Chapter 20: Biotechnology 11/18/2015
... A DNA microarray is a solid surface containing a precise array of single-stranded DNA sequences from 1000s of different genes in an organism. • labeled cDNA is produced from test cells and allowed to hybridize with sequences in the ...
... A DNA microarray is a solid surface containing a precise array of single-stranded DNA sequences from 1000s of different genes in an organism. • labeled cDNA is produced from test cells and allowed to hybridize with sequences in the ...
5. Related viruses can combine/recombine
... They can be spontaneous errors in replication or they can be caused by mutagens (environmental factors like radiation, chemicals, cigarette smoke, etc.) If a mutagen causes changes in genes that regulate the cell cycle / cell division it is considered a carcinogen (a cancer-causing factor) Som ...
... They can be spontaneous errors in replication or they can be caused by mutagens (environmental factors like radiation, chemicals, cigarette smoke, etc.) If a mutagen causes changes in genes that regulate the cell cycle / cell division it is considered a carcinogen (a cancer-causing factor) Som ...
14_lecture_ppt - Tracy Jubenville Nearing
... repeated many times along the length of one or more chromosomes. Transposons are specific DNA sequences that have the remarkable ability to move within and between chromosomes. ...
... repeated many times along the length of one or more chromosomes. Transposons are specific DNA sequences that have the remarkable ability to move within and between chromosomes. ...
REVIEW UNIT 4 & 5: HEREDITY & MOLECULAR GENETICS SAMPLE QUESTIONS
... The trait for yellow seed color is dominant (Y) and the trait for green seed color is recessive (y). A cross between two plants results in 296 tall yellow plants and 104 tall green plants. Which of the following are most likely to be the genotypes of the parents? (1999:28) a. TTYY x TTYY b. Ttyy x T ...
... The trait for yellow seed color is dominant (Y) and the trait for green seed color is recessive (y). A cross between two plants results in 296 tall yellow plants and 104 tall green plants. Which of the following are most likely to be the genotypes of the parents? (1999:28) a. TTYY x TTYY b. Ttyy x T ...
No Slide Title
... ˚A rough definition of a gene is a stretch of DNA that encodes one protein (polypeptide). •To allow different cell type to form, or for an organism to respond to changing conditions, only a subset of genes can be “expressed” (actively organizing amino acid chain formation) in any one cell or time. T ...
... ˚A rough definition of a gene is a stretch of DNA that encodes one protein (polypeptide). •To allow different cell type to form, or for an organism to respond to changing conditions, only a subset of genes can be “expressed” (actively organizing amino acid chain formation) in any one cell or time. T ...
12.6 DNA Repair
... Photoreactivation repair uses light energy to split pyrimidine dimers that kink the DNA. Pyrimidine dimers - bonds between C’s and/or T’s on the same strand. Photolyases - enzymes that absorb light energy and use it to detect and bind to pyrimidine dimers, then break the extra bond. Humans do no ...
... Photoreactivation repair uses light energy to split pyrimidine dimers that kink the DNA. Pyrimidine dimers - bonds between C’s and/or T’s on the same strand. Photolyases - enzymes that absorb light energy and use it to detect and bind to pyrimidine dimers, then break the extra bond. Humans do no ...
cells
... Chromosomes are divided into segments called Gene genes. • A small segment of DNA that codes for a protein that results in a particular trait. • Alternate forms of a gene are called alleles. ...
... Chromosomes are divided into segments called Gene genes. • A small segment of DNA that codes for a protein that results in a particular trait. • Alternate forms of a gene are called alleles. ...
Lecture8-Chap5 Sept26
... • There are extensive syntenic relationships between the mouse and human genomes, and most functional genes are in a syntenic region. • synteny – A relationship between chromosomal regions of different species where homologous genes occur in the same order. Figure 05.08: Mouse chromosome 1 has 21 se ...
... • There are extensive syntenic relationships between the mouse and human genomes, and most functional genes are in a syntenic region. • synteny – A relationship between chromosomal regions of different species where homologous genes occur in the same order. Figure 05.08: Mouse chromosome 1 has 21 se ...
Jeopardy
... That the DNA could just be active or inactive at the wrong places, and that by using the tags, we can modify gene expression to its normal state ...
... That the DNA could just be active or inactive at the wrong places, and that by using the tags, we can modify gene expression to its normal state ...
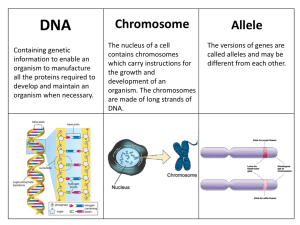
Chromosome Allele - GZ @ Science Class Online
... The versions of genes are called alleles and may be different from each other. ...
... The versions of genes are called alleles and may be different from each other. ...
