Transcription and Translation Review Lesson Plan
... Explain how genetic combinations produce visible effects and variations among visible features and cellular functions of organisms. ...
... Explain how genetic combinations produce visible effects and variations among visible features and cellular functions of organisms. ...
Chapter 19 - Microbiology and Molecular Genetics at Oklahoma
... • Used for microbial classification and determination of phylogenetic relationships • Used because of multicopies of highly conserved and repetitive DNA sequences present in most gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria • Uses restriction enzymes to recognize specific nucleotide sequences – cle ...
... • Used for microbial classification and determination of phylogenetic relationships • Used because of multicopies of highly conserved and repetitive DNA sequences present in most gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria • Uses restriction enzymes to recognize specific nucleotide sequences – cle ...
Photosynthesis - Cathedral High School
... the HEXA gene on chromosome 15 This causes a stop codon in the wrong location Deficient hexosaminidase (hex A). ...
... the HEXA gene on chromosome 15 This causes a stop codon in the wrong location Deficient hexosaminidase (hex A). ...
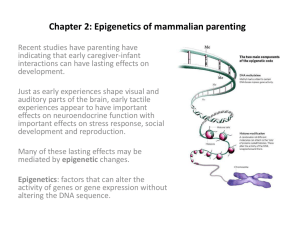
Chapter 2: Epigenetics of mammalian parenting
... histone proteins around DNA, not directly targeted at DNA. Can have either activating or repressing effects on gene expression. ...
... histone proteins around DNA, not directly targeted at DNA. Can have either activating or repressing effects on gene expression. ...
Chapter 4A
... as operons. Operons are transcribed from a single promoter and usually contain genes that participate in a common process such as synthesis of tryptophan, e.g., the trp operon of E. coli (Fig. 4.13a). The trp operon mRNA is polycistronic and encodes 5 different proteins. Each cistron coding sequence ...
... as operons. Operons are transcribed from a single promoter and usually contain genes that participate in a common process such as synthesis of tryptophan, e.g., the trp operon of E. coli (Fig. 4.13a). The trp operon mRNA is polycistronic and encodes 5 different proteins. Each cistron coding sequence ...
19. IMG-ER Curation Environment
... EC number and PUBMED ID – see explanation Notes are free text (goes to “note” in GenBank submission) Gene symbol is “gene name” – 4 letter abbreviation; goes to “gene” in GenBank submission ...
... EC number and PUBMED ID – see explanation Notes are free text (goes to “note” in GenBank submission) Gene symbol is “gene name” – 4 letter abbreviation; goes to “gene” in GenBank submission ...
2014
... combines with the ________________ subunit to form the RNA polymerase holoenzyme complex which then binds to the DNA promoter to form the __________________ complex. Melting of the DNA duplex by the polymerase then forms the ___________________ complex. After elongation, termination of transcription ...
... combines with the ________________ subunit to form the RNA polymerase holoenzyme complex which then binds to the DNA promoter to form the __________________ complex. Melting of the DNA duplex by the polymerase then forms the ___________________ complex. After elongation, termination of transcription ...
PCR-technique Applications
... Molecular methods: FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridization) • Species composition of a sample: Use of: - group specific sequences in 16S rRNA as probes (species, ….domains) - different fluorescent dyes attached to the probe - the cells are fixated and made permeable to the probe/s - hybridization di ...
... Molecular methods: FISH (fluorescent in situ hybridization) • Species composition of a sample: Use of: - group specific sequences in 16S rRNA as probes (species, ….domains) - different fluorescent dyes attached to the probe - the cells are fixated and made permeable to the probe/s - hybridization di ...
2017 - Barley World
... 11. Mutation is the source of new alleles and recombination is the source of new combinations of alleles a. T b. F 12. You are offered a job breed a new variety of tomato with great flavor and long shelf life. Experience and data confirm that poor flavor and long shelf life are associated. Which of ...
... 11. Mutation is the source of new alleles and recombination is the source of new combinations of alleles a. T b. F 12. You are offered a job breed a new variety of tomato with great flavor and long shelf life. Experience and data confirm that poor flavor and long shelf life are associated. Which of ...
Chapter 12 HW Packet
... to make the other strand, the strands are said to be complementary. DNA copies itself through the process of replication: The two strands of the double helix unzip, forming replication forks. New bases are added, following the rules of base pairing (A with T and G with C). Each new DNA molecule has ...
... to make the other strand, the strands are said to be complementary. DNA copies itself through the process of replication: The two strands of the double helix unzip, forming replication forks. New bases are added, following the rules of base pairing (A with T and G with C). Each new DNA molecule has ...
RNA-Seq - iPlant Pods
... • Accesses XSEDE system through the iPlant Agave API • Co-localizes up to 100 GB of data in iPlant Data Store • Look for differential gene expression in different tissues, life stages, or treatment • Generate lists of expressed genes and fold-changes • Annotate sequenced genomes; add results to Red ...
... • Accesses XSEDE system through the iPlant Agave API • Co-localizes up to 100 GB of data in iPlant Data Store • Look for differential gene expression in different tissues, life stages, or treatment • Generate lists of expressed genes and fold-changes • Annotate sequenced genomes; add results to Red ...
Teacher quality grant
... • Students will describe the process of DNA replication and/or its role in the transmission and conservation of genetic information. • Students will describe gene and chromosomal mutations in the DNA sequence. • Students will explain how gene and chromosomal mutations may or may not result in a phen ...
... • Students will describe the process of DNA replication and/or its role in the transmission and conservation of genetic information. • Students will describe gene and chromosomal mutations in the DNA sequence. • Students will explain how gene and chromosomal mutations may or may not result in a phen ...
