes these genes impart One phenotype: plaque formation Lytic phages lyse bacteria in regions within the lawn of organims, producing zones of ...
Mutations
... signal" (or "stop" codon), causing the protein to be shortened. Silent mutations are point mutations that do not cause amino acid changes within the protein. ...
... signal" (or "stop" codon), causing the protein to be shortened. Silent mutations are point mutations that do not cause amino acid changes within the protein. ...
Mutations - Miss Garry`s Biology Class Website!
... A genetic disorder is a disease that is caused by an abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from a small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of an entire chromosome or set of chromosomes. ...
... A genetic disorder is a disease that is caused by an abnormality in an individual's DNA. Abnormalities can range from a small mutation in a single gene to the addition or subtraction of an entire chromosome or set of chromosomes. ...
Biotechnology - Biology Junction
... if you are going to engineer DNA & genes & organisms, then you need a set of tools to work with this unit is a survey of those tools… ...
... if you are going to engineer DNA & genes & organisms, then you need a set of tools to work with this unit is a survey of those tools… ...
HEREDITY - Susquehanna University
... Dominant and recessive phenotypes. (1) Parental generation. (2) F1 generation. (3) F2 generation. Dominant (red) and recessive (white) phenotype look alike in the F1 (first) generation and show a 3:1 ratio in the F2 (second) generation. ...
... Dominant and recessive phenotypes. (1) Parental generation. (2) F1 generation. (3) F2 generation. Dominant (red) and recessive (white) phenotype look alike in the F1 (first) generation and show a 3:1 ratio in the F2 (second) generation. ...
Anth. 203 Lab, Exercise #1
... Below is the base sequence for a small section of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) for 5 species of primate, as determined by Wesley Brown at U.C. Berkely. For the human and gibbon DNA codons, show the corresponding mRNA codons (on page 2) that would be synthesized during transcription and carry the messag ...
... Below is the base sequence for a small section of mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) for 5 species of primate, as determined by Wesley Brown at U.C. Berkely. For the human and gibbon DNA codons, show the corresponding mRNA codons (on page 2) that would be synthesized during transcription and carry the messag ...
Mutations - Kaikoura High School
... non-inheritable, if in gametes then can be passed on to offspring. • Can be due to mistakes in DNA replication (spontaneous) or caused by mutagenic agents e.g. UV light, ionising radiation, Xrays, chemicals, viruses ...
... non-inheritable, if in gametes then can be passed on to offspring. • Can be due to mistakes in DNA replication (spontaneous) or caused by mutagenic agents e.g. UV light, ionising radiation, Xrays, chemicals, viruses ...
New Patient Questionnaire
... We’re open Monday – Friday (except for major holidays) from 8am to 5pm. Appointment times vary depending on the service provided. Early morning or evening appointments may be available – please inquire at front desk. For approximate times of most common appointment types please see below: Ultrasound ...
... We’re open Monday – Friday (except for major holidays) from 8am to 5pm. Appointment times vary depending on the service provided. Early morning or evening appointments may be available – please inquire at front desk. For approximate times of most common appointment types please see below: Ultrasound ...
Nucleic Acids, the Genetic Code, and the Synthesis of
... Both DNA and RNA chains are produced by copying of template DNA strands Nucleic acid strands (poly-nucleotides) grow by the addition of one nucleotide at a time, and always in the 5’ -> 3’ direction RNA polymerases can initiate strand growth but DNA polymerases require a primer strand The primary po ...
... Both DNA and RNA chains are produced by copying of template DNA strands Nucleic acid strands (poly-nucleotides) grow by the addition of one nucleotide at a time, and always in the 5’ -> 3’ direction RNA polymerases can initiate strand growth but DNA polymerases require a primer strand The primary po ...
Chapter 8 DNA Fingerprinting and Forensic Analysis
... • In the United States the FBI has standardized a set of 13 STR assays (13 different locations on the chromosomes) for DNA typing, and has organized the CODIS database for forensic identification in criminal cases. • The United States maintains the largest DNA database in the world: The Combined DNA ...
... • In the United States the FBI has standardized a set of 13 STR assays (13 different locations on the chromosomes) for DNA typing, and has organized the CODIS database for forensic identification in criminal cases. • The United States maintains the largest DNA database in the world: The Combined DNA ...