The human genome
... The cells of all organisms, from bacteria to humans, contain one or more sets of a basic DNA complement that is unique to the species. This fundamental complement of DNA is called a genome. The genome may be subdivided into chromosomes, each of which is a very long single continuous DNA molecule. In ...
... The cells of all organisms, from bacteria to humans, contain one or more sets of a basic DNA complement that is unique to the species. This fundamental complement of DNA is called a genome. The genome may be subdivided into chromosomes, each of which is a very long single continuous DNA molecule. In ...
dna replication - MacWilliams Biology
... 1. The tips of chromosomes are known as telomeres. 2. Particularly difficult to copy. 3. Over time, DNA may actually be lost from telomeres each time a chromosome is replicated. 4. Enzyme called telomerase compensates for this problem by adding short, repeated DNA sequences to telomeres lengthens ...
... 1. The tips of chromosomes are known as telomeres. 2. Particularly difficult to copy. 3. Over time, DNA may actually be lost from telomeres each time a chromosome is replicated. 4. Enzyme called telomerase compensates for this problem by adding short, repeated DNA sequences to telomeres lengthens ...
Showing the 3D shape of our chromosomes
... a role in all sorts of vital processes, including gene activation, gene silencing, DNA replication and DNA repair. In fact, just about any genome function has a spatial component that has been implicated in its control. Dr Fraser added: “These unique images not only show us the structure of the chro ...
... a role in all sorts of vital processes, including gene activation, gene silencing, DNA replication and DNA repair. In fact, just about any genome function has a spatial component that has been implicated in its control. Dr Fraser added: “These unique images not only show us the structure of the chro ...
August 2007
... Color blindness is linked to testosterone levels. Color blindness is the dominant condition in males. Human females have two X chromosomes. The gene for color blindness is autosomal. ...
... Color blindness is linked to testosterone levels. Color blindness is the dominant condition in males. Human females have two X chromosomes. The gene for color blindness is autosomal. ...
Field Guide to Methylation Methods
... Expected/observed CpG ratio The human genome contains 25% of the expected number of C-G pairs due to spontaneous deamination of meC to T over evolutionary time scales. Genomic imprinting An epigenetic process causing genes to be expressed only from one of the parental chromosomes. ...
... Expected/observed CpG ratio The human genome contains 25% of the expected number of C-G pairs due to spontaneous deamination of meC to T over evolutionary time scales. Genomic imprinting An epigenetic process causing genes to be expressed only from one of the parental chromosomes. ...
Test Info Sheet
... Analysis is performed by bi-directional sequencing of the coding regions (exons 1-5) and splice sites of the EFNB1 gene. In cases where (1) no small intragenic mutation is identified and (2) no heterozygous positions are observed, focused array CGH analysis with exon-level resolution (ExonArrayDx) i ...
... Analysis is performed by bi-directional sequencing of the coding regions (exons 1-5) and splice sites of the EFNB1 gene. In cases where (1) no small intragenic mutation is identified and (2) no heterozygous positions are observed, focused array CGH analysis with exon-level resolution (ExonArrayDx) i ...
Review packet midterm 2016
... 4. The atomic number of an element tells the number of 5. The mass number of an element tells the number of ...
... 4. The atomic number of an element tells the number of 5. The mass number of an element tells the number of ...
Lecture 5
... Eukaryotic chromosomal organization • Many eukaryotes are diploid (2N) • The amount of DNA that eukaryotes have varies; the amount of DNA is not necessarily related to the complexity (Amoeba proteus has a larger amount of DNA than Homo sapiens) • Eukaryotic chromosomes are integrated with proteins ...
... Eukaryotic chromosomal organization • Many eukaryotes are diploid (2N) • The amount of DNA that eukaryotes have varies; the amount of DNA is not necessarily related to the complexity (Amoeba proteus has a larger amount of DNA than Homo sapiens) • Eukaryotic chromosomes are integrated with proteins ...
Genetics - Mrs. Yu`s Science Classes
... Alternative splicing allows different mRNA’s to be generated from the same RNA transcript. By selectively removing different parts of an RNA transcript, different mRNA’s can be produced, each coding for a different protein product. ...
... Alternative splicing allows different mRNA’s to be generated from the same RNA transcript. By selectively removing different parts of an RNA transcript, different mRNA’s can be produced, each coding for a different protein product. ...
AP Biology Fall Semester Review
... Forms parts of the ribosome. Serves as a template for protein synthesis. Is synthesized from a DNA template in the nucleus. Carries the code for a particular protein to the ribosome. ...
... Forms parts of the ribosome. Serves as a template for protein synthesis. Is synthesized from a DNA template in the nucleus. Carries the code for a particular protein to the ribosome. ...