DNA - Gulf Coast State College
... • Students will describe the process of DNA replication and/or its role in the transmission and conservation of genetic information. • Students will describe gene and chromosomal mutations in the DNA sequence. • Students will explain how gene and chromosomal mutations may or may not result in a phen ...
... • Students will describe the process of DNA replication and/or its role in the transmission and conservation of genetic information. • Students will describe gene and chromosomal mutations in the DNA sequence. • Students will explain how gene and chromosomal mutations may or may not result in a phen ...
Domain Three (3_genetics)
... Suppose that a gene for growth hormone is discovered in cats. If a drug company wanted to mass-produce the hormone by cloning the gene into bacteria, what would it need to do? A. place the cat gene into a plasmid and place the plasmid into bacteria B. make a DNA fingerprint of the cat gene and inser ...
... Suppose that a gene for growth hormone is discovered in cats. If a drug company wanted to mass-produce the hormone by cloning the gene into bacteria, what would it need to do? A. place the cat gene into a plasmid and place the plasmid into bacteria B. make a DNA fingerprint of the cat gene and inser ...
Cryptography and Linguistics of Macromolecules Cryptography and
... Since the purpose of aligning sequences is to discover patterns, it only makes sense to align those kinds of information that can be partitioned in different, comparable sequences, and where recurrent patterns can be found. ...
... Since the purpose of aligning sequences is to discover patterns, it only makes sense to align those kinds of information that can be partitioned in different, comparable sequences, and where recurrent patterns can be found. ...
overexpression of mcm protein potentially causes cancer
... cells containing RPA-GFP or Rad52-GFP foci will be scored using fluorescence microscopy. Plasmid loss is described as an event where daughter cell does not obtain one copy of plasmid from mother cell during replication. [8] Normally, yeast will replicate and segregate plasmids with good efficiency. ...
... cells containing RPA-GFP or Rad52-GFP foci will be scored using fluorescence microscopy. Plasmid loss is described as an event where daughter cell does not obtain one copy of plasmid from mother cell during replication. [8] Normally, yeast will replicate and segregate plasmids with good efficiency. ...
Zinc-finger proteins act as site-specific adapters for DNA
... team led by Takashi Morii at the University of Kyoto (Japan) has now introduced a new method for attaching the proteins by means of special "adapters" known as zinc-finger proteins. ...
... team led by Takashi Morii at the University of Kyoto (Japan) has now introduced a new method for attaching the proteins by means of special "adapters" known as zinc-finger proteins. ...
5. Nucleic Acids-Structure, Central Dogma – Bio 20
... 2. Structure (DNA, RNA) III.Looking at the Central Dogma ...
... 2. Structure (DNA, RNA) III.Looking at the Central Dogma ...
Bacterial Genetics
... Prokaryote Basics • The largest and most obvious division of living organisms is into prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. • Eukaryotes are defined as having their genetic material enclosed in a membrane-bound nucleus, separate from the cytoplasm. In addition, eukaryotes have other membrane-bound organelles ...
... Prokaryote Basics • The largest and most obvious division of living organisms is into prokaryotes vs. eukaryotes. • Eukaryotes are defined as having their genetic material enclosed in a membrane-bound nucleus, separate from the cytoplasm. In addition, eukaryotes have other membrane-bound organelles ...
HotStart DNA Polymerase
... activating the enzyme at a temperature well above optimal annealing. During hot start, primers bind only to their specific target, and polymerase activity is directed exclusively to that target. Only the region of interest is amplified, which increases sensitivity and yield while reducing non-specif ...
... activating the enzyme at a temperature well above optimal annealing. During hot start, primers bind only to their specific target, and polymerase activity is directed exclusively to that target. Only the region of interest is amplified, which increases sensitivity and yield while reducing non-specif ...
Chapter 25: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
... Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels to bring additional nutrients and oxygen to a tumor; cancer cells stimulate angiogenesis. Metastasis is invasion of other tissues by establishment of tumors at new sites. A patient’s prognosis is dependent on the degree to which the cancer has prog ...
... Angiogenesis is the formation of new blood vessels to bring additional nutrients and oxygen to a tumor; cancer cells stimulate angiogenesis. Metastasis is invasion of other tissues by establishment of tumors at new sites. A patient’s prognosis is dependent on the degree to which the cancer has prog ...
Genetics I Exam 5 Review Sheet - Poultry Science
... 45. A genetic disorder of DNA repair in which the body's normal ability to remove damage caused by ultraviolet light is deficient. This leads to multiple basaliomas and other skin malignancies at a young age. In severe cases, it is necessary to avoid sunlight. What is the name of this genetic disord ...
... 45. A genetic disorder of DNA repair in which the body's normal ability to remove damage caused by ultraviolet light is deficient. This leads to multiple basaliomas and other skin malignancies at a young age. In severe cases, it is necessary to avoid sunlight. What is the name of this genetic disord ...
Extrachromosomal DNA

Extrachromosomal DNA is any DNA that is found outside of the nucleus of a cell. It is also referred to as extranuclear DNA or cytoplasmic DNA. Most DNA in an individual genome is found in chromosomes but DNA found outside of the nucleus also serves important biological functions.In prokaryotes, nonviral extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in plasmids whereas in eukaryotes extrachromosomal DNA is primarily found in organelles. Mitochondrial DNA is a main source of this extrachromosomal DNA in eukaryotes. Extrachromosomal DNA is often used in research of replication because it is easy to identify and isolate.Extrachromosomal DNA was found to be structurally different from nuclear DNA. Cytoplasmic DNA is less methylated than DNA found within the nucleus. It was also confirmed that the sequences of cytoplasmic DNA was different from nuclear DNA in the same organism, showing that cytoplasmic DNAs are not simply fragments of nuclear DNA.In addition to DNA found outside of the nucleus in cells, infection of viral genomes also provides an example of extrachromosomal DNA.