The Molecular - MolGen | RuG
... (This use of the word transformation should not be confused with the conversion of a normal animal cell to a cancerous one, discussed near the end of Concept 12.3) Grifflth's work set the stage for a l4-year effort by American bacteriologist Oswald Avery to identify the transforming substance. Avery ...
... (This use of the word transformation should not be confused with the conversion of a normal animal cell to a cancerous one, discussed near the end of Concept 12.3) Grifflth's work set the stage for a l4-year effort by American bacteriologist Oswald Avery to identify the transforming substance. Avery ...
doc bio 202 2009
... 16. (1 point) An individual who is heterozygous has brittle bone disease disease (in the mutant heterozygote an abnormal copy of the protein wraps around one or two copies of the other and distorts the conformation of the functional trimeric molecule). This type of mutation is called a: a. a leaky m ...
... 16. (1 point) An individual who is heterozygous has brittle bone disease disease (in the mutant heterozygote an abnormal copy of the protein wraps around one or two copies of the other and distorts the conformation of the functional trimeric molecule). This type of mutation is called a: a. a leaky m ...
Chp. 3, Section E: How Does a Genetic Counselor Detect Mutant
... DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY (DMD), which is the subject of the following exercise, is a relatively common sex-linked disease. It affects about 1 boy in 3000, most of whom appear to be healthy until age 4 or 5, whereupon they begin to develop muscular weakness. Frequently, the first symptoms are prob ...
... DUCHENNE MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY (DMD), which is the subject of the following exercise, is a relatively common sex-linked disease. It affects about 1 boy in 3000, most of whom appear to be healthy until age 4 or 5, whereupon they begin to develop muscular weakness. Frequently, the first symptoms are prob ...
Practice Test - Cardinal Newman High School
... Binary fission is a form of sexual reproduction in bacteria. Human sperm and egg cells have 23 chromosomes. Trisomy is the addition or removal of a single nitrogen-containing base. During telophase, a nuclear envelope usually surrounds each new set of chromosomes. Chromatids separate from each other ...
... Binary fission is a form of sexual reproduction in bacteria. Human sperm and egg cells have 23 chromosomes. Trisomy is the addition or removal of a single nitrogen-containing base. During telophase, a nuclear envelope usually surrounds each new set of chromosomes. Chromatids separate from each other ...
Karyotype
... • Symptoms similar to mental retardation • Approx 1 in 800 babies born in U.S. • Chances of having a baby with Down Syndrome increases with the age of the mother. ...
... • Symptoms similar to mental retardation • Approx 1 in 800 babies born in U.S. • Chances of having a baby with Down Syndrome increases with the age of the mother. ...
The spectrum of human diseases
... – Solution – exclude all nondisease individuals form analysis – Requires many more families for study ...
... – Solution – exclude all nondisease individuals form analysis – Requires many more families for study ...
Ch 11 Standards Test Practice
... to become reddish brown. During the cold temperatures of winter, these enzymes do not function. As a result, the fox has a white coat that blends into the snowy background. What explains this change in color? A The genes of a fox are made of unstable DNA. B Mutations can be caused by temperature ...
... to become reddish brown. During the cold temperatures of winter, these enzymes do not function. As a result, the fox has a white coat that blends into the snowy background. What explains this change in color? A The genes of a fox are made of unstable DNA. B Mutations can be caused by temperature ...
Leukaemia Section t(3;11)(p21;q23) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... by the AF3p21 gene is fused to MLL in a therapy-related leukemia with t(3; 11)(p21;q23). Blood. 1999 ; 94 (numero Suppl 1). ...
... by the AF3p21 gene is fused to MLL in a therapy-related leukemia with t(3; 11)(p21;q23). Blood. 1999 ; 94 (numero Suppl 1). ...
BioPHP - Minitools Chaos Game Representation of DNAGraphical
... BioPHP tools DNA to protein translation This program translates the input DNA sequence into protein sequence. Translation can be carried out in 1, 3 or all the six frames. DNA sequence may be added as shown in the example input or in any other format (number, spaces and line feeds are removed). Also ...
... BioPHP tools DNA to protein translation This program translates the input DNA sequence into protein sequence. Translation can be carried out in 1, 3 or all the six frames. DNA sequence may be added as shown in the example input or in any other format (number, spaces and line feeds are removed). Also ...