Biotechnology
... In every case, the recombinant DNA must be taken up by the cell in a form in which it can be replicated and expressed. This is achieved by incorporating the DNA in a vector. an example of cloning using E. coli as the host and a plasmid as the vector. vector Plasmids are sometimes called "vectors", b ...
... In every case, the recombinant DNA must be taken up by the cell in a form in which it can be replicated and expressed. This is achieved by incorporating the DNA in a vector. an example of cloning using E. coli as the host and a plasmid as the vector. vector Plasmids are sometimes called "vectors", b ...
Ch. 11
... of amino acids in a protein. There are 20 amino acids used to build proteins 1. _____________________– set of 3 nitrogen bases that represents an amino acid E. Translation: From mRNA to Protein – translation takes place in the ribosome. Transfer RNA (tRNA) bring amino acids to the ribosomal RNA for ...
... of amino acids in a protein. There are 20 amino acids used to build proteins 1. _____________________– set of 3 nitrogen bases that represents an amino acid E. Translation: From mRNA to Protein – translation takes place in the ribosome. Transfer RNA (tRNA) bring amino acids to the ribosomal RNA for ...
2.5 Genetics - Rocoscience
... The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template A haploid sex cell which is capable of fusion The fusion of 2[haploid] gametes to form a [diploid] zygote An alternative form of a gene Has identical alleles [for a trait] Has different alleles [for a trait] The genetic make-up of an ind ...
... The process of making a protein using the mRNA code a template A haploid sex cell which is capable of fusion The fusion of 2[haploid] gametes to form a [diploid] zygote An alternative form of a gene Has identical alleles [for a trait] Has different alleles [for a trait] The genetic make-up of an ind ...
Fathers and Mothers of Genetics
... (Early 1900’s) Creator of the Punnett square, a tool in genetics which is used by biologists to predict the probability of possible genotypes of offspring. ...
... (Early 1900’s) Creator of the Punnett square, a tool in genetics which is used by biologists to predict the probability of possible genotypes of offspring. ...
Chapter 10 The Code of Life Test Review Name
... 28. The only way that a mutation can be passed on to offspring is if it is found in the sex cells of the parent ...
... 28. The only way that a mutation can be passed on to offspring is if it is found in the sex cells of the parent ...
Evelyn Section A
... G+C are possible combination and A+T is not the same as T+A as well as C+G is not the same as G+C (1).The DNA contains the hereditary information that is innate by the brood of an organism; ‘this information is determined by the sequence of the base pair along its length"(1). ...
... G+C are possible combination and A+T is not the same as T+A as well as C+G is not the same as G+C (1).The DNA contains the hereditary information that is innate by the brood of an organism; ‘this information is determined by the sequence of the base pair along its length"(1). ...
Quiz 2 Practice - philipdarrenjones.com
... 10. The ______________ is surrounded by a double membrane with pores and contains genetic material. a. rough endoplasmic reticulum b. Golgi complex c. nucleus d. lysosome e. smooth endoplasmic reticulum 11. Which of the following organelles performs sorting, modifying, packaging and shipping functio ...
... 10. The ______________ is surrounded by a double membrane with pores and contains genetic material. a. rough endoplasmic reticulum b. Golgi complex c. nucleus d. lysosome e. smooth endoplasmic reticulum 11. Which of the following organelles performs sorting, modifying, packaging and shipping functio ...
IMPLICATIONS OF ANTHROPGENY FOR MEDICINE AND
... Histones: Chief protein components of chromatin and can be chemically modified as part of epigenetics. Karyotype: Chromosome number in the cell nucleus. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA): Maternally inherited DNA found only in mitochondria (the energy generators of cells). Mutation: Change of a DNA sequence ...
... Histones: Chief protein components of chromatin and can be chemically modified as part of epigenetics. Karyotype: Chromosome number in the cell nucleus. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA): Maternally inherited DNA found only in mitochondria (the energy generators of cells). Mutation: Change of a DNA sequence ...
PCR-assay of intragenic DNA lesions induced by ionizing radiation
... observed; To detect the intragenic distribution of different DNA alterations relative to the exon-intron structure of the gene under study ...
... observed; To detect the intragenic distribution of different DNA alterations relative to the exon-intron structure of the gene under study ...
Microbial Genetics - University of Montana
... – Transmission of antibiotic resistance, virulence & pathogenicity factors – Transfer of new genes or gene homologues • Genomic stability: housekeeping functions ...
... – Transmission of antibiotic resistance, virulence & pathogenicity factors – Transfer of new genes or gene homologues • Genomic stability: housekeeping functions ...
Genes to Proteins Nucleic Acid Structure
... construct restriction maps of DNA. These are diagrams of specific DNA molecules that show the sites where the restriction enzymes cleave the DNA. To construct a restriction map, purified samples of DNA are treated with restriction enzymes, either alone or in combination, and then the reactio ...
... construct restriction maps of DNA. These are diagrams of specific DNA molecules that show the sites where the restriction enzymes cleave the DNA. To construct a restriction map, purified samples of DNA are treated with restriction enzymes, either alone or in combination, and then the reactio ...
Chapter 16 notes
... • Process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself as a result of complementary base pairing: 1) molecule unwinds, then unzips (2 strands separate) due to helicase 2) new DNA nucleotides line up on both strands ...
... • Process where DNA makes an exact copy of itself as a result of complementary base pairing: 1) molecule unwinds, then unzips (2 strands separate) due to helicase 2) new DNA nucleotides line up on both strands ...
Prokaryotes, Viruses, and Protistans
... Prior to prokaryotic fission, the chromosome and integrated viral DNA are replicated. ...
... Prior to prokaryotic fission, the chromosome and integrated viral DNA are replicated. ...
student worksheet
... Title: Origami DNA Introduction: Origami is an art form based on paper folded into elaborate designs that often look like a real object. To make the designs, detailed instructions must be provided. For example, “fold the paper in half twice”. Is this a good description? Why or why not? In living thi ...
... Title: Origami DNA Introduction: Origami is an art form based on paper folded into elaborate designs that often look like a real object. To make the designs, detailed instructions must be provided. For example, “fold the paper in half twice”. Is this a good description? Why or why not? In living thi ...
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA)
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the chemical compound that contains the instructions needed to develop and direct the activities of nearly all living organisms. DNA molecules are made of two twisting, paired strands, often referred to as a double helix. Each DNA strand is ...
... Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) is the chemical compound that contains the instructions needed to develop and direct the activities of nearly all living organisms. DNA molecules are made of two twisting, paired strands, often referred to as a double helix. Each DNA strand is ...
Lecture 2 - Organic Origins Debate
... Males have 1 X and 1 Y (heterogametic) Little genetic information, “SRY” ...
... Males have 1 X and 1 Y (heterogametic) Little genetic information, “SRY” ...
DNA Notes Part 1
... 1. Adenine always pairs with Thymine. 2. Cytosine always pairs with Guanine. - The different order of these bases is ...
... 1. Adenine always pairs with Thymine. 2. Cytosine always pairs with Guanine. - The different order of these bases is ...
Biology Formative Assessment #7 Multiple
... B. Mutations that involve the translocation of chromosomes in gametes during meiosis. C. Mutations that occur during crossing over during the prophase stage of mitosis. D. Mutations that occur in somatic cells during cell division. ...
... B. Mutations that involve the translocation of chromosomes in gametes during meiosis. C. Mutations that occur during crossing over during the prophase stage of mitosis. D. Mutations that occur in somatic cells during cell division. ...
Biology (056) (E) CHAPTER
... (A)The gene responsible for the character is recessive in females and dominant only in males (B)The character is induced in males as males produce testosterone (C)The female sex hormone estrogen suppresses the character in females (D)The gene responsible for the character is present on the Y chromos ...
... (A)The gene responsible for the character is recessive in females and dominant only in males (B)The character is induced in males as males produce testosterone (C)The female sex hormone estrogen suppresses the character in females (D)The gene responsible for the character is present on the Y chromos ...
Chapter 20 - BEHS Science
... –They grow quickly like bacteria –They are eukaryotes (similar enzymes, metabolic mechanisms, protein mods) –They have plasmids (rare for eukaryotes) –Can replicate artificial chromosomes as well as DNA in plasmids ...
... –They grow quickly like bacteria –They are eukaryotes (similar enzymes, metabolic mechanisms, protein mods) –They have plasmids (rare for eukaryotes) –Can replicate artificial chromosomes as well as DNA in plasmids ...
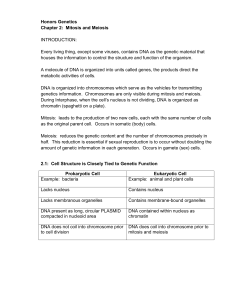
Honors Genetics Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION
... Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION: Every living thing, except some viruses, contains DNA as the genetic material that houses the information to control the structure and function of the organism. A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic acti ...
... Chapter 2: Mitosis and Meiosis INTRODUCTION: Every living thing, except some viruses, contains DNA as the genetic material that houses the information to control the structure and function of the organism. A molecule of DNA is organized into units called genes, the products direct the metabolic acti ...
Biotechnology Pre/PostTest Key (w/citations)
... Piecescan of DNA from twoown different organisms can be joined They produce their pesticides They can grow larger than unmodified crops Genescannot from complex such as animals can be inserted into simpler organisms They cause an organisms allergic reaction Theysuch can as contain extra nutrients ba ...
... Piecescan of DNA from twoown different organisms can be joined They produce their pesticides They can grow larger than unmodified crops Genescannot from complex such as animals can be inserted into simpler organisms They cause an organisms allergic reaction Theysuch can as contain extra nutrients ba ